Highlights of the Land Biomes
advertisement

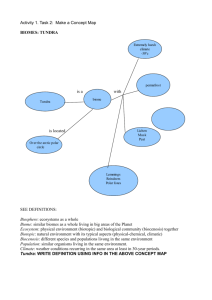
Highlights of the Land Biomes Tundra • Biome that has little precipitation (a type of desert) and low temperatues. • Freezing and Thawing cycle is crucial to the survival of tundra organisms. • Life fills the Tundra during several months of thaw. • Permanently frozen ground is called permafrost. (This layer allows for low drainage and causes rich marshes and pools during thaw) Tundra • Common tundra plants include lichens, mosses, grass, wildflowers, and shrubs. (Why no larger trees?) • How animals survive: • Tough out the cold (emperor penguins) • Hibernate during cold (polar bears, insects) • Migrate away and return for thaw (artic birds, caribou) • Challenges the tundra faces: • Global Warming (disrupts freeze/thaw) • Air Pollution (ie: kills liches: How does this effect the food web?) • Poaching Desert • • • • Biome with low precipitation and higher temperatures. Great variety of different deserts on earth. Extreme daily temperature swings. Desert plants conserve and store water. Roots cover large area to absorb moisture. • Desert animals: many have features that allow them to conserve water/deal with heat (reptiles, foxes, etc) • Some adjust behavior (ie: hunt at night) • Issues in the Desert: Desertification Grasslands / Savanah • These Biomes have more water than a desert, but not enough to support a forest. • Usually are near deserts and are in danger of desertification. • Amount of rain limits organisms and also susceptible to fires (which can rejuvenate the land) • Animals include insects, birds, rodents, grazing animals and their predators. • Waterholes and migration during dry season help many organisms to survive. • Issues in the Grasslands: • Overgrazing and drought (can cause dust storms) • Habitat loss and interruption of migration patterns • Poaching (Many African animals depend on wildlife preserves to survive) Rainforest / Jungle • Stable temperatures and abundant water make these Biomes have a vast variety of organisms (great Biodiversity) • Soil nutrients absorbed and cycled quickly. • Layers of the Forest • Emergent, Canopy, Understory, Forest Floor • Light levels at different layers determine which organisms live there and the niche they fill. • Issues in the Rainforest: • Loss of habitat and biodiversity (What is one way habitat is lost?) Deciduous Forest and Coniferous Forest (Tiaga) • Deciduous trees lose their leaves during colder season. • About 6 months growth. • Trees photosynthesize to prepare for cold. • Rich Soil, Abundant Water and Food, Variety of Habitats. These all allow for Biodiversity. • Coniferous Forests consists of evergreen trees and usually encompass colder regions. • Taiga are a very important producer of oxygen for earth. • Snow provides and important layer in the forest (insulating the ground and protecting roots, prevents permafrost, and warmth for animals) • Some animals hibernate or migrate. Deforestation • Permanent Destruction of Forest • Know causes of Deforestation • Know negative results of Deforestation • Know how humans are Impacted • Know some solutions to Deforestation