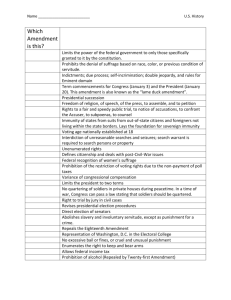
Unit 3 Vocabulary and People filled in
advertisement
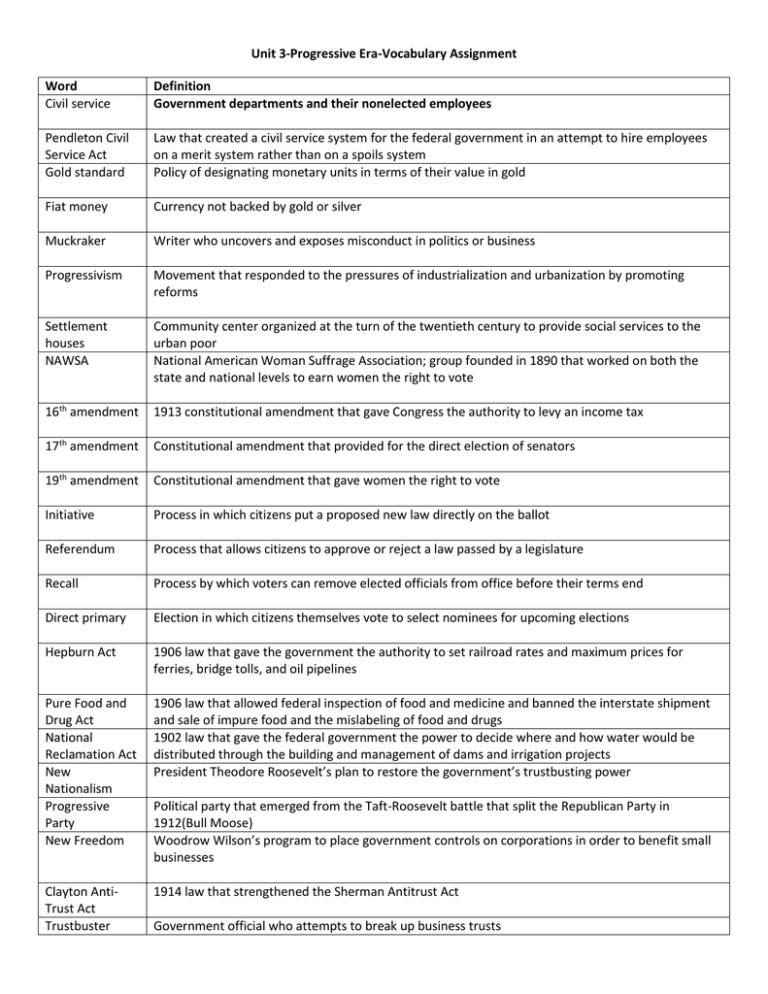
Unit 3-Progressive Era-Vocabulary Assignment Word Civil service Definition Government departments and their nonelected employees Pendleton Civil Service Act Gold standard Law that created a civil service system for the federal government in an attempt to hire employees on a merit system rather than on a spoils system Policy of designating monetary units in terms of their value in gold Fiat money Currency not backed by gold or silver Muckraker Writer who uncovers and exposes misconduct in politics or business Progressivism Movement that responded to the pressures of industrialization and urbanization by promoting reforms Settlement houses NAWSA Community center organized at the turn of the twentieth century to provide social services to the urban poor National American Woman Suffrage Association; group founded in 1890 that worked on both the state and national levels to earn women the right to vote 16th amendment 1913 constitutional amendment that gave Congress the authority to levy an income tax 17th amendment Constitutional amendment that provided for the direct election of senators 19th amendment Constitutional amendment that gave women the right to vote Initiative Process in which citizens put a proposed new law directly on the ballot Referendum Process that allows citizens to approve or reject a law passed by a legislature Recall Process by which voters can remove elected officials from office before their terms end Direct primary Election in which citizens themselves vote to select nominees for upcoming elections Hepburn Act 1906 law that gave the government the authority to set railroad rates and maximum prices for ferries, bridge tolls, and oil pipelines Pure Food and Drug Act National Reclamation Act New Nationalism Progressive Party New Freedom 1906 law that allowed federal inspection of food and medicine and banned the interstate shipment and sale of impure food and the mislabeling of food and drugs 1902 law that gave the federal government the power to decide where and how water would be distributed through the building and management of dams and irrigation projects President Theodore Roosevelt’s plan to restore the government’s trustbusting power Clayton AntiTrust Act Trustbuster 1914 law that strengthened the Sherman Antitrust Act Political party that emerged from the Taft-Roosevelt battle that split the Republican Party in 1912(Bull Moose) Woodrow Wilson’s program to place government controls on corporations in order to benefit small businesses Government official who attempts to break up business trusts Secret ballot Voting in private Third party A political party in addition to the Republican and Democratic parties Social Gospel Reform movement that emerged in the late nineteenth century that sought to improve society by applying Christian principles The Jungle A book written by Upton Sinclair which exposed the despair of immigrants working in Chicago’s stockyards and the unsanitary conditions in the meatpacking industry; eventually prompted legislation to ensure food safety Meat Inspection Act Suffrage 1906 law that allowed the federal government to inspect meat sold across state lines and required federal inspection of meat processing plants The right to vote Square Deal President Theodore Roosevelt’s program of reforms to keep the wealthy and powerful from taking advantage of small business owners and the poor National Consumers League Temperance movement Federal Reserve Act Group organized in 1899 to investigate the conditions under which goods were made and sold and to promote safe working conditions and a minimum wage Federal Trade Commission Hull House Movement aimed at stopping alcohol abuse and the problems created by it 1913 law that placed national banks under the control of a Federal reserve board, which runs regional banks that hold the reserve funds from commercial banks, sets interest rates, and supervises commercial banks Government agency established in 1914 to identify monopolistic business practices, false advertising, and dishonest labeling Settlement house opened by Jane Addams in Chicago; the success of Hull House inspired other college-educated, middle-class women to become social workers