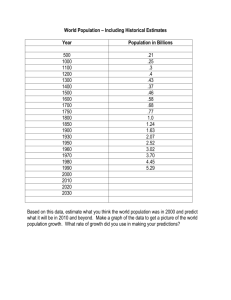
levittowns - Advance Placement US History
advertisement

1950’s America: An Era of Prosperity Prosperous America • Entering the 1950’s most Americans owned the 3 symbols of American Prosperity. – 1. A new suburb home. – 2. A car – 3. Television • Children got into the act buying and using consumer items such as: – Gum, Cokes, Hamburgers, Records, Clothes, hula hoops, plastic toys. Prosperous America • 1950’s saw a shift in media moving from radio and film to TV. • People were “Keeping up with the Jones’s” • Many people flaunted their extravagant items. • Caused some to be rebellious because of conformity. People often turned to drugs, music, alcohol, and religion to help ease their anxiety. (These were luxury items now) WWII Aftermath: Baby Boom • In the mid 1950’s almost 30% of the population was 15 years or younger. • This created a HUGE demand in products for kids (toys, diapers, bikes, games) which helped fuel our post war economy. • Polio Vaccine was introduced in 1952. – But not made for the public until a little later. • Death rate dropped, birth rate was up. • Penicillin was now common. • People were living longer (thus creating more of a consumer demand) Booming Suburbs • People started to move away from the busy urban cities into the suburbs (owning a car allowed for further daily travel) • This caused a high demand for houses and “planned” neighborhoods. “Levittown's” • People moved south to rising job markets after the war. Prosperous America 1950’s • In the 1950’s unemployment remained low • Purchasing power was up (meaning the dollar value was strong) • People could afford more things than they ever thought possible. (People were living above their previous Standard of Living) • Purchasing on credit became popular. Credit Cards • 1950 Diner’s Club issued the 1st “general credit card” – General Credit Card was a card that could be used at all stores that accepted credit (not store specific) • Private debt rose drastically. – Private debt is not governmental loans. It’s debt to individual department stores and personal debt to banks etc. (It also refers to purchasing debt not investment debt) Automobile Expansion The Trickle Down Effect • By the late 1950’s almost 2/3 of all Americans commuted to their jobs by car. • Demand for cars had a trickle down effect – This caused a demand for more service stations, gas stations, motels, garages, and road crews. – This caused the US Government to tax gasoline. (To pay for road paving etc) Industrial Growth • Industries began pumping out products such as… – Dacron (Polyester fiber) used in clothing and plastics. – Teflon (Nonstick chemical used on cooking surfaces) – Aerosol Spray Cans (did contain CFC’s) – Hairdryers, Air Conditioners, Electric Blankets, Washer and Dyers, Portable “transistor radios” Crabby Old Man – Everything was about speed and convenience. – Marketing campaigns advertised how much more time women would have if they purchased their product. Industrial Growth • With all these inventions and chemical advancements certain industries started to slide. – Coal couldn’t compete with Natural Gas, and Oil. – Trucking and Air travel hurt the Railroad industries – Cotton and wool were losing out to synthetic fibers made in labs (nylon, rayon, and Dacron) – Small farms couldn’t compete with large farm corporations (because large farms could afford fertilizers, pesticides and used mass machines) Industrial Growth—Labor Unions • Labor unions and corporations agreed to “automatic annual cost of living raises” – They simply passed the increase of wages onto the consumers by raising prices. • Labor Unions though became very powerful during the 1950’s and often became corrupt. • Robert Kennedy was chief council on an investigation into the crookedness of the Teamsters Union Unions Weaken • In the late 1950’s unions started to weaken because jobs were moving south (where unions weren’t present) • Also people in the north would not join unions because of high union dues and they could make more $ and better benefits by negotiating directly with their employer. • Our country was shifting from blue collar jobs to white collar jobs by the late 1950’s. Unions Weaken • 1956 white collar jobs outnumbered blue collar jobs in our country for the 1st time. • Technological advances also reduced the amount of labors need in blue collar jobs. • Some unions did manage to get into the white collar sector though. (meaning unionized white collar workers) Good and Bad • While we had a rise in middle class in the 1950’s the number of people below the poverty line also rose. • 25% of the population were considered poor in 1960. • The elderly were 65% of the poor class. • The poor began to move to the cities: – Raising crime rates – Raising homeless rates in cities Good and Bad • 1960’s: Statistics – 5% of the nation held 50% of the wealth. – 50% of the nation had no savings. – Wage laws and legislation didn’t reach to many of the low income jobs and wages. – Welfare programs for the poor kept them at poor levels and had stipulations that more or less kept them dependent on the program. (didn’t provide a solution/avenue to get out of poverty) – The poorer class was often swept under the rug. (not focused on) Levittown NY Wonder Years SURBURBIA!!! • Following WWII people fled cities and settled in the Suburbs. – Wanted to escape city taxes, smog, traffic jams, crime, overcrowding and wanted little contact with mixing races. • Suburbia life was very appealing: – Spacious housing (wanted a yard) – A fraction of the cost of living compared to the city – Privacy (quiet neighborhoods) – Community involvement. (Like neighborhoods) SURBURBIA!!! • Suburbia life was very appealing: (Cont) – Low interest mortgage loans (people could afford them who couldn’t have prior to the loan rates) – Shopping centers were built to accommodate the suburbs (so no more traveling to the city to shop) – Freeways were constructed (made travel easier) LEVITTOWN LEVITTOWNS USA!!!! • William Levitt “The Father of Modern Suburbia” • First one was on Long Island NY between 19471952. • Originally Levitt designed this town for 2000 military families coming home to have an affordable place to stay. • But the demand became so high they had to alter their construction plans and add an additional 4000. LEVITTOWNS USA!!!! • Built on concrete slabs (no basements) • Had unfinished 2nd floors so the family could expand if they wanted. • Assembly line houses. (Workers moved not the house or product) • Workers specialized in doing 1 aspect of the home then moved onto the next. • They used precut lumber shipped from their own lumber yards. This allowed for speed building. LEVITTOWNS USA!!!! • They were able to turn out 30,000 houses a day. (combining all their building sites) • The Levittown became a community with its own post office, schools, shops, police force, etc. The became very centralized. LEVITTOWNS USA!!!! • Originally they were rental houses. (for military families) – Could rent for $65 per month with $0 down. – Within 2 years he stopped renting and only sold houses. Selling price was $8,000 which was only $58 per month and that included a Refrigerator and washer! ($0 down for vets) LEVITTOWNS USA!!!! • YouTube - Levittown (song) by Bob Koenig LEVITTOWNS USA!!!! • Levittown’s also had criticisms. – They were Ticky Tacky houses. Little Boxes • Ticky Tacky: Poor quality houses. Built with cheap materials and no finishing touches. – They were almost always white neighborhoods. – By 1960 Levittown's were almost 98% white. – People didn’t want to live in the same community as black people so Levitt’s sales people wouldn’t sell to blacks because they didn’t want to alienate the white population who bought most of the homes. – Levittown's still today are predominantly white. LEVITTOWNS USA!!!! • There was no individuality in the neighborhoods or with the people. • The people all were the same, (white/middle class) doing the same thing, living the same life, the complaint was that the house were the same causing the people to be the same. • Sometimes this lead to people having a feeling of drones (where they were nothing special so they sometimes turned to drugs/alcohol because of depression)---but not the norm. Culture Shift • Teenagers were becoming abundant in the 1950’s. • They were setting trends because of their shear population numbers. • This lead marketing departments to target the youth and their “extra” cash to spend. • This lead to……….. The Birth of McDonalds McDonalds • “McDonald’s Restaurant” was originally owned by Richard and Maurice McDonald and began serving food in 1940. • In 1948 they went to the “Speedy Service System” which meant a limited menu: – Burgers – Fries – Cooked in volume – (Milkshakes added later) Original Mascot…. Changed to Ronald McDonald in 1968 McDonalds • 1953 the McDonalds brothers franchised the “Speedy Service System” only to Neil Fox. – This meant they allowed Fox to copy the idea of fast food service. (Not specifically the McDonalds product or name etc.) – Fox copied everything including the name. – After that, the McDonalds brothers began franchising their entire restaurant. McDonalds • 1954 milkshake machine salesman Ray Kroc from Illinois was traveling through California and stumbled the original McDonalds. • He saw huge potential for the concept of fast food by taking it further with the assembly line approach and creating standard burgers. • He sold McDonalds their milkshake machines and partnered with the brothers to open a franchise in Illinois in 1955. McDonalds • Kroc helped open up several more McDonalds restaurants. • He became annoyed that the Mac Brothers were not onboard to open up a ton of restaurants and decided to buy the franchise rights of the company outright. (Bought it in 1961)—Shrewd businessman. • He implemented the Standardization of his resturants. McDonalds • Standardization of restaurants: – This meant that all Big Macs would be identically tasting regardless of the restaurant. (Strict rules were required for food preparation in all franchises to be uniform. • Ex. Quantities were pre-portioned, cook times were standard, weight of burgers, size of packages, etc. • Franchisers were able to experiment with some different styles of food though. McDonalds • Jim Delligatti created the 1st Big Mac in Uniontown PA!!!!! (1967) Big Mac – He noticed sales were slipping because of Elby’s Big Boy burger and petitioned McDonalds to try his own version. – It worked so well that before the year was out it was nationally adopted by McDonalds Corp. – Mcdonald's Rap • The Big Mac is now used as an economic indicator. Disneyland • Opened in Anaheim California 1955 (Same year as Kroc’s McDonalds) • Offered a family theme park. – Fun or the family. – HUGE attraction (Autopia) – Had separate sections of the park (Adventureland, Frontierland, Main Street etc.) – Disneyland was a clear sign that the nation was far removed from the Great Depression and the age of consumerism was upon us. – YouTube - Disneyland history Women and Family: Women in the 1950’s • “American Women’s Dilemma” – Concept of being a stay at home mom and working outside in the workforce. • During WWII a ton of women worked in factories. • Now the war was over and men came back and a baby boom followed women were torn on being the “typical” homemaker or continuing to work. Women in the 1950’s • Dr. Benjamin Spock published his “Baby and Child Care Book” (1947) – It really took off in the 1950’s and 1960’s – He stated that women that they should make child rearing their most important task. – Put children’s needs first. – Advised women to stay out of the workforce because they were needed at home where their babies were. Women in the 1950’s • Some psychologists suggested that women who worked outside of the home were trying to “Imitate men” and that their true happiness should be found in being domesticated. – Root of this was the “Feminine Mystique” • The concept that women formed the foundation of society. • They were what kept the family together by being home and taking away stress from the family. • They were the organizers. Marjorie Sutton • Highlighted in 1956 Life Magazine. – As a successful woman who fulfilled her duties. • Worked in the home. • Was active in Campfire Girls, PTA, and charities. • Chauffeured children to and from actives • Helped her husband entertain his business clients. Women gotta look good! Women’s appearance • 1950’s also highlighted the idea of femininity. • Women were expected to sacrifice comfort and practicality for fashion. – High heals – Hair always done to the “T” – Always in make up Working Women of the 1950’s • The tide shifted in the late 50’s toward women working outside the home. • By 1960, 40% of women were working outside the home. – Usually they were married mothers. – But most were working part time “women’s work jobs”. – They were not being equally treated as men in the workplace in terms of salary and or professionalism. Working Women of the 1950’s • These women primarily worked part time to supplement their family income so they could have: – A second car – A color TV – A larger house • Women working in the 1950’s-1960’s didn’t destroy families. Often times it brought them together because the extra income allowed them to do leisure activities with the family. Togetherness: • The word first appeared in the 1950’s. • It meant a blended, happy, loving family who spends time together who shares values and is essentially “good”. • It instituted family life. Sticking together was important. Religion • Besides family gatherings… helped keep family together in the 1950’s. Religion • 1950’s we were involved in the Cold War • Pres Eisenhower tied religion to patriotism to help fight the communist menace. He stated: – “God was the first and most basic of Americanism” – Communists were “Godless” • Atheism was associated with communism. • Religion was also associated with the family and “Togetherness” --”The family that prays together stays together.” Religion • The notion of religion = family = patriotism = not being a communist became popular. • The Bible topped the chart as the best seller in the 1950’s. • 1954 the words “Under God” were added to the Pledge of Allegiance. • 1956 the words “In God We Trust” became the new official US Motto replacing “E Pluribus Unum” • 1957 “In God We Trust” was put on US Currency. Religion • Southern Baptist and evangelical leader Billy Graham lead a mass movement back to bible fundamentalism. • Founded the Billy Graham Evangelical Association in 1950. – It’s focus was to spread the Gospel of Jesus – Focused on the crusade style of preaching. Dr. Reverend Billy Graham He had a TV show called “Hour of Decision” that ran for 50 years. Evangelical= relaying a set of beliefs to those who do not share the same beliefs Religion • Over 95% of Americans in the mid 1950’s believe in religion. • Religion and attending services became a “social activity”. – It was the “thing to do” – Religion found it’s way into such things as High School Sports (prayers before games), Bingo games. (Helped add the acceptableness to the activity. • Religion helped add the sense of “togetherness”