Chapter 1
advertisement

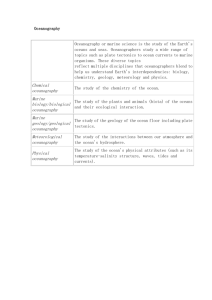
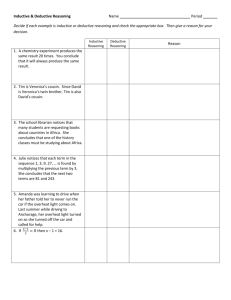
Marine Biology Michael Slemp • Named “elephant” because the nose of and adult male resembles an elephant’s trunk • Found in the North Pacific • During breeding they live on beaches, rest of the year off shore • Young pups nurse about 28 days and gain about 10 pounds a day • Adult male may reach 13 feet • Can stay under water for up to 2 hours at a time • Eat deep-water, bottom-dwelling marine animals such as ratfish, swell sharks, spiny dogfish, eels, rockfish, and squid • were hunted to the brink of extinction, primarily for their blubber, which was used for lamp oil • For more info see links in Chapter 1 “Northern Elephant Seals” Someone who uses the process of science to find answers about how and why things work in the world and in the observable universe. Science is not just facts Science is the way we analyze the facts We know very little in the big scheme of things There are depths that we are still unable to measure Life that we have not seen, species that have yet to be discovered Resources that are still unknown Bathynomus giganteus For more info see links in Chapter 1 “Deep sea creatures” Oceans influence the weather and world climate patterns which dictate how warm, cold, wet, or dry a region will be Oceans determines where organisms live Oceans provide important resources (food, oxygen, and natural resources such as oil). Commercial fishing has severely depleted many types of fish Pollution has deteriorated many marine environments. Coral reefs and mangroves are dying off in record numbers Complete the activity on page 1-6 Go step by step Answer questions 1-7 under Reflecting on your learning Write out the question Your answers must be in complete sentences Process of discovering facts, processes, and unifying principles that explain the nature of the oceans and their associated life forms. Oceanography is the science of recording and describing the ocean’s contents and processes 1. Biological oceanography (marine biology) studies the diversity of life in the ocean and the oceans role as their habitat 2. Chemical oceanography studies the chemistry of the seawater. Examines chemical changes brought about by nature and people. 3. Geological oceanography is the study of the geology of the ocean. This examines the composition of marine sediments and rocks. Studies underwater volcanoes, seabed movement, earthquakes Molokini crater in Hawaii For more info see links in Chapter 1 “Underwater volcanoes” 4. Physical Oceanography is the study of physics in the marine environment. This examines water movement such as waves, currents and tides. Studying marine science combines traditional science concepts to marine science concepts Integrated different fields of science allows an individual to understand that many branches of science are interconnected. Marine science works closely with the physical sciences (chemistry/ physics), life sciences (biology, physiology and ecology) and Earth and space science ( study of the physical earth, and the universe) Science as inquiry- way to solve problems Science and technology- how science and technology work hand in hand with each other Science in personal and social perspectives- how science affects you and society Historical nature of sciencehow science evolved as a discipline A body of knowledge and organized method used to gain knowledge about the observable universe. Is a material system that produces results What are some examples of technology? How do we come up with technology? What are some early examples of technology? Is all technology good? What are some downsides or negative effects of technology? If you were top scientists how would you argue for technology that negatively affects nature? Now argue against current technology that affects nature negatively. 1. Disregard (ignore) the effects of technology 2. Dismiss the effects of technology (not agree with scientists) humans go extinct humans go extinct 3. Prioritize developing technologies that positively affect the environment we live This should be review for everyone. Write the 5 steps below. If you need to review these 5 steps re-read pages 1-24 through 1-28 for a detailed explanation of each 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Identify the problem ( or questions) Make a hypothesis (educated guess) Test the hypothesis Interpret and analyze the results Report results, procedures and conclusions Inductive/ deductive reasoning should take place during step 2 of the scientific method Use inductive reasoning to propose a process that explains the facts you observed Use deductive reasoning to propose what you would observe should a known process take place Observe a fact (F) Inductive (I) reasoning Bubbles in the water Inductive reasoning Propose a process (P) that explains the fact Scuba diver in a water Observe known process Deductive reasoning Propose what should be observed Scuba diver in the water Deductive reasoning Bubbles in the water Always changing Remember some scientist thought the earth was flat and we just fell off the edge if we got too close to the edge Not all theories are correct Scientist thought earth was the center of the universe for centuries Scientists need to stay current on advances and current theories Staying current can help society come to understand either positive or negative effects Example would be human cloning Twins are human clones, Not all what the media writes is the most current based on the scientific theories currently presented Complete the activity on page 1-28 Answer question 1-5 under Reflecting on Our learning. Write out question Answer must be in complete sentence