Forces PPT - Purvis' Science Spot
advertisement

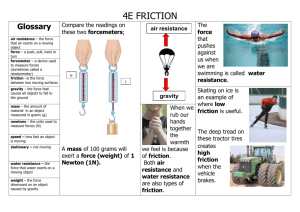
CHAPTER 3 SECTION 1 Forces IPC Types of Friction Foldable • Make a foldable to help you keep track of the types of friction • 3 Headings on cover flaps: • Static Friction • Sliding Friction • Rolling Friction What is force and what does it do? • Force: a push or a pull • A force can cause the motion of an object to change Net Force • Net Force: the sum of all forces acting on an object • As we move forward keep in mind the rules for adding forces Balanced and Unbalanced Forces Which is balanced? Which is unbalanced? Why? • Balanced forces do not cause a change in motion. • The net force will be the difference between the two forces if they are in opposite directions. Friction • Friction: the force that opposes the sliding motion of two surfaces that are touching each other • What causes friction? • Surfaces that appear smooth actually have many bumps and dips Types of Friction • Static friction: frictional force that prevents two surfaces from sliding past each other, caused by microwelds that form between two surfaces • These microwelds are stronger when pushed together with larger force • This means that when you are pushing an object and it is not moving the force opposing you is static friction Types of Friction cont. • Sliding friction: frictional force that opposes the motion of two surfaces sliding past each other • Think about the resistance you feel when trying to slide your shoes along carpet • The force of sliding friction is usually smaller than the force of static friction! • This is why once you get an object moving it is easier to keep it moving. Types of Friction cont. • Rolling friction: friction between an object that is rolling in one direction and the surface of another object • Rolling friction, aka traction, is very useful and is the reason your tires move on your vehicles • In icy weather sand is used to increase the friction with vehicle tires or people’s shoes Gravity • Gravity: an attractive force between any two objects that depends on the masses of the objects and the distance between them • Gravity is one of four fundamental forces • Newton’s Law of Universal Gravitation: the relationship between the gravitational force between two objects, the object’s masses, and the distance between them •F = G×m1m2 d2 G = universal gravitational constant (6.67×10-11 m3/kg×s2) m1 and m2= the masses of the two objects d= the distance between the centers of the two masses In the 1660’s, British scientist Sir Isaac Newton used data on the motions of planets to write the law of universal gravitation. More About Gravity • Why do I not feel the gravity of the textbook on my desk? • While the distance from the book to me is very close, the mass of the book is not enough for me to feel it’s gravitational pull • The range of gravity • According to Newton’s law of universal gravitation, the gravitational force between two objects decreases rapidly as the distance between the masses increases • However, no matter how far apart the gravitational force between two objects is never zero • Gravitational fields • A field is a region of space that has a physical quantity (such as force) at every point. • All objects are surrounded by a gravitational field that becomes weaker as distance from the object increases Weight • Weight: the gravitational force exerted on an object results in the object’s weight • Weight Equation: • Weight (N) = mass (kg) × gravitational strength (N/kg) Fg = mg Do you think the weight of a plane is the same on earth’s surface as it is in earth’s atmosphere? Why? Weight and Mass • Weight and mass are NOT the same • Weight is a force • Mass is a measure of the amount of matter an object contains • Weight on earth and weight on the moon are not the same… Why? • Is the mass on earth the same as the mass on the moon? Why? Force Activity • In groups of 3-4, model one of the following forces • Balanced/unbalanced forces • Static/sliding friction • Gravity • Weight (on and off earth) • Be able to justify your reasoning and explain the finer details behind your chosen force Homework • Complete the handout and turn it in next class time Wrap Up • Are mass and weight the same thing? • What happens to gravitational force the further you get from an object? • What are three types of friction? • What is net force? Why is it useful? Have a Great Day!