Progressive Era Pt. 2
advertisement

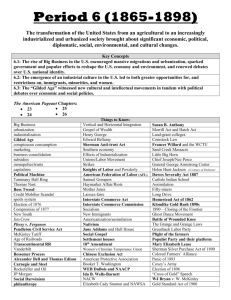
When you come in, answer the following in your notebook in 3-5 sentences: Who were the Progressives? Did the federal government do its job in regulating business? Or was it overstepping its boundaries? Progressives sought to permanently address many problems brought on during the Gilded Age To regulate means the US Government would make laws to oversee, adjust, fine tune and correct the unfair business tactics in industry and big business. Not take over or control it. Does this fit any particular idea we have discussed? Does it have to? Interstate Commerce Act (1887) Sherman Antitrust Act (1890) These are the first laws to regulate industry and big business. Congress passed Interstate Commerce Commission (ICC). U.S. government regulated interstate trade within the country. End railroad corruption of charging high prices to ship goods and Rockefeller’s illegal deals. Rebates/kickbacks/drawbacks were illegal. In 1890, Congress passed a law which made trusts/monopolies illegal or any business that prevented fair competition. How did the government try to regulate Big Business? Interstate Commerce Commission (1887)- First U.S. gov’t organization to regulate the railroads Sherman Antitrust Act (1890)First law to monitor business practices and limit the power of Big Business. Who would enforce such laws??? Our muckraking/progressive president He saw the problems of the Gilded Age and sought widespread government reform! Roosevelt Rises to the Presidency Graduate of Harvard Loved wildlife Named Assistant Secretary of the Navy under President McKinley. Formed Rough Riders in Spanish American War. (Calvary Unit) Elected Governor of N.Y. Progressive beliefs Vice President under McKinley and became President when he was assassinated • Teddy Bear named after him. • Square Deal=keep the wealthy from taking advantage of the poor and small business owners. Square Deal •TR believed in the “capitalistic system” but believed that the system must be regulated by US Govt. •for the betterment of the “common man” as opposed to benefit the elite. •TR believed the U.S. Government was running the country and not the rich and corrupt industrialists…. •U.S. Government involvement with “regulatory agencies”….Similar to “checks and balances” Square Deal •Reforms of the Progressives start with President Roosevelt…. •Areas which he wanted to reform and use the “bully pulpit” of the Presidency were the following: •Bad Trusts vs. Good Trusts •Take the side of labor •Railroads •Limiting corruption in the workplace •Conservation “Trust-Busting” – developed by Teddy Roosevelt Breaking up monopolies ▪ 1902 – US vs. Northern Securities ▪ Hepburn Act (1905) ▪ 1910 – US vs. US Steel ▪ 1911 – US vs. American Tobacco ▪ 1911 – US vs. Standard Oil of New Jersey Enforces Sherman Anti-Trust Act Sherman Anti-Trust Actbanned any trust that restrained interstate trade or commerce. Broke up many trusts including Northern Securities Company (r.r. company) and beef trusts. Supported large corporations as long as they did business fairly (under TR’s watch.) The Trustbuster Coal miners strike 1902- Threatens to send in federal troops to end strike. Federal government steps in for 1st time and helped workers in a labor dispute. Formed Department of Commerce and Labor Railroads Railroad Reforms to boost the Interstate Commerce Commission. •Elkins Act •Anti-Rebate Act or AntiKick Back Act •Regulates common carriers of people and freight, UPS, Greyhound, Amtrak, etc. •Hepburn Act •Regulates rates for passengers and freight •Air travel cost controls •Air freight price controls Meat Inspection Act (1906) Required meat factories be inspected (that goes across state lines) Animals inspected before & after slaughter Created supervision (USDA) ** Remember: Which muckraker initiated these concerns? Pure Food and Drug Act (1906) Allowed gov’t to fine non-compliant businesses Label ingredients Later we get the FDA (Food and Drug Administration) ALL HAPPEN UNDER TEDDY’s ADMINISTRATION TR’s Conservation Policy •125,000 acres in reserve •National Reclamation Act 1902 •25 water projects •Founding of the National Park System National Forests Conserved and preserved forests. Gifford Pinchot- Led Division of Forestry in U.S. Department of Agriculture. Idea that forest be preserved for public use. John Muir-Created Yosemite National Park in 1890. At this time they would preserve forests for logging, it later changed into public parks. •National Reclamation Act gave birth to the Newlands Irrigation Project. •Free land to Homesteaders who wanted to farm Lahontan Valley. •Dairy farming, hay, beef and sugar beets •Lake Lahontan and dam built in operation by 1914 Roosevelt Changes Water Policy Water was fought over in Southwest. Private irrigation companies were taking over riverbeds so farmers couldn’t reclaim lost land. National Reclamation Act 1902- Fed. Government decides where and how water could be distributed. Build and managed dams. Roosevelt and Hoover Dams on Colorado River. Salt Valley Project in Arizona. OTHER REFORMS Child Labor Reform National Child Labor Committee Florence Kelly Keating-Owens Act (1916) = outlawed child labor But ruled unconstitutional in 1918– federal government cannot regulate INTRAstate commerce Impact? Reforms for the Poor Settlement houses Community centers providing services to the urban poor Jane Addams Hull House Chicago, 1889 Impact? Workers’ Reform Bad Conditions Long hours Unsafe machinery Work related injuries/death Triangle Shirtwaist Factory Fire Reform: Workers’ Compensation Laws Impact? One of the most influential events in labor history was a direct result of sweatshop conditions. The Triangle Shirt Factory Fire killed 146 workers. There were no real fire escapes and the doors opened out into the hall. The doors where blocked locking the workers in. As a result, stricter building codes and fire regulations where passed. 1911 New York City Locked doors 800 trapped 146 people (123 were women) died Female labor, bad working conditions, immigrant rights Led to stricter building codes and regulations 16th Amendment 1913 Progressive Tax Income based 17th Amendment 1913 Direct Election of Senators Goal: End Corruption 18th Amendment 1919/1920 Temperance Prohibition Ban Sale and Distribution of “intoxicating liquors” Since the Seneca Falls Convention of 1848, the Women’s Rights movement went on throughout the 19th century. Susan B. Anthony led the charge to get women the vote until 1906. Shortly after her death, in 1920, women will achieve the right to vote in the 19th Amendment. 19th Amendment 1920 Women’s Suffrage (the right to vote) Key Suffragettes: ▪ Susan B. Anthony ▪ Alice Paul ▪ Carrie Chapman Catt Susan B. Anthony Number of children is affecting family life for women Margaret Sanger; American Birth Control League Family planning info reaches women