Mutations 2016 - Willimon-PHS
advertisement

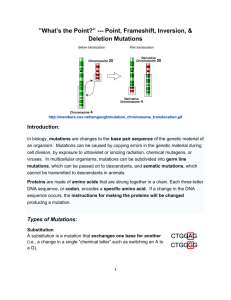
T U E S D AY I N B I O L O GY BUILD-A-BUG ACTIVIT Y Build your bug and turn in to your box Mutations Notes Mutations practice QUIZ NEXT CLASS: Transcription and Translation REMINDERS THAT YOU NEED TO KNOW!!! Transcription: transcribing DNA into mRNA Example DNA: T A C A A AT T A G C G mRNA: AUG-UUU-AAU-CGC DNA RNA A T G C U A C G Translation: translating the message in RNA into an amino acid sequence ( us e yo ur c o do n c h a r t ) Example mRNA: A U G - U U U - A A U - C G C AA: Meth-Phen-Asp-Arg Gene expression: What traits does your bug have? Build a bug to express the genes!! MUTATIONS What are DNA Mutations? • Mutation – a random change in the sequence of a gene • Caused by: – Mistakes in DNA replication process – Environmental agents that damage DNA ATCGA TAGCT ATCGA TAGCT ATCAA TAGCT Types of DNA Mutations • • • • • Point mutation/Substitution Inversion Insertion Deletion Translocation C T C G A T A Types of DNA Mutations • Point mutation/Substitution – one base replaced with another base • Inversion – order of two or more bases is reversed Types of DNA Mutations • Insertion – addition of one or more new bases • Deletion – removal of one or more bases Types of DNA Mutations • Translocation – movement of one or more bases to a new location in a different DNA sequence DNA Mutations • Changes in sequence of a gene can cause changes to the protein that is produced during translation • Can affect proteins produced in different ways: – – – – Silent mutations Missense mutations Nonsense mutations Frameshift mutations Silent Mutations Silent mutation – mutation that causes no change in amino acid sequence • Genetic code has redundancies • Caused by point mutations …TACAACCTCACC… …ATGTTGGAGTGG… …AUGUUGGAGUGG… DNA (transcription) RNA …TACAATCTCACC… …ATGTTAGAGTGG… …AUGUUAGAGUGG… (translation) Met-Leu-Glu-Trp… Protein Met-Leu-Glu-Trp… Missense Mutations Missense mutation – mutation that changes the identity of an amino acid added • Most often because of point mutations • May be because of inversions …TACAACCTAACC… …ATGTTGGATTGG… …AUGUUGGAUUGG… DNA (transcription) RNA …TACAACCTCACC… …ATGTTGGAGTGG… …AUGUUGGAGUGG… (translation) Met-Leu-Asp-Trp… Protein Met-Leu-Glu-Trp… Nonsense Mutations Nonsense mutations – mutation that shortens a protein by replacing an amino acid codon with a stop codon • Most often because of point mutations • Large impact on protein produced …TACAACATGACC… …ATGTTGTACTGG… …AUGUUGUACUGG… DNA (transcription) RNA …TACAACATCACC… …ATGTTGTAGTGG… …AUGUUGUAGUGG… (translation) Met-Phen-Tyr-Trp… Protein Met-Phen-STOP Frameshift Mutations Frameshift mutation – mutation that alters the reading frame in which codons are translated • Caused by insertions, deletions, and translocations • Large impact on protein produced …TACAACATGACCCTA… …ATGTTGTACTGGGAT… …AUGUUGUAUUGGGAU… DNA (transcription) RNA …TACAACTATGACCCTA… …ATGTTGATACTGGGAT… …AUGUUGAUAUUGGGAU… (translation) Met-Leu-Tyr-Trp-Asp… Protein Met-Leu-Ile-Leu-Gly… DNA Mutations and Survival Mutations can be organized by their effect • Neutral mutations – no effect on organism’s survival – Increase genetic diversity in a species – Example: human eye color • Harmful mutations – decrease organism’s survival – Produce genetic disorders or unfavorable traits – Example: cancers • Beneficial mutations – increase organism’s survival – Produce favorable traits – Example: antibiotic resistance in bacteria