DNA to Proteins
advertisement

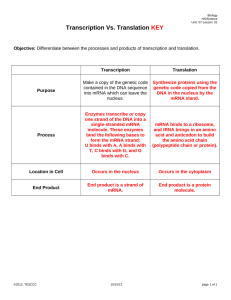
Protein Synthesis (making proteins) This is called the genetic code (or Protein Synthesis) Also known as the ‘Central Dogma’ The DNA inside of the Nucleus gives the RNA instructions for making Proteins. Since the DNA cannot leave the nucleus, the mRNA travels through the cytoplasm to the ribosomes. Changing DNA – RNA is called “TRANSCRIPTION” To ‘transcribe’ is to ‘re-write’ something. This means there will be a change in base pairing. A=U (this is different, no THYMINE in RNA) C=G (this is the same) Practice Transcription AAA – TAG – GAT – CCC – TAT - ATT Practice Transcription-answer = AAA – TAG – GAT – CCC – TAT - ATT mRNA =UUU – AUC – CUA –GGG – AUA - UAA DNA Remember: There is no T (thymine) in RNA; instead there is U (uracil) The series of 3 bases is called a triplet or CODONS Messenger RNA (mRNA) being translated into an amino acid is called TRANSLATION. You will need page 292 of the blue Glencoe Textbooks for the Amino Acid Codon Chart Translate the mRNA to Amino Acids You will need the chart on page 292 in blue text books mRNA =UUU – AUC – CUA –GGG – AUA – UAA AA = PHEN – ISOL – LEU – GLYC – ISOL - STOP Translation Your amino acid strand should read this mRNA =UUU – AUC – CUA –GGG – AUA – UAA AA = PHEN – ISOL – LEU – GLYC – ISOL - STOP Every amino acid sequence (protein strand) has a start codon (AUG) and a stop codon (UAA, etc.) This is telling where protein synthesis STARTS, and STOPS On your own paper, Practice DNA replication 1. ATA – CAT – GGG – CCC- TAT- ATT – CGC 2. TTA – CCT – CCA – GGA – ATA – TTG – CCT 3. ATC – GAT- CTA – TCG – ATC – GAC – GAG 4. GCT – AGA – TAA – AGG – CAA –GAA - AAA Practice Protein Synthesis (change each strand to mRNA , THEN to Proteins). 1. ATA – CAT – GGG – CCC- TAT- ATT – CGC 2. TTA – CCT – CCA – GGA – ATA – TTG – CCT 3. ATC – GAT- CTA – TCG – ATC – GAC – GAG 4. GCT – AGA – TAA – AGG – CAA –GAA - AAA









![THE S I S A Patho1oioa]. Survey of In partial fulfillment of](http://s2.studylib.net/store/data/013277278_1-40dc1e91b68a0656174aa23ea07c9ea3-300x300.png)