Section 1.3 - Edvantage Science
advertisement
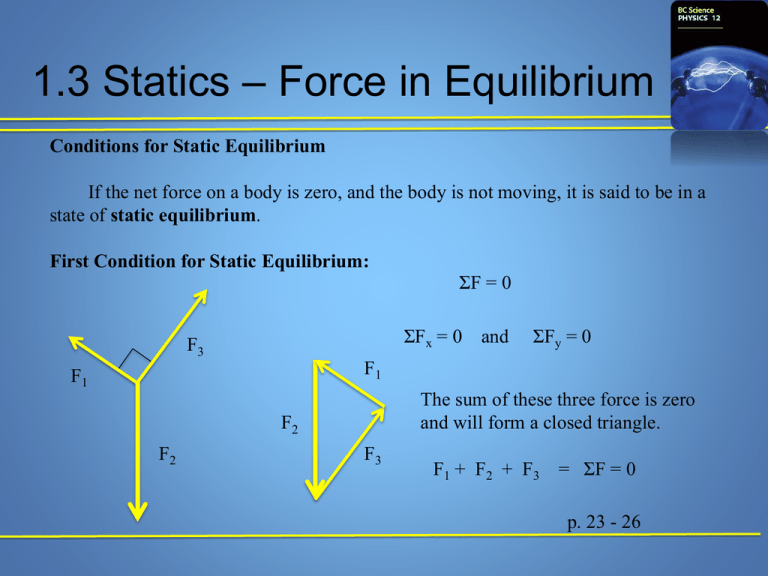
1.3 Statics – Force in Equilibrium Conditions for Static Equilibrium If the net force on a body is zero, and the body is not moving, it is said to be in a state of static equilibrium. First Condition for Static Equilibrium: ΣF = 0 ΣFx = 0 F3 and ΣFy = 0 F1 F1 The sum of these three force is zero and will form a closed triangle. F2 F2 F3 F1 + F2 + F3 = ΣF = 0 p. 23 - 26 1.3 Statics – Force in Equilibrium Second Condition for Static Equilibrium or Rotational Equilibrium (Torque) F1 ΣF = 0 F2 pivot F1 + F2 = 0 In this situation the sum of the forces is zero, but the object is NOT stationary. The beam would rotate about it’s pivot point. To understand this type of motion we need to understand the concept of torque. p. 27 1.3 Statics – Force in Equilibrium Torque is equal to the force applied multiplied by the lever arm length at which the force is applied. Lever arm length l F τorque = Force x length τ = F┴ x l pivot F Where F┴ is the perpendicular force τ = F x l x sin ѳ l ѳ or τ = F x sin ѳ x l p. 27 - 28 1.3 Statics – Force in Equilibrium Center of Gravity There is a single point in a body where the force of gravity may be considered to act. A body supported at its center of gravity by a force equal to the force of gravity on the body (but in the opposite direction) will NO translational or rotational motion as a results of the supporting force. cg p. 29 1.3 Statics – Force in Equilibrium Center of Mass This is the point at which all the mass of an object is considered to be concentrated for the purpose of calculation. For most situations that you will encounter center of mass = center of gravity. How ever if the gravitational field is non-uniform then the center of mass and center of gravity could be located at different points. Second Condition for static Equilibrium To keep an object from rotating, the sum of the toques about a pivot point must be equal to zero. Στ = 0 Στclockwise = Στcounterclockwise p. 29 - 30 1.3 Statics – Forces in Equilibrium Key Questions In this section, you should understand how to solve the following key questions. Page #26 – Practice Problem 1.3.1 #1 - 3 Page #28 – Quick Check #1 – 3 Page #33 1.3 Review Questions # 1 – 5 Page #34 – 38 Chapter 1 Review Questions #1 - 21







