23RoadtotheCivilWar2
advertisement

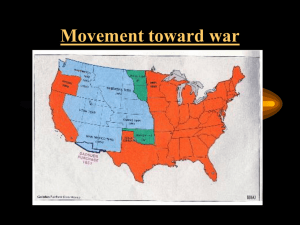
Notes 3 7. Conflicts over slavery and Compromises Slavery in Louisiana Purchase? Manifest Destiny---1840 to 1850 President James K. Polk—1845 to 1849 Oregon Territory---1846 Texas Statehood--1845 Mexican War---1846 to 1848 US acquired the Mexican Cession Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo—1848 Slavery in the Mexican Cession? Compromise of 1850 Calif. Admitted as a free state Create 2 new territories = Popular Sovereignty •South: Enforce the Fugitive Slave Law •North: stop the slave trade in Washington, D.C. •Gadsden Purchase----1853 •Kansas-Nebraska Act----1854 •Stephen Douglas---build railroad in the North •Organize Kansas and Nebraska Territory and open it up to Popular Sovereignty •Effects •Abolitionists against it •Ruined the Missouri Compromise •led to violence----Bleeding Kansas---1856 •Republican Party---1856---political party organized to stop the expansion of slavery notes 4 8. Judicial Arguments •Dred Scott—1857-----slave sued for his freedom •Supreme Court Decision •Constitution did not apply to slaves •Legalized slavery in the U.S. •All compromises were unconstitutional 9. John Brown’s Raid---1859 Harper’s Ferry Reactions North---martyr for the abolitionist cause South---no other choice but secede notes 5 12. Election of 1860 Lincoln wins election South Carolina secedes from the U.S., Dec of 1860. 10 other Southern States would secede in 1861 formed the CSA---Confederate States of America Why? notes 6 Missouri Comp Americans began moving into Texas in the 1820’s and brought their slaves with them. War fought by Texans against Mexico because they believed their rights had been violated. Won by Texans in 1836 and requests to enter the U.S. Texas War of Independence Texas War of Independence President Jackson and Van Buren refused to recognize Texas statehood because of slavery. Texas became its own country with Sam Houston president, 1836 to 1845. Mexico never recognized the independence of Texas. Texas entered as a U.S. state in 1845. Mexico vowed if Texas became part of the U.S., this would be an act of war. One cause of the war with Mexico in 1846. Texas War of Independence1 •James K. Polk, Democrat • President from 1845 to 1849 •Responsible for the Manifest Destiny •Expansionist •Acquired the Oregon Territory from Great Britain in 1846 •54’, 40’ or Fight •49th Parallel •Mexican War acquired Mexican Cession and completed U.S. control of the continent from ocean to ocean Picture/Polk Oregon dispute •Treaty with Great Britain in 1846 •President Polk campaign slogan was 54,40 or fight… •Compromised with British and divided the Oregon Country at the 49th parallel •American belief that U.S. would control the continent from the Atlantic to the Pacific. KEY EVENTS •Texas statehood •Oregon territory •Mexican War •Mexican Cession Picture/M.Destin y KEY EVENTS •Pioneers Trek West •California trail •Oregon trail •Mormon’s trail •Gold discovered •Gold Rush Picture/M.Destin y Trails Long Term Causes •Manifest Destiny •California Immediate Causes •Texas statehood, 1845 •Mexico refusing to sell California •Border dispute Effects •US receives Mexican Cession •Disputes over expansion of slavery will lead to Mexican the CivilWar War Mexican War Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo •Mexico ceded the Mexican Cession to U.S. •Rio Grande River boundary between U.S. and Mexico •U.S. paid Mexico $15 million Map expansion Most intense debate in U.S. History •John C. Calhoun •North should honor the Constitution and enforce the Fugitive Slave Law •South wanted California •threatened to secede from U.S. •U.S. should have two Presidents--one from the North and one for the South •Daniel Webster •Henry Clay •The Great Compromiser, with John C. Calhoun, Daniel Webster and Stephen Douglas, propose this compromise. •Secession is impractical & impossible •How would we split the land? •The military? •Compromise at all cost •Preserve the Union Comp of 1850 •U.S. Senator from the state of Illinois •Solve the slavery issue was through Popular Sovereignty •let the people in each territory decide through the process of voting whether they want slavery or not. •Along with Henry Clay, Daniel Webster and John C. Calhoun they proposed the Compromise of 1850 •Calif. A free state •enforce Fugitive Slave Law •Popular Sovereignty •stop slave trade in Washington, D.C. Picture/S.Douglas Popular Sovereignty Allow the people in a territory to vote on whether they want slavery to exist or not in their state. Map Comp of 1850 ABOLITIONISTS RESPOND Denounced by Abolitionists Harriet Beecher Stowe’s, Uncle Tom’s Cabin is published Abolitionists refuse to enforce the law Underground Railroad becomes more active Map expansion •Build a transcontinental connecting California to the East Coast either in the South or North •Stephen Douglas wanted the railroad built in the North but had to convince the South otherwise. •Proposed a plan that Kansas and Nebraska territories be opened up to slavery in return for building the railroad in the North. •Popular Sovereignty Kan. & Neb Act Map Bleeding Kan •Kansas/Nebraska Act led to several acts of violence between proslavery settlers and anti-slavery settlers. •First violent outbreaks between north/south. (Led by John Brown) Attacks by free-states Attacks by pro-slavery states •First battles of the Civil War begin in Kansas in 1856. •Over 200 killed After the passage of the Kansas-Nebraska Act in 1854, the Kansas territory became a battleground. Pro-slavery and antislavery supporters rushed to settle in Kansas. The territory was torn by battles and massacres. The issue also bitterly divided the nation and led to the formation of the Republican Party. The first shots of the Civil War were in Bleeding Kansas. Bleeding Kan Free Soil Party against the expansion of slavery Democrats opposed the expansion of slavery Formed to stop the expansion of slavery REPUBLICAN PARTY National Republican which become the Whigs. Chart/Rep. Party Abolitionists Know Nothing Party against immigration Popular Sovereignty Allow the people in a territory to vote on whether they want slavery to exist or not in their state. Map Kan/Neb Act •Slave from Missouri traveled with his owner to Illinois & Minnesota both free states. •His master died and Scott wanted to move back to Missouri---Missouri still recognized him as a slave. •Court case went to the Supreme Court for a decision-----National issue •Can a slave sue for his freedom? •Is a slave property? •Is slavery legal? Picture/Dred Scott •Supreme Court hands down the Dred Scott decision •North refused to enforce Fugitive Slave Law •Free states pass personal liberty laws. •Republicans claim the decision is not binding •Southerners call on the North to accept the decision if the South is to remain in the Union. Chart/Effect of Scott •Slaves cannot sue the U.S. for their freedom because they are property. •They are not citizens and have no legal right under the Constitution. •Supreme Court legalized slavery by saying that •Congress could not stop a slaveowner from moving his slaves to a new territory •Missouri Compromise and all other compromises were unconstitutional •Violent abolitionist •Involved in the Bleeding Kansas •Murdered 5 pro-slavery men in Kansas •Wanted to lead a slave revolt throughout the South by raising an army of freed slaves and destroying the South. •Attacked a U.S. Ammunition depot in Harper’s Ferry, Virginia in Oct. of 1859 to capture weapons and begin his slave revolt. •He was found guilty of treason and sentenced to death. •His last words were to this effect: “I believe that the issue of slavery will never be solved unless through the shedding of blood.” •Northerners thought of John Brown as a martyr to the abolitionist cause. •Southerners were terrified that if John Brown almost got away with this, there must be others like him in the North who are willing to die to end slavery. •South’s outcome: To leave the U.S. and start their own country. Picture/J.Brown Hanging •Lincoln and Douglas both running for the U.S. Senate in Illinois. •The debates were followed by the country because both candidates were interested in running for the Presidency in 1860. •Slavery was the issue •Lincoln stated: A House Divided against itself cannot stand. Either we become one or the other. •was against the expansion of slavery •Douglas believed that slavery should be decided by the people. •Popular sovereignty Chart/L&D Debates Lincoln got Douglas to admit that Popular Sovereignty could work against the expansion of slavery….. Southerners would not support Douglas for the presidency in 1860 Country is polarized (divided) over the issue of slavery. Once Lincoln is elected as president, South Carolina will secede from the U.S. along with several other Southern States. •303 total electoral votes and 152 to win. They will form the Confederate States of America---CSA Election of 1860 Secession