UNDERSTANDING THEORY Chapter 2
advertisement

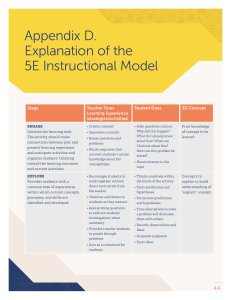
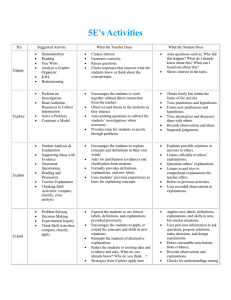
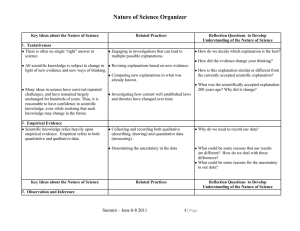
UNDERSTANDING THEORY Chapter 2 EXPLANATIONS • • • • • Deductive Probabilistic Functional Causal Empathetic Quantitative Evidence • Is based on objective, verifiable, controlled observations and is communicated in a precise ( unambiguous) manner. • Objective- observations are free from bias • Verifiable-info can be confirmed by tests conducted by others • Controlled observations-confounding factors are minimized or taken into account Qualitative Evidence • The explanations and descriptions must ring true to both the researcher and to the people experiencing the phenomena. • The evidence is based on anlaysis of documents, and/or in-depth interviews of focus groups, or lengthy participation in a group. Flaws in Explanation • • • • • • • Illegitimate appeal to authority Provincialism False dilemma Missing data Anecdotal evidence Selected evidence Unwarranted conclusions THEORY • A systematic vision of reality that describes, explains, or predicts something • Its primary goal is to provide a framework that links research and practice and contributes to making findings meaningful and generalizable Functions Theory Provides • a structure for interpretation of findings • a means of imposing order on experiences • a means for summarizing and explaining observations from isolated studies • a source to generate hypotheses • a framework for guiding research • a guide in selecting the appropriate method • a basis to describe, explain, or predict factors influencing nursing outcomes Classification of Theory • Grand Theories • Middle- Range Theories • Practice Theories Levels of Theory • Level 1 - factor-isolating, descriptive in nature • Level 2 - factor-relating, asks the question, What is happening here? • Level 3 - situation-relating, explains and predicts how situations are related, asks What will happen if? • Level 4 - situation-producing, prescriptive in nature, asks How can I make X happen? Building Blocks of Theory • CONCEPTS • CONSTRUCTS • VARIABLE Building Blocks of Theory • PROPOSITIONS • HYPOTHESES VARIABLES • • • • • Dependent Variable Independent Variable Control Variable Conditional Variable Source of Spuriousness or (Confounding) Variable TESTING THEORY • • • • • Axiomatic Derivations Replacement of Terms Structural Equation Modeling Testing Alternative Explanations Theoretical Triangulation Points of Agreement on Research and Theory • Study the full range of behavior in health and illness states • Use the methodology appropriate to the question asked • Use systematic explanation • Subject our scholarly work to peer review