Ancient Mali
advertisement
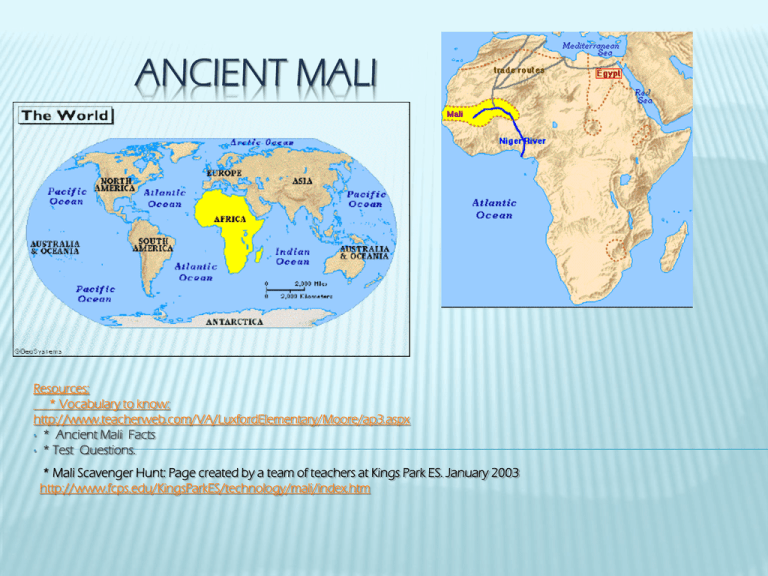
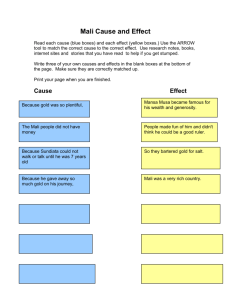
ANCIENT MALI Resources: * Vocabulary to know: http://www.teacherweb.com/VA/LuxfordElementary/Moore/ap3.aspx • * Ancient Mali Facts • * Test Questions. * Mali Scavenger Hunt: Page created by a team of teachers at Kings Park ES. January 2003 http://www.fcps.edu/KingsParkES/technology/mali/index.htm Vocabulary to know Contribution – act of giving or doing something Africa is the continent where Mali is located. Mali is in West Africa. SAHARA DESERT It is a desert that covers a good part of Mali. MEDITERRANEAN SEA. It was used by the people of Mali for "trade routes." TIMBUKTU It was an important city in Mali. It had a famous university with a large library containing Greek and Roman books GRIOT It is a storyteller West Africa has a great oral tradition. A griot is a learned storyteller, entertainer, and historian. Often a griot will memorize the genealogy, or family history, of everyone in a village going back centuries. TO LISTEN TO SOME GRIOT FROM AFRICA CLICK ON THE FOLLOWING LINK. http://youtu.be/zQMFN-whbEU (3:23 minutes) GOLD It was mined in the desert of West Africa. It is a natural resource. NATURAL RESOURCE It is a resource that comes from earth. Salt is an example. Can you think of another? KINGS They were rich, powerful men who controlled trade in West Africa. HUMAN CHARACTERISTICS - JOBS People from Mali were: Farmers Traders miners EMPIRE It means power or authority. An empire is a big group of states and peoples- ethnic groups- united and ruled either by an emperor or king. TRADITION It is a custom or belief that happens over a long period of time Thanksgiving, a tradition in America CLICK ON THE FOLLOWING LINK TO LISTEN TO AND WATCH A TRADITIONAL MUSIC VIDEO FROM MALI. http://youtu.be/Q2O93A8m1Dw (1:23 minutes) GENERATION It is the time of an individual’s descent. It is a succession of natural descent as a grandfather, a father, and the father's son comprise three generations. How many generations are in this family? And in this one? WEALTHY it is someone who has lots of money or power. Important Facts about Ancient Mali Ancient Mali Africa was the home to several great empires. One of the most prosperous was the empire of Mali. Ancient Mali Mali today ANCIENT MALI Mali was located in West Africa near the Niger River. Mali lay between salt in the Sahara Desert and gold mines in West Africa. ANCIENT MALI The kings of Mali were rich and powerful men who controlled trade in West Africa. Mali became one of the largest and wealthiest empires in the region and was an important trade center. ORAL TRADITION Many storytellers or griots in Mali passed on traditions and stories from one generation to the next. NATURAL RESOURCES IN ANCIENT MALI: Mali lay across the trade routes between the sources of salt in the Sahara Desert and the gold region mines of West Africa. For the people of the desert, salt was a natural resource. People used salt for their health and for preserving foods. Miners found gold in Western Africa. Salt was traded for gold. TIMBUKTU Timbuktu was an important city in Mali. It had a famous university with a large library containing Greek and Roman books. Early Mali was a wealthy trading empire before Christopher Columbus sailed to America. http://www.fcps.edu/KingsParkES/technology/mali/index.htm TEST QUESTIONS Are you ready? 1- WHY WERE STORYTELLERS SO IMPORTANT IN THE EMPIRE OF MALI? YOU GOT IT! Storytellers in Mali passed on traditions and stories from one generation to another. We know about Mali’s history because of storytellers. 2- What do we know about the leaders of the empire of Mali? AWESOME! King’s of Mali were rich, and powerful men who controlled trade in West Africa. They were the head of the government in Ancient Mali. 3- Why was the empire of Mali so wealthy? GREAT JOB! Mali became one of the largest and wealthiest empires because it was an important trade center. Ancient Mali saw the rise of trade and commerce as Mali served as a major trade route for caravans to pass. 4- What do we know about Mansa Musa? FANTASTIC! Mansa Musa, was the tenth mansa, which translates as "king of kings" or "emperor", of the Malian Empire. He was perhaps the wealthiest ruler of his day. 5- Where was the empire of Mali located? INCREDIBLE! It was located in West Africa near the Niger River. Mali lay between salt in the Sahara Desert and gold mines in West Africa. 6- Why was salt so important? EXTRAORDINARY! Salt was a natural resource. People of the desert used the salt for health and for preserving their foods( remember, there were not refrigerators!). Miners found gold in West Africa and the gold was traded for salt. 7. WHO FOUNDED ANCIENT MALI? ARE YOU SURE? You got it!!! Ancient Mali was founded under the leadership of King Sundiata. Sundiata was the most famous and powerful ruler of Mali. Sundiata was popularly referred to as 'the Lion King‘. Being the king of a vast region, he gave rise to the ancient Mali Empire. Sundiata's glorious rule was from 1230-1255. Under his rule, the Mali Empire extended its territories very fast. After the death of Sundiata, Mansa Musa was the next great ruler who contributed to the fast rise of the ancient Mali Empire. 8. WHAT IS THE RIVER THAT RUNS THROUGH MALI? A) Nile B) Niger C) Amazon CORRECT! The Niger River runs through Mali. Mali Scavenger Hunt Ancient Mali.pptx Read the next information to answer the questions Fill in the correct answers (Click on the next web page to answer all the questions.) HTTP://WWW.FCPS.EDU/KINGSPARKES/TECHNOLOGY/MALI/MALI MAP.HTM NAME ____________________ MALI SCAVENGER HUNT 1. On which continent was Ancient Mali located? (H/Ge) ________________ 2. What river provided water for farming, laundering (washing) and bathing? (Ge) ____________________ 3. What desert is located in the northwest region of Mali? (Ge) __________ 4. Give two reasons why Timbuktu was important in Ancient Mali. (Ge) ________________________________________ 5. Who was responsible for passing on stories and traditions from one generation to the next? (H) _______________ 6. Who ruled Ancient Mali? (H/Go) _______________ 7. Name one famous ruler of Mali. (H/Go) ___________________________ 8. What is known as the “Sea of Sand”? (Ge) __________________________ 9. What is a “Ship of the Desert”? (E) __________________________ 10.Name two natural resources important to Mali? (E) __________________ 11.Which resource did the people of Mali need? (*hint- they traded gold to get this important resource) (E) ___________________ 12.Name three jobs that the people of Ancient Mali specialized in? (E) ___________________________________________________________________________________________ 13.Name a type of trading where no one needs to talk. (E) ___________________________________________________________ 14.Who protected the caravans? (Go) _________________ MORE FACTS ABOUT MALI The following reading selections have been extracted are from the following web page, and go with the Scavenger Hunt. http://www.fcps.edu/KingsParkES/technology/mali/malimap.htm GEOGRAPHY OF ANCIENT MALI Location: Western Africa Continent: Africa Rivers: The Niger River is the largest river. In the south, this river provided water for farming, laundering and bathing. Terrain: The northwestern region of the empire extends into the Sahara desert. It is almost entirely arid, without water. In the central and southern areas, the Niger River has an annual flood cycle with high water between August and November. A savannah or grassland stretches across the southern region. GEOGRAPHY OF ANCIENT MALI Sahara Desert: This desert, known as the "Sea of Sand," is the largest desert in the world. Sahara means "desert" in Arabic. Sahel means "shore." It is not really a shoreline but a place where short grasses and shrubby bushes grow at the edge of the desert. This sahel is in between the desert and the savannah. Camels are called the "ships of the desert." Important Cities: Both of these cities were important because they lay along the trans-Saharan trade routes where gold was traded for salt. Wealthy merchants lived in these cities. Once the Portuguese explorers started sailing the seas to trade, however, these landlocked cities fell into ruins. Timbuktu: a great trading center and home of an ancient university and library which contained Greek and Roman books. Djenne: home of the grand mud-brick mosque Page created by Brooks Widmaier January 2003 HISTORY OF ANCIENT MALI Meaning of the word Mali: Mali means "hippopotamus" or "where the king resides." Timeline: 500-1700 . West Africa was home to three rich and powerful civilizations, each gaining more power than the previous. These civilizations were called Ghana, Mali and Songhay. Ghana, known as Land of Gold, was eventually conquered. The next kingdom to rise was Mali. 1230: A young, strong, courageous man named Sundiata, became the king of Mali. Through his great leadership with agriculture and trade, he was able to build one of the greatest empires ever known. Future kings continued to increase the power of the empire and increase its riches through gold and salt trade. HISTORY OF ANCIENT MALI Kings: Mali was ruled by rich and powerful kings. Two of the greatest kings were Sundiata and Mansu Musa. Sundiata founded the empire of Mali. Sundiata means "hungering lion" and was called the Lion King of Mali. Mansa Musa ruled Mali in 1300 and doubled its size. Through his actions, he opened the way for Muslim merchants, scholars, and architects to come to Mali. The king ruled the entire empire and had control of the gold-salt trade. Griots: Old French for "Keeper of Memories." This is the term for the singers, storytellers, historians, and musicians who traditionally retold Mali's history. Griots exist today in Mali. They are also called Djali's (JAH-lees) or Djeli's (JAY-lees). They often play musical instruments to accompany their histories. Most of what we know about Mali's history comes from oral accounts that were handed down from storytellers. In Mali, the griots were political advisors to the king and memorized all of the history, which they told through stories, poetry, music, and dance. Families lived in clans and most of them had a griot who told the family history. The griots were so important to the king that when one king stole another's griot it was an act of war. Page created by: Michelle Crabill and Bruce Tiso Curator: Brooks Widmaier January 2003 GOVERNMENT OF ANCIENT MALI Ancient Mali was ruled by powerful kings. They wore clothing made of gold and silk thread. Gold bars were reserved for the kings. Only gold dust was used in trading. The king's griots or storytellers were the most powerful griots in the empire. Famous leaders: Sundiata Keita: His name means "hungering lion." He was called the Lion King. He united many people and built a strong military to protect the trade routes. Sundiata had his army clear new farmland for planting crops and introduced cotton which became an important export. He is known for taking a kingdom and building an empire. He died after ruling for approximately 25 years. GOVERNMENT OF ANCIENT MALI Mansa Musa: Mansa means "sultan, emperor or chief." Musa means "Moses." Mansa Musa become known as Mali's "Black Moses." He also ruled for 25 years and doubled the size of Mali. He described his kingdom as "a year's journey in length." Mansa Musa was a Muslim and Islamic law requires that all faithful Muslim's make a visit to the city of Mecca where their religion was started. This pilgrimage is called a haj. During the haj, Mansa Musa traveled 3,000 miles by camel caravan. He took many powerful people with him so that they would not take over the country in his absence. He also took a great amount of gold which he spent and gave away along the route. He had to borrow money for his return trip. Mansa Musa established the first Islamic university in Timbuktu where scholars studied Arabic, surgical procedures, science and math. During his rule, the army kept the peace and patrolled the trade routes. The empire was divided into provinces with its own governor and towns that were led by a mochrif or mayor. Online slide show of Sundiata's life. Online story of Sundiata's life. Information on Sundiata, a king of ancient Mali. Website about griots from the Kennedy Center for Performing Arts. Find out about Mansa Musa. Page created by: Sang Im and Brooks Widmaier Curator: Brooks Widmaier January 2003 ECONOMICS OF ANCIENT MALI Natural resources: Water near the Niger River. Gold was also a resource. Industries: Farming, mining, trading, defense (army) Agricultural crops: Beans, rice, onions, sorghum, millet, papaya, gourds, cattle, sheep, goats, poultry, cotton, and peanuts. Exports: Gold Silent barter: trading without talking. Traders did not speak each other's language. To perform silent barter, one tribe would go to a certain location and leave their goods and depart. Then the other tribe would come and inspect the goods, and if they liked them, they would take them and leave their goods. Some of the most common goods were salt and gold. ECONOMICS OF ANCIENT MALI Interdependence: Mali traded gold for salt. Mali had gold and its citizens needed salt to preserve their food and for their bodies. In those days, there were no refrigerators and by salting the food, it lasted longer. Salt is also an important mineral for our health. When we sweat in warm climates, we lose salt. In order to get more into our bodies we must eat salt. Economic specialization: Traders, miners, farmers, blacksmiths, soldiers (army) Caravans: Camels were ships of the desert. Traders traveled together in large groups on the trade route. The caravans were protected by the army. Page created by: Roxanne Edwards and Nancy Spaulding Curator: Brooks Widmaier January 2003 MALI TODAY Country name: conventional long form: Republic of Mali conventional short form: Mali former: Gold Coast Capital: Bamako Flag description: three equal vertical bands of green, yellow and red. - Green stands for nature/agriculture - Yellow stands for wealth (Gold) - Red stands for sacrifice made by their forefathers for independence. The flag was adopted March 1, 1961. MALI TODAY Nationality: noun: Malian(s) Currency: franc Languages: French (official), Bambara 80% and other numerous African languages National holiday: Independence Day, September 22 (independence from France in 1960) Economics: Mali is one of the poorest countries in the world. About 10% of the population are nomads. 70% of the workers work in farming and fishing. The main products are cotton, millet, rice, corn, vegetables and peanuts. Cattle, sheep and goats are also raised. Cotton is its main export. Life expectancy: 47 years Page created by Brooks Widmaier January 2003 MALI SCAVENGER HUNT 1. On which continent was Ancient Mali located? (H/Ge) ________________ 2. What river provided water for farming, laundering (washing) and bathing? (Ge) ____________________ 3. What desert is located in the northwest region of Mali? (Ge) __________ 4. Give two reasons why Timbuktu was important in Ancient Mali. (Ge) _______________________________________________________ 5. Who was responsible for passing on stories and traditions from one generation to the next? (H) __________________ 6. Who ruled Ancient Mali? (H/Go) _______________ 7. Name one famous ruler of Mali. (H/Go) ___________________________ 8. What is known as the “Sea of Sand”? (Ge) __________________________ 9. What is a “Ship of the Desert”? (E) __________________________ 10.Name two natural resources important to Mali? (E) __________________ 11.Which resource did the people of Mali need? (*hint- they traded gold to get this important resource) (E) ___________________ 12.Name three jobs that the people of Ancient Mali specialized in? (E) _______________________________________________________ 13.Name a type of trading where no one needs to talk. (E) ________________________________ 14.Who protected the caravans? (Go) _________________ KEY Teachers: The letters in parentheses indicate which webpage where the answer can be located. Several questions have multiple answers and in the word find all answers will be included. In the crossword puzzle, students must figure out which answer is being used by the length of the word and the existing letters. Mali Scavenger Hunt 1. On which continent was Ancient Mali located? (H/Ge) Africa 2. What river provided water for farming, laundering (washing) and bathing? (Ge) Niger River 3. What desert is located in the northwest region of Mali? (Ge) Sahara Desert 4. Give two reasons why Timbuktu was important in Ancient Mali. (Ge) trade center, library, university 5. Who was responsible for passing on stories and traditions from one generation to the next? (H) griots 6. Who ruled Ancient Mali? (H/Go) kings 7. Name one famous ruler of Mali. (H/Go) Sundiata, Mansa Musa 8. What is known as the “Sea of Sand”? (Ge) Sahara Desert 9. What is a “Ship of the Desert”? (E) camel 10. Name two natural resources important to Mali? (E) gold, salt 11. Which resource did the people of Mali need? (*hint- they traded gold to get this important resource) (E) salt 12. Name three jobs that the people of Ancient Mali specialized in? (E) farming, trading, mining, army 13. Name a type of trading where no one needs to talk. (E) silent barter 14. Who protected the caravans? (Go) army OTHER RESOURCES http://www.vmfa.state.va.us/mali_geo_hist.ht ml