IP Notes
advertisement
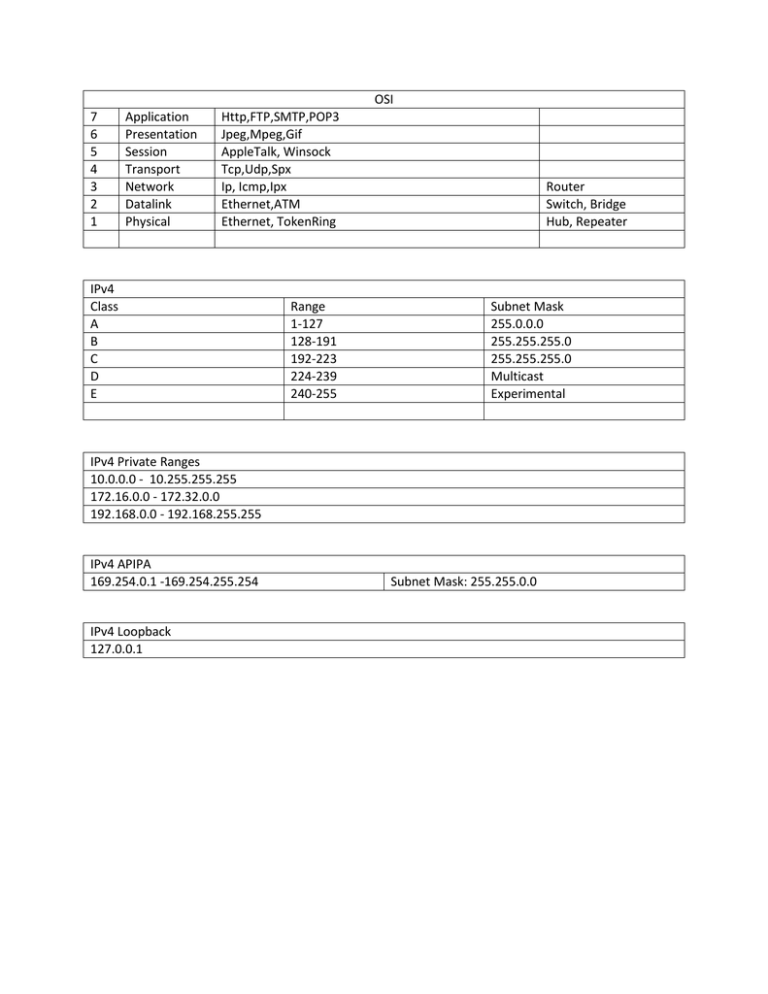
OSI 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 Application Presentation Session Transport Network Datalink Physical Http,FTP,SMTP,POP3 Jpeg,Mpeg,Gif AppleTalk, Winsock Tcp,Udp,Spx Ip, Icmp,Ipx Ethernet,ATM Ethernet, TokenRing IPv4 Class A B C D E Range 1-127 128-191 192-223 224-239 240-255 Router Switch, Bridge Hub, Repeater Subnet Mask 255.0.0.0 255.255.255.0 255.255.255.0 Multicast Experimental IPv4 Private Ranges 10.0.0.0 - 10.255.255.255 172.16.0.0 - 172.32.0.0 192.168.0.0 - 192.168.255.255 IPv4 APIPA 169.254.0.1 -169.254.255.254 IPv4 Loopback 127.0.0.1 Subnet Mask: 255.255.0.0 IPv6 16+16+16+16+16+16+16+16=128 Bits IPv6 Address 128 Bits 16 16 16 Network ID Subnet Mask 16 16 16 16 Host ID 16 Global Unicast Address (Public) ex. start with a 2 or 3 Routable Unique (Site)-Local Unicast Address (Private) ex.fec0 Private Routable within Intranet NOT Internet Link-Local Address (APIPA) ex. Start with fe80 Non-Routable LoopBack ::1 IPv6 Address Syntax The IPv6 128-bit address is divided at 16-bit boundaries, and each 16-bit block is converted to a 4-digit hexadecimal number. Colons are used as separators. This representation is called colon-hexadecimal. Global unicast IPv6 addresses are equivalent to IPv4 public unicast addresses. To illustrate IPv6 address syntax, consider the following IPv6 global unicast address: 21cd:0053:0000:0000:03ad:003f:af37:8d62 IPv6 representation can be simplified by removing the leading zeros within each 16-bit block. However, each block must have at least a single digit. With leading-zero suppression, the address representation becomes: 21cd:53:0:0:3ad:3f:af37:8d62 A contiguous sequence of 16-bit blocks set to 0 in the colon-hexadecimal format can be compressed to ::. Thus, the previous example address could be written: 21cd:53::3ad:3f:af37:8d62 Note Ipv6 abbreviation You cannot use :: twice in the same address. Some types of addresses contain long sequences of zeros and thus provide good examples of when to use this notation. For example, the multicast address ff05:0:0:0:0:0:0:2 can be compressed to ff05::2 Note IPv6 does not us e dotted decimal notation in subnet masks Only prefix length notation is supported in IPv6. IPv4 dotted decimal subnet mask representation (such as 255.255.255.0) has no direct equivalent.











