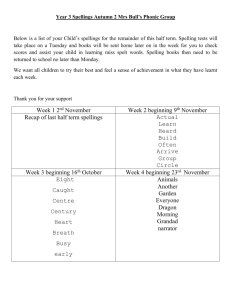
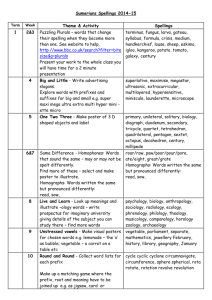
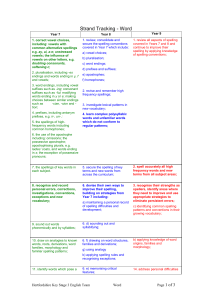
Learning Objectives
advertisement
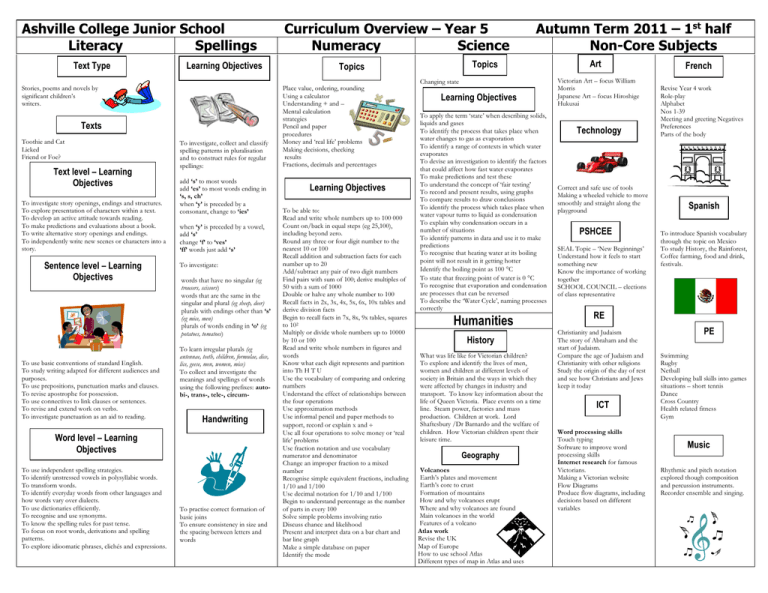
Ashville College Junior School Literacy Spellings Text Type Learning Objectives Stories, poems and novels by significant children’s writers. Texts Toothie and Cat Licked Friend or Foe? Text level – Learning Objectives To investigate story openings, endings and structures. To explore presentation of characters within a text. To develop an active attitude towards reading. To make predictions and evaluations about a book. To write alternative story openings and endings. To independently write new scenes or characters into a story. Sentence level – Learning Objectives To use basic conventions of standard English. To study writing adapted for different audiences and purposes. To use prepositions, punctuation marks and clauses. To revise apostrophe for possession. To use connectives to link clauses or sentences. To revise and extend work on verbs. To investigate punctuation as an aid to reading. To investigate, collect and classify spelling patterns in pluralisation and to construct rules for regular spellings: add ‘s’ to most words add ‘es’ to most words ending in ‘s, s, ch’ when ‘y’ is preceded by a consonant, change to ‘ies’ when ‘y’ is preceded by a vowel, add ‘s’ change ‘f’ to ‘ves’ ‘ff’ words just add ‘s’ To investigate: words that have no singular (eg trousers, scissors) words that are the same in the singular and plural (eg sheep, deer) plurals with endings other than ‘s’ (eg mice, men) plurals of words ending in ‘o’ (eg potatoes, tomatoes) To learn irregular plurals (eg antennae, teeth, children, formulae, dice, lice, geese, men, women, mice) To collect and investigate the meanings and spellings of words using the following prefixes: autobi-, trans-, tele-, circum- Handwriting Word level – Learning Objectives To use independent spelling strategies. To identify unstressed vowels in polysyllabic words. To transform words. To identify everyday words from other languages and how words vary over dialects. To use dictionaries efficiently. To recognise and use synonyms. To know the spelling rules for past tense. To focus on root words, derivations and spelling patterns. To explore idioomatic phrases, clichés and expressions. To practise correct formation of basic joins To ensure consistency in size and the spacing between letters and words Curriculum Overview – Year 5 Numeracy Science Topics Topics Place value, ordering, rounding Using a calculator Understanding + and – Mental calculation strategies Pencil and paper procedures Money and ‘real life’ problems Making decisions, checking results Fractions, decimals and percentages Learning Objectives To be able to: Read and write whole numbers up to 100 000 Count on/back in equal steps (eg 25,100), including beyond zero. Round any three or four digit number to the nearest 10 or 100 Recall addition and subtraction facts for each number up to 20 Add/subtract any pair of two digit numbers Find pairs with sum of 100; derive multiples of 50 with a sum of 1000 Double or halve any whole number to 100 Recall facts in 2x, 3x, 4x, 5x, 6x, 10x tables and derive division facts Begin to recall facts in 7x, 8x, 9x tables, squares to 102 Multiply or divide whole numbers up to 10000 by 10 or 100 Read and write whole numbers in figures and words Know what each digit represents and partition into Th H T U Use the vocabulary of comparing and ordering numbers Understand the effect of relationships between the four operations Use approximation methods Use informal pencil and paper methods to support, record or explain x and Use all four operations to solve money or ‘real life’ problems Use fraction notation and use vocabulary numerator and denominator Change an improper fraction to a mixed number Recognise simple equivalent fractions, including 1/10 and 1/100 Use decimal notation for 1/10 and 1/100 Begin to understand percentage as the number of parts in every 100 Solve simple problems involving ratio Discuss chance and likelihood Present and interpret data on a bar chart and bar line graph Make a simple database on paper Identify the mode Autumn Term 2011 – 1st half Non-Core Subjects Changing state Learning Objectives To apply the term ‘state’ when describing solids, liquids and gases To identify the process that takes place when water changes to gas as evaporation To identify a range of contexts in which water evaporates To devise an investigation to identify the factors that could affect how fast water evaporates To make predictions and test these To understand the concept of ‘fair testing’ To record and present results, using graphs To compare results to draw conclusions To identify the process which takes place when water vapour turns to liquid as condensation To explain why condensation occurs in a number of situations To identify patterns in data and use it to make predictions To recognise that heating water at its boiling point will not result in it getting hotter Identify the boiling point as 100 C To state that freezing point of water is 0 C To recognise that evaporation and condensation are processes that can be reversed To describe the ‘Water Cycle’, naming processes correctly Humanities History What was life like for Victorian children? To explore and identify the lives of men, women and children at different levels of society in Britain and the ways in which they were affected by changes in industry and transport. To know key information about the life of Queen Victoria. Place events on a time line. Steam power, factories and mass production. Children at work. Lord Shaftesbury /Dr Barnardo and the welfare of children. How Victorian children spent their leisure time. Geography Volcanoes Earth’s plates and movement Earth’s core to crust Formation of mountains How and why volcanoes erupt Where and why volcanoes are found Main volcanoes in the world Features of a volcano Atlas work Revise the UK Map of Europe How to use school Atlas Different types of map in Atlas and uses Art Victorian Art – focus William Morris Japanese Art – focus Hiroshige Hukusai Technology Correct and safe use of tools Making a wheeled vehicle to move smoothly and straight along the playground PSHCEE SEAL Topic – ‘New Beginnings’ Understand how it feels to start something new Know the importance of working together SCHOOL COUNCIL – elections of class representative French Revise Year 4 work Role-play Alphabet Nos 1-39 Meeting and greeting Negatives Preferences Parts of the body Spanish To introduce Spanish vocabulary through the topic on Mexico To study History, the Rainforest, Coffee farming, food and drink, festivals. RE Christianity and Judaism The story of Abraham and the start of Judaism. Compare the age of Judaism and Christianity with other religions Study the origin of the day of rest and see how Christians and Jews keep it today ICT Word processing skills Touch typing Software to improve word processing skills Internet research for famous Victorians. Making a Victorian website Flow Diagrams Produce flow diagrams, including decisions based on different variables PE Swimming Rugby Netball Developing ball skills into games situations – short tennis Dance Cross Country Health related fitness Gym Music Rhythmic and pitch notation explored though composition and percussion instruments. Recorder ensemble and singing.