Unit 3 Optics: Chapter 5 Law of Reflection To show how light is from
advertisement
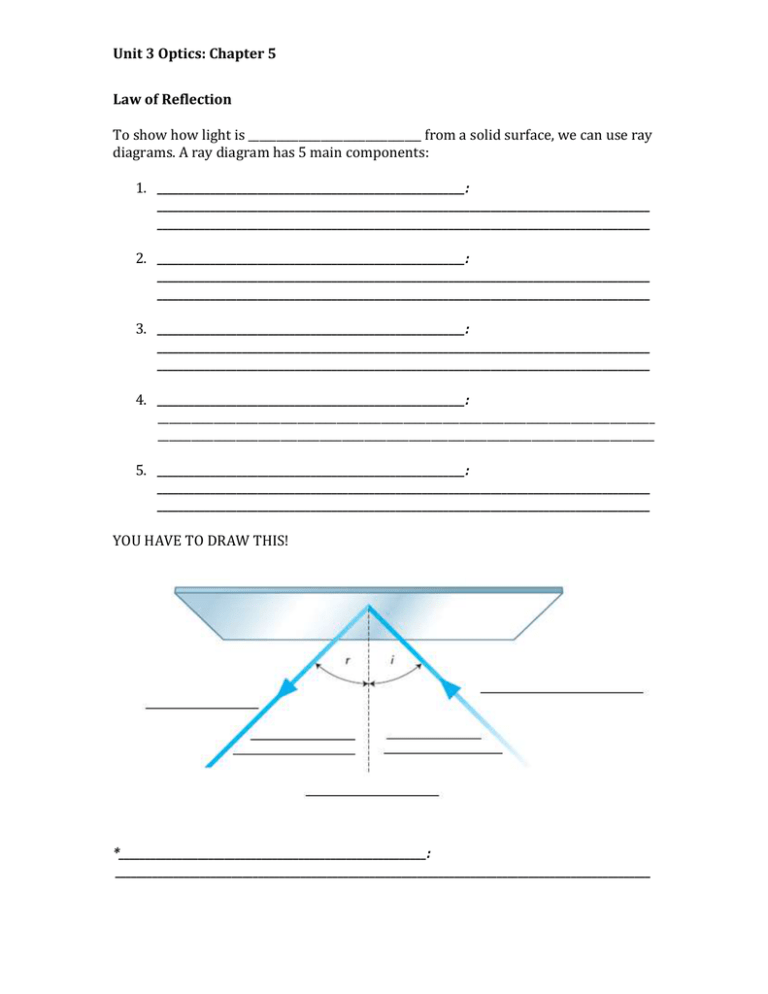
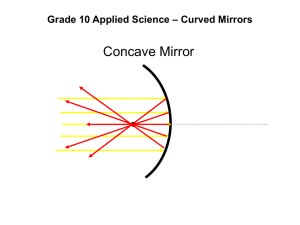
Unit 3 Optics: Chapter 5 Law of Reflection To show how light is _______________________________ from a solid surface, we can use ray diagrams. A ray diagram has 5 main components: 1. __________________________________________________________: _____________________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________________ 2. __________________________________________________________: _____________________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________________ 3. __________________________________________________________: _____________________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________________ 4. __________________________________________________________: _________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________ 5. __________________________________________________________: _____________________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________________ YOU HAVE TO DRAW THIS! *__________________________________________________________: _____________________________________________________________________________________________________ Recall: _______________________________________________________ (reflection from a mirror-like surface) ________________________________________________________________________________ For a surface to act as a mirror and produce _____________________________ reflection, it must be _______________________ compared to the wavelength of the light striking the surface. YOU HAVE TO DRAW THIS! _____________________________________________________________ (reflection from a rough surface). No clear image produced, but you can see the surface the light is bouncing off. Light bounces off in random directions Example: A piece of paper (the black ink absorbs all the light and the white paper reflects all the light in random directions ) YOU HAVE TO DRAW THIS! How Do We Use Specular and Diffuse Reflection Everyday? _________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________ Types of Mirrors 1. ______________________________________________________: _________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________ 2 2. ______________________________________________________: _________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________ 3. ______________________________________________________: _________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________ Examples: Plane: ________________________________________________________________________________ Concave: _____________________________________________________________________________ Convex: ______________________________________________________________________________ Images in a Plane Mirror The angle of incidence and the angle of reflection are always ___________________________ (law of reflection). The image and the object distance from the mirror are always _________________________. 3 Ray diagram of a Plane Mirror (Page 189) ***Core Lab Page 192*** Images in Concave Mirrors Reflected light rays travel __________________________________________________________________. _______________________________: ________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________: ________________________________________________________________________________ If you then draw rays of light approaching the mirror parallel to the principal axis, you will see that all of the reflected rays intersect at one point. This is the ____________________________________________________________________________________. Ray diagrams for Concave Mirrors Object is between Focal point and Mirror (See Page 198) The image will be … 1. 2. 3. 4. Size Position Orientation (upright/inverted) Type of image (Real/virtual) 4 YOU TRY IT!!! 5 1. 2. 3. 4. Object is between the focal point and 2X the focal length. (See Page 200) The image will be … Size Position Orientation (upright/inverted) Type of image (Real/virtual) YOU TRY IT! 6 Object is beyond 2X the focal length. (See Page 202) The image will be … 1. 2. 3. 4. Size Position Orientation (upright/inverted) Type of image (Real/virtual) YOU TRY IT! Textbook: page 202 #'s 1-2 7 Images in Convex Mirrors Reflected rays __________________________________________________. But, if you extend the rays _______________________________ the mirror, the extended rays will intersect at the ________________________________________________________, F. The focal point for a convex mirror is _____________________________________________. Ray diagrams for Convex Mirrors When drawing ray diagrams for a convex mirror, you follow the same steps no matter where the object is in relation to the mirror (the object distance doesn’t matter). Remember in convex mirrors the focal point is always BEHIND THE MIRROR. See Page 205 1. 2. 3. 4. The image will be … Size Position Orientation (upright/inverted) Type of image (Real/virtual) YOU TRY IT! 8 ***Textbook: page 206 #'s 1-3*** Summary: There are two types of curved mirrors: 1) ______________________________________________ have a reflective surface that curves inward. Depending on the location of the object relative to the focal point of the mirror, images in these mirrors can be: 1) ______________________ or ____________________________ ( a real image is formed when reflected rays meet). 2) ______________________ or _____________________________ 3) ____________________________ or _______________________ than the object 2. ______________________________________________ have a reflective surface that curves outward. Images in convex mirrors are: 1. ________________________________________________________________________________ 2. ________________________________________________________________________________ 3. ________________________________________________________________________________ 4. ________________________________________________________________________________ 9 WHAT WILL IT LOOK LIKE! (SPOT) Mirror/Object type Size Position Orientation Type Concave mirror (Object between focal point and mirror) Concave Mirror (Object between focal point and two times the focal length) Concave mirror (Object beyond two times the focal length) Convex mirror Real Vs. Virtual Images Describe the difference between real and virtual images. Use your notes and your textbook: _________________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________________ P. 187, #s 2, 7a, 9a&b, and 10; P. 209, #s 1-12 10