11.9 Convex Mirrors fill
advertisement

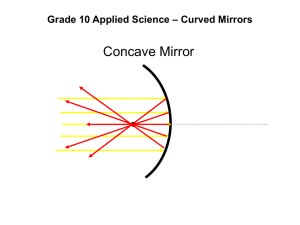
Convex Mirrors Convex mirrors are spherical mirrors that curve outwards. This causes reflected light rays to _____________ and travel away from each other when they hit the mirror. The principal focus (F) and centre of curvature (C) are _________ because they are located behind the mirror. For this reason their values are negative numbers. C Rules for Ray Diagrams of Convex Mirrors are the same as for Concave mirrors. The only difference is that the rays only appear to pass through the points behind the mirror. Here is a list of rules for BOTH types of mirrors: 1. A Ray that travels _________ to the principal axis is reflected ________ (or as if it had gone through) the principal focus. 2. A ray that travels _______ (or appearing to pass through) the principal focus is reflected _________ to the principal axis. 3. A ray that passes _________ (or appears to pass through) the centre of curvature will reflect back along the same path. Unlike the concave mirror which produces both real and virtual images, convex mirrors only produce virtual images. They are all upright, smaller than the object and located between the vertex and the focal point. S: Smaller than object A: upright L: behind the mirror (btw V and F) T: Virtual Example: A 1.5cm object is located 2.0cm away from a convex mirror that has a focal length of -3.0cm and a centre of curvature of – 6.0cm. Describe the image using SALT.