The codon for the amino acid serine is UCA
advertisement

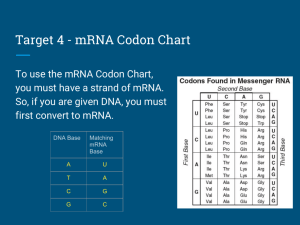
How are these pieces of music similar? How are they different? What is the result of their difference Compare and contrast the DNA molecule on the left with the RNA molecule on the right Include 3 similarities and 3 differences between the two molecules Break into equal lab groups and use your Outreach Notes to create a flow map showing how and where the process of protein synthesis takes place within a cell. Must include: Transcription & Translation (what & where and how) & Organelles Involved Lets take a look at the other groups projects We have looked at DNA. But how is this gentic code actually used for anything? Lets See! The genetic code is used as a blueprint to make proteins. Proteins are widely used in cells to serve diverse functions. Some proteins provide the structural support for cells while others act as enzymes to catalyze certain reactions. But, where do proteins come from? Since the beginning of evolution, cells have developed the ability to synthesize proteins. They can produce new proteins either for reproduction or to simply replace a degraded one. Within the coil of DNA lies all the information needed to produce everything in the human body. A strand of DNA may be millions, or billions, of base-pairs long. Different segments of the DNA molecule code for different characteristics in the body. DNA is a complex double stranded molecule that carries an organisms genetic information in the form of a code of repeating sub units. What do we call the DNA sub-unit identified by the X in the diagram on the right? A chromosome is a large collection of DNA that contains many genes and the support proteins needed to control these genes. A gene is a section of a chromosome (DNA) that codes for a protein However, cells don't express all of their genes all of the time. The Lipizzaner horses from Spain are pure white as adults . . . . . . but are born black To manufacture proteins, cells follow a very systematic 2 step procedure that first transcribes DNA in the nucleus into mRNA and then translates the mRNA into chains of amino acids in the cells ribosomes. RNA is very similar to DNA except that it: has only a single strand of nucleotides instead of two strands contains a different sugar (ribose instead of deoxyribose) contains the nitrogen base uracil (U) instead of thymine (T) • Ribosomal RNA (rRNA), along with protein, makes up the ribosomes • Messenger RNA (mRNA) copies DNA’s code & carries the genetic information to the ribosomes • Transfer RNA (tRNA) transfers amino acids to the ribosomes where proteins are synthesized The “m” in “mRNA” stands for “messenger,” because mRNA copies genetic information from DNA (which is found in the nucleus) and carries it to another part of the cell (the ribosomes). Transcribe the DNA sequence below into a strand of mRNA G T T C C G A T C ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? Where in a cell does the process below take place? A A A G G C T A G T T T C C G A T C U U U C C G A U C What product is produced as a result of this process? A A A G G C T A G T T T C C G A T C U U U C C G A U C Think of the genetic code the mRNA is carrying as a series of three-letter “words.” Each of these three-letter words is called a codon. Codon Codon Codon Codon Codon Codon Different codons code for different amino acids. For example, the codon for the amino acid methionine is AUG (adenine, uracil, guanine). The codon for the amino acid serine is UCA (uracil, cytosine, adenine). Another type of RNA, called tRNA (“t” stands for “transfer”) matches the codons in mRNA to the correct amino acids. As the mRNA strand moves along the ribosome, the amino acids are joined in the correct sequence to form a protein. This process is called translation. U C G A C C G G A G Codon Codon Codon Codon Codon Codon The diagram below shows a codon chart. A codon chart shows which codons code for which amino acids. This chart shows the amino acids coded for by each of the 64 possible mRNA codons. To find which amino acid the codon CAA codes for, follow these steps. (1) Look on the left side of the chart to find the large row of codons that begin with C. (2) Move across this row until you get to the column of codons whose second base is A. (3) Move down this column until you get to the row of codons whose third base is A. The codon CAA codes for the amino acid glutamine. Suppose a DNA mutation led to a change in a single mRNA codon. Now suppose this codon changed from GCC to GCG. By looking at the codon chart, you can see that both of these codons code for the amino acid alanine. So even though the DNA and mRNA have changed, there is no change in the protein! AUG CCU AUU GAU GGC CCA UAA GUU How would a change in the sequence of nucleotides in a DNA molecule affect the mRNA transcribed from the DNA molecule? Any change in the DNA would cause a change in the mRNA molecule Methionine (start) Leucine Theronine Stop AUG AAU AAC GUU GUC GUA GUG CAU CAC Compare and contrast the DNA molecule on the left with the RNA molecule on the right Include 3 similarities and 3 differences between the two molecules Think of the genetic code the mRNA is carrying as a series of three-letter “words.” Each of these three-letter words is called a codon. Codon Codon Codon Codon Codon Codon Different codons code for different amino acids. For example, the codon for the amino acid methionine is AUG (adenine, uracil, guanine). The codon for the amino acid serine is UCA (uracil, cytosine, adenine). Another type of RNA, called tRNA (“t” stands for “transfer”) matches the codons in mRNA to the correct amino acids. As the mRNA strand moves along the ribosome, the amino acids are joined in the correct sequence to form a protein. This process is called translation. U C G A C C G G A G Codon Codon Codon Codon Codon Codon The diagram below shows a codon chart. A codon chart shows which codons code for which amino acids. This chart shows the amino acids coded for by each of the 64 possible mRNA codons. To find which amino acid the codon CAA codes for, follow these steps. (1) Look on the left side of the chart to find the large row of codons that begin with C. (2) Move across this row until you get to the column of codons whose second base is A. (3) Move down this column until you get to the row of codons whose third base is A. The codon CAA codes for the amino acid glutamine. Suppose a DNA mutation led to a change in a single mRNA codon. Now suppose this codon changed from GCC to GCG. By looking at the codon chart, you can see that both of these codons code for the amino acid alanine. So even though the DNA and mRNA have changed, there is no change in the protein! AUG CCU AUU GAU GGC CCA UAA GUU How would a change in the sequence of nucleotides in a DNA molecule affect the mRNA transcribed from the DNA molecule? Any change in the DNA would cause a change in the mRNA molecule Methionine (start) Leucine Theronine Stop AUG AAU AAC GUU GUC GUA GUG CAU CAC