Dichotomous Key
advertisement
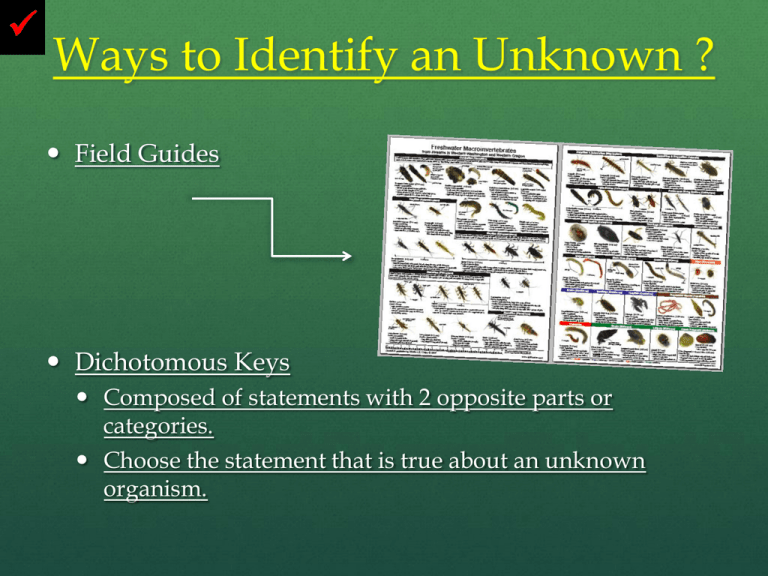
Ways to Identify an Unknown ? Field Guides Dichotomous Keys Composed of statements with 2 opposite parts or categories. Choose the statement that is true about an unknown organism. Dichotomous Key Look out for the special check mark to know which notes to write! On a checked slide, write all notes, unless … On a checked slide with lots of notes, just write underlined text! Classification System that groups organisms based on common features that they share Aristotle First man to develop a system to classify organisms 2 kingdoms He subdivided each kingdom Plant- based division on size Herbs Shrubs Trees Animals- based division on habitat Air Land Sea Animals: Air Land Sea Carolus Linnaeus Improved classification system Based his grouping on physical features Linnaeus =Universal name= Binomial Nomenclature All organisms are given a universal name Used by all scientists Helpful when many common names are used Name is composed of 2 names Genus name Capitalized and comes first! Species name lower case and comes second Both names are underlined Example: Tolypeutes matacus – Three Banded Armadillo Common names are misleading Puma Cougar Mountain Lion A seahorse is not a horse, but a fish. Scientific name Myotis macrotarsus “Mouse-eared bat with big feet” Cat Genus name= Felis Species name= domesticus=house cat sylvestris=wildcat Human Genus name=Homo Species=sapien Kingdom: Animalia (mobile critters; have many cells; can’t make their own food) Phylum: Chordata (flexible skeletal rod with accompanying nerves) Class: Chondrichthyes (‘fish’ with a cartilaginous skeleton) Order: Lamniformes (‘Mackerel’ sharks) Family: Lamnidae (‘Mackerel’ sharks) Genus: Carcharodon (from the Greek carcharos meaning “ragged” or “pointed” and odon meaning “tooth”) Species: carcharias (Greek for “shark”) Modern classification system Uses Linnaeus system but adds: comparison of body chemistry and development features DNA sequence Cytochrome C Hemoglobin Developmental stages of embryos Reclassified Modern Classification System Domain= Eubacteria Kingdom=Eubacteria Prokaryotic Bacteria Domain=Archaea Kingdom=Archaebacteria Extreamophiles Domain Eukarya Contains 4 kingdoms Kingdom=Protista Kingdom=Fungi Kingdom=Plant Kingdom=Animal Classification Groups =Taxa A Mnemonic Device: Dear King Philip Came Over For Ginger Snaps Each division contains fewer organisms, but shares more features in common. Classification Taxa Domain is the largest Taxa Domain contains one or more kingdoms Domain contain the most organisms Each kingdom is then subdivided into: Phylum, Class, Order, Family, Genus, Species Species contain the fewest organisms but with the most physical features in common Classification Which two animals are most closely related?