Ch. 5 Greek Civilization Ch. 5:1 The Culture of Ancient Greece – The
advertisement
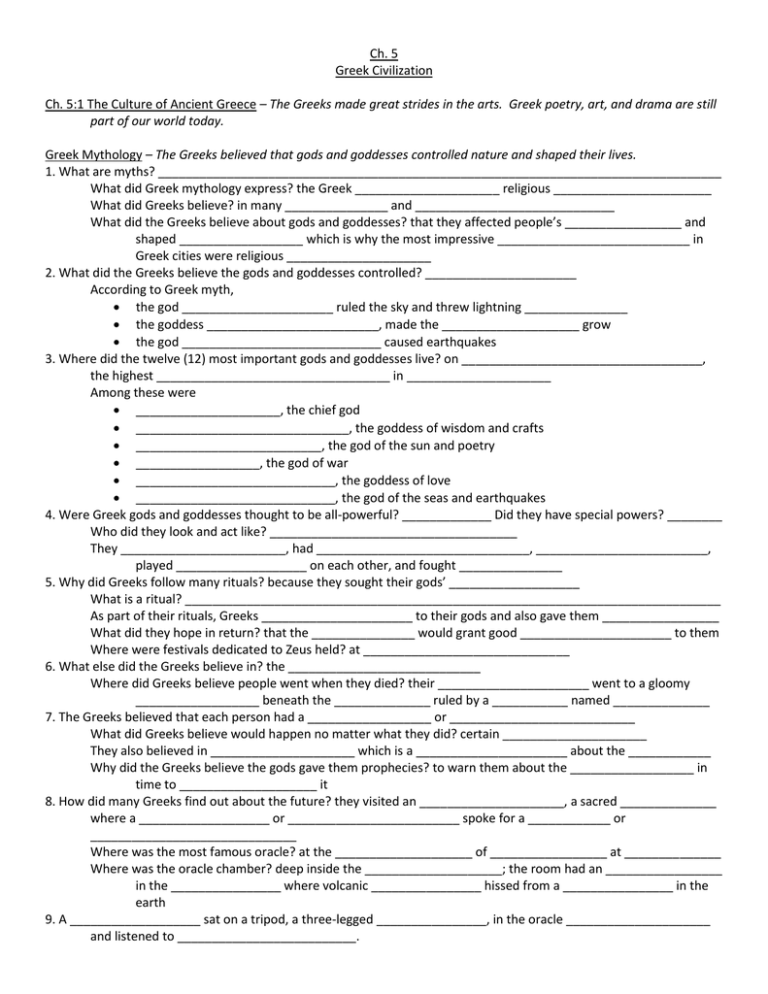
Ch. 5 Greek Civilization Ch. 5:1 The Culture of Ancient Greece – The Greeks made great strides in the arts. Greek poetry, art, and drama are still part of our world today. Greek Mythology – The Greeks believed that gods and goddesses controlled nature and shaped their lives. 1. What are myths? __________________________________________________________________________________ What did Greek mythology express? the Greek _____________________ religious _______________________ What did Greeks believe? in many _______________ and _____________________________ What did the Greeks believe about gods and goddesses? that they affected people’s _________________ and shaped __________________ which is why the most impressive ____________________________ in Greek cities were religious _____________________ 2. What did the Greeks believe the gods and goddesses controlled? ______________________ According to Greek myth, the god ______________________ ruled the sky and threw lightning _______________ the goddess _________________________, made the ____________________ grow the god _____________________________ caused earthquakes 3. Where did the twelve (12) most important gods and goddesses live? on ___________________________________, the highest __________________________________ in _____________________ Among these were _____________________, the chief god _______________________________, the goddess of wisdom and crafts ___________________________, the god of the sun and poetry __________________, the god of war _____________________________, the goddess of love _____________________________, the god of the seas and earthquakes 4. Were Greek gods and goddesses thought to be all-powerful? _____________ Did they have special powers? ________ Who did they look and act like? ____________________________________ They ________________________, had _______________________________, _________________________, played ___________________ on each other, and fought _______________ 5. Why did Greeks follow many rituals? because they sought their gods’ ___________________ What is a ritual? ______________________________________________________________________________ As part of their rituals, Greeks ______________________ to their gods and also gave them _________________ What did they hope in return? that the _______________ would grant good ______________________ to them Where were festivals dedicated to Zeus held? at ______________________________ 6. What else did the Greeks believe in? the ____________________________ Where did Greeks believe people went when they died? their ______________________ went to a gloomy __________________ beneath the ______________ ruled by a ___________ named ______________ 7. The Greeks believed that each person had a __________________ or ___________________________ What did Greeks believe would happen no matter what they did? certain _____________________ They also believed in _____________________ which is a ______________________ about the ____________ Why did the Greeks believe the gods gave them prophecies? to warn them about the __________________ in time to ____________________ it 8. How did many Greeks find out about the future? they visited an _____________________, a sacred ______________ where a ___________________ or _________________________ spoke for a ____________ or ______________________________ Where was the most famous oracle? at the ____________________ of _________________ at ______________ Where was the oracle chamber? deep inside the ____________________; the room had an _________________ in the ________________ where volcanic ________________ hissed from a ________________ in the earth 9. A ___________________ sat on a tripod, a three-legged ________________, in the oracle _____________________ and listened to __________________________. Who translated her answers? _____________________ Who traveled to Delphi to ask advice from the oracle of Apollo? state _______________________ or their _____________________________ How did the priestess often give answers? in __________________________ Greek Poetry and Fables – Greek poetry and fables taught Greek values. 10. Where are Greeks’ poems and stories the oldest? in the ______________________ world. Who have used these early works as models for their own poems and stories? ________________________ and __________________________ Who borrowed many Greek plots and settings? _________________________________ 11. The earliest Greek stories were _______________ which are long _________________ that told about heroic _________________ What were the first great epics of early Greece? the _______________ and the ________________________ Who wrote these epics? ______________________ When? the ________________ B.C. What did he base them on? stories of a _____________ between ___________________ and the city of _____________ which is in what is today northwestern ______________________ 12. Describe the story of the Iliad. ______________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________________ 13. Describe the story of the Odyssey___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________________ 14. Did the Greeks believe the Iliad and the Odyssey were more than stories? ____________ They looked upon them as real _____________________ What did these stories give the Greeks? an ideal _______________ with a cast of __________________ What did Homer’s stories teach? ______________________ and _____________________ that it was important to be _____________________ to your __________________ and to value the _________________________ between husband and _________________ 15. The stories showed heroes striving to be the ______________ they could be and heroes fought to protect their own __________________ and their family’s ________________. They also became _____________ models for Greek boys 16. Who was Aesop? a Greek ___________________ What did he write? _________________ What is a fable? a short ________________ that teaches a __________________ 17. In most of Aesop’s fables, who talked and acted like people? _______________________ What did these funny stories often point out? human __________________ as well as _____________________ What did each fable end with? a ______________________ or a _____________________ 18. What is one of Aesop’s most famous fables? the _________________________ and the _______________ Describe the story ____________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________________ What is the moral of the story? __________________________________________________________________ What are some other of Aesop’s famous phrases?__________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________________ 19. For how long were Aesop’s fables part of Greece’s oral tradition? __________ years What does that mean? ________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________________ Greek Drama – Greek drama still shapes entertainment today. 20. What is drama? __________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________________ What do actors do in a drama? they _________________, show ___________________, and imitate the __________________ of the ___________________________ they represent 21. Where did Greeks perform their plays? in outdoor ____________________ as part of their religious _____________ What two (2) types of dramas did they develop? _______________________ and _________________________ 22. What is a tragedy? _______________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________________ In early Greek tragedies, what did people struggle against? their ________________ Later what did Greek tragedies show? how a person’s _________________________ flaws caused them to ____________ 23. How does a comedy end? _______________________ What does the word comedy mean? any _______________ that has a happy ___________________ 24. What big questions did Greek stories deal with? ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ 25. Who were three (3) of the best-known writers of Greek tragedies? _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ 26. How many actors did early Greek tragedies have? ____________ What did they give? __________________ Who sung songs that described the events? a _________________________ Who was the first to introduce the idea of having two (2) actors? ________________________________ What else did Aeschylus introduce? ___________________________, ______________________, and stage _______________________________ 27. What was one of Aeschylus’s best-known plays? the _____________________________ What does it describe? ________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________________ What does the Oresteia teach? __________________________________________________________________ What triumphs over evil? _________________________ What is the moral of these plays? ________________________________________________________________ 28. How many actors did Sophocles use? _____________ What did he paint behind the stage as a backdrop to the action? _______________________ What are two of Sophocles’ most famous plays? ______________________________ and __________________ What does Sophocles ask in Antigone? ____________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________________ 29. Who tried to take Greek drama beyond heroes and gods? __________________________________ His characters were more __________________ to ___________________ What did Euripides’ plots show a great deal of interest in? ____________________________________________ What did he question? traditional _________________________ especially about _______________ Who did Euripides believe war was especially cruel to? ___________________ and ______________________ 30. Whose works were good examples of comedies? ______________________________ Who did they make fun of? ________________________ and __________________________ What did they encourage the audience to do? _______________________ as well as _____________________ Greek Art and Architecture – Greek art and architecture expressed Greek ideas of beauty and harmony. 31. What did artists in ancient Greek believe? in certain _______________ and tried to show those ________________ in their ________________ Have these ideas ever gone out of style? ____________ 32. What did Greek artists want people to see in their work? ______________________ ___________________________ _____________________ _____________________ What did they hope their art would inspire people to do? to base their ________________ on these same __________________ 33. What do we know Greeks painted although none have survived? __________________ What two (2) colors were used on most pictures on pottery from ancient Greece? ________ and ____________ What scenes were often on large vases? from Greek __________________ What scenes were on small drinking cups? from everyday ______________ 34. The Greeks were also skilled ______________________________ What is architecture? the ______________ of _____________________ and _____________________ structures In Greece, what was the most important architecture? the ____________________ dedicated to a _________ or ___________________________ What is the best-known example? the _____________________________ What were kept in the walled room in the center of these temples? ______________________ of gods and goddesses and the ________________ offered to them 35. What supported many Greek buildings? large ___________________ carved from ________________ What did the Greeks begin to use to make columns in 500 B.C.? _______________________ How were the columns kept from toppling? sections were joined with wooden _______________ Where are marble columns common features of today? ____________________ and government ________________________ such as the White _______________________ and the _______________ in our nation’s capital. 36. What were many Greek temples decorated with? _________________________ What was sculpture used to express? Greek _____________________ What was the favorite subject of Greek artists? the human ______________ Did Greek sculptors copy their subjects exactly? _________ Why? they tried to show their ideal ______________________ of ___________________ and _______________ Identify Homer Aesop Sophocles Euripides Ch. 5:2 Greek Philosophy and History – The Greeks’ love of wisdom led to the study of history, politics, biology, and logic. Greek Philosophers – Greek philosophers developed ideas that are still used today. 1. What does the word philosophy come from? the Greek word for “_____________________ of __________________” What did Greek philosophy lead to? the study of __________________________ ________________________________________ __________________________ ___________________________________ 2. Who were philosophers? Greek ______________________ who believed the human _______________ could understand ______________________________ 3. Many philosophers were __________________________. What did Pythagoras teach his pupils? that the ___________________________ followed the same ________________ that governed __________________ and ____________________________ What did Pythagoras believe that all relationships in the world could be expressed in? _____________________ What did he develop? many new _____________________ about ________________________________ What theorem is named for Pythagoras? the ______________________________ theorem which is a way to determine the ________________ of the sides of a __________________________ 4. Who were Sophists? professional ___________________________ in ancient ______________________ How did they make a living? by ________________________________________________ What did Sophists believe? that students should use their ______________ to improve ____________________ What did many teach their students? how to win an _____________________________ how to make good political _______________________ 5. Did Sophists believe that gods and goddesses influenced people? _________ Did they believe in the idea of absolute right or wrong? _________ What did they believe? that what was _______________ for one ___________________ might be ___________ for ________________________ 6. Who was a critic of the Sophists? ___________________________ Who was Socrates? an Athenian ________________________ whose true love was _______________________ Did Socrates leave any writings behind? ________ How do we know about him? ___________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ 7. What did Socrates believe? _________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________________ What did he invent? the _______________________ method of teaching that asked pointed _______________ to force his ____________________ to use their _______________________ and to see ____________ for _____________________________ 8. What did some Athenian leaders consider the Socratic method to be? a ________________ to their _______________ Athens had a ________________________ of questioning ______________________ and speaking __________ 9. What changed the Athenians? their defeat in the _____________________________ War How? they no longer trusted open ____________________ What did the leaders accuse Socrates of teaching young Athenians in 399 B.C.? to _________________ against the ________________ Was he found innocent or guilty? _______________________ He was sentenced to ________________. Could he have fled the city? ____________ Did he? ___________ Why not? ___________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ How did Socrates carry out the jury’s sentence? ____________________________________________________ 10. Who was Plato? one of Socrates’ _________________________ How are we able to learn a lot about Plato? from his ______________________ What was the Republic about? it explains Plato’s ____________________ about _________________________ Did Plato believe democracy was a good system of government? _________ What didn’t Plato believe democracy produced? ____________________________________________________ What did Plato believe people needed to live good lives? a ______________ and _________________________ government 11. In the Republic, what did Plato describe? his ideal _____________________________ He divided people into __________ basic groups: ______________________________________ who ruled using _____________ and ________________ ________________________ who defended the _________________ from ___________________ the rest of the _____________________ who were driven by _____________________, not by ______________________ . They produced the state’s _________________, ____________________, and _______________________ 12. Plato believed that men and women should have the same _______________________ and an equal ____________ to have the same _______________ What was the school Plato established in Athens? the _____________________ 13. Who was Plato’s best student? ________________________ How many books did Aristotle write? more than _______ on topics ranging from _______________________ to the _________________ and _______________ What is the name of the school that Aristotle opened? the ______________________ What did Aristotle teach his students at the Lyceum? the “___________________ ________________” What does this idea hold? that a ___________________ should do _________________ in ________________ 14. How did Aristotle help to advance science? he urged ____________________ to use their __________________ to make _____________________ What was Aristotle the first to do? to group _____________________________ according to their ________________________ and _________________________ Then he made _________________________ based on the ________________ of ________________ 15. How did Aristotle find the best form of government? he __________________ and __________________ the governments of 158 different ______________ Describe the three (3) types of government by Aristotle: ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ 16. According to Aristotle, in the governments run by a few people, who were the ones that usually ran the government? the ______________ What did Aristotle’s ideas shape? the way ____________________ and ____________________ thought about __________________________ Whose government tried to create a mixed government that balanced the different types Aristotle had identified? the ________________________________________________________________________ Greek Historians – Greeks wrote the first real histories in Western civilization. 17. In most places in the ancient world, what was not written? ________________________ What explained their past? _____________________ and _________________ 18. Who wrote the history of the Persian Wars? a Greek named ________________________ What did Herodotus try to separate? ________________ from _____________________ He asked _______________________, recorded _______________________, and checked the _________________________ of his ____________________ What do Western historians call him? the “_________________ of ___________________” 19. Who is considered to be the greatest historian of the ancient world? ________________________________ What did he write? ______________________________________________________ What did Thucydides see war and politics as the activities of? ______________ beings, not ______________ What else did he stress? the __________________________ of having accurate ___________________ Identify: Pythagoras Socrates Plato Aristotle Herodotus Thucydides Ch. 5:3 Alexander the Great – Alexander the Great was only 25 years old when he conquered the Persian Empire. As a result of his conquests, Greek art, ideas, language, and architecture spread throughout southwest Asia and North Africa. Macedonia Attacks Greece - Philip II of Macedonia united the Greek states. 1. Where does Macedonia lay? _______________ of __________________ What did the Macedonians raise in their river valleys? ______________________ and __________________ What did they grow? __________________ They were a _____________________ people who fought on ______________________ 2. Who looked down on the Macedonians? the _________________________ By ___________ B.C., who had become a powerful kingdom? _________________________________ 3. Who rose to the throne by 359 B.C.? ______________________ What did he admire about the Greeks? their ______________, their ______________, and their _____________ Who did Philip II want to defeat? the mighty __________________ Empire What did he have to do to be able to do this? to _______________ the Greek ______________________ with his own ______________________ 4 What did Philip II raise to fight like the Greeks? a vast _______________ of foot ______________________ Did he unite Greek city-states with his own kingdom? ___________ How? he took some by ________________ and _______________ the leaders of _______________ to surrender; some __________________ with his kingdom _____________________________ 5. Who was a lawyer and one of Athens’s great public speakers? ___________________________ What did he warn? that ___________________ was a threat to Greek ______________________ What did he urge? __________________ and other __________________________ join together to fight the _____________________________ Did the Greeks listen to him? __________ 6. What left the Greeks weak and divided? the _____________________________ War As a result: the population _________________________ fighting had destroyed many _________________ and left ____________________ with no way to earn a ____________________ thousands of young __________________ left Greece to join the Persian _______________ many who stayed behind began fighting among __________________________ the city-states grew _____________________ 7. Could they stop the invasion by Philip’s army? ___________ What is the name of the battle where the Macedonians crushed the Greeks? the Battle of __________________ near _______________ Who now controlled all of Greece? _______________________ Alexander Builds an Empire – Alexander the Great conquered the Persian Empire and spread Greek culture throughout southwest Asia. 8. How did Philip plan to conquer the Persian Empire? with the ___________________ help What happened to Philip before he could do this? he was ____________________________ So then, who had to invade Asia? his son, _____________________________ 9. How old was Alexander when he became king of Macedonia? _________ years old Philip had carefully trained his son for ____________________________ How old was Alexander when he rose to commander in the Macedonian army? ___________ years old After Philip’s death, was Alexander ready to invade the Persian Empire? _________ 10. In the spring of 334 B.C., where did Alexander invade? __________________________ with about ______________ Macedonian and Greek foot ________________________ and ________________ mounted warriors Did Alexander win? __________ at the Battle of ___________________ 11. By the next year, Alexander had freed the Greek _______________ in _______________________ from Persian rule and defeated a large Persian _______________ at ______________________ By the winter of 332 B.C., he had captured ____________________ and _____________________ 12. Where did he build a center of business and trade? at _____________________________ What did the city become? one of the most important ________________ in the ancient __________________ 13. In 331 B.C., Alexander headed _____________ and defeated the Persians at _____________________, near ______________________, then easily overran the rest of the Persian _____________________ Did Alexander stop at Persia? _________ He went as far as modern __________________________ After entering India, what did Alexander’s soldiers do? _______________________________________________ Did Alexander agree to lead them home? ___________ 14. What killed thousands of soldiers as they crossed a desert in what is now Iran?___________ and _____________ 15. How did Alexander die? he came down with a bad _________________ How old was he when he died? _________ years old 16. Alexander was a great military __________________ Was he courageous? ___________ What could have been the key to his courage? his childhood ________________________ What is Alexander called today? Alexander the ___________________ 17. What is a legacy? what a ___________________ leaves ________________ when he or she _____________ What created Alexander’s legacy? his ______________ and ________________ What did he help extend? _________________ and ___________________________ rule over a vast ____________ What did he and his armies spread? Greek ____________, ___________________, _____________________, and _______________________________ wherever they went What did the Greeks bring back from Asia and Africa? new _______________ 18. What did Alexander’s conquests mark the beginning of? the _________________________ Era What does Hellenstic mean? “like the ________________” and refers to a ______________ when the Greek ______________________ and Greek _______________ spread to the non-Greek _________________ of southwest ___________ 19. Who did Alexander the Great plan to unite under his new empire? _________________________________ _____________________ ___________________________ He used Persians as ______________________ and encouraged his soldiers to marry Asian ______________. Who fought for power after Alexander died? his _______________________ 20. What happened as a result? the empire fell _______________ What four (4) kingdoms took its place? ______________________________ ______________________________ ______________________________ ______________________________ 21. In what language was business conducted in the Hellenistic kingdoms? ____________________ Who were the only ones who could apply for government posts? ________________ and _________________ who spoke _________________ Who did kings prefer to give the jobs to? ______________________ and _____________________________ 22. What was the largest city in the Mediterranean world by 100 B.C.? ___________________________________ 23. What did new Greek cities need? _________________________ _________________________ _________________________ _________________________ _________________________ 24. What did Greeks and Macedonians who settled in southwest Asia provide? new _______________ for the ________ and a _________________ of government _________________ and __________________ What did they help spread? Greek ___________________ into _________________ and as far ____________ as modern-day ___________________________ and ____________________ Identify: Philip II Alexander the Great Ch. 5:4 The Spread of Greek Culture – Greek cities became centers of learning and culture. Greek scientists developed advanced ideas about astronomy and mathematics. Greek Culture Spreads – Hellenistic cities became centers of learning and culture. 1. During the Hellenistic Era, who flocked to the new Greek cities in southwest Asia? ______________________________ _________________________ ________________ ________________ Why? they came to take __________________________ of Alexandria’s __________________ How many scrolls did they have? _____________ What did Alexandria have that researchers went to do their work? a ___________________________ 2. What were Hellenistic kingdoms? lands of ________________________________ for Greek _____________________ What did Hellenistic kings want to make cities like? cultural ____________________ of ______________ What did they pay to line the streets with baths, theaters, and temples? handsome _________________ 3. Who filled towns and cities with thousands of statues? Greek ________________________ hired by Hellenistic _____________________ and other wealthy _________________________ These statues showed the same _____________________ of _____________________________ as the statues from Greece’s ________________________ ________________. 4. Who else did Hellenistic leaders also admire? talented ________________________ Who spent generous sums of money supporting writers’ work? _____________ and leading ________________ What did this produce? a large _______________ of ______________________________ Did much of this writing survive? ___________ 5. Who wrote Argonautica? _______________________ of Rhodes Describe this epic poem: _______________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________________ 6. Who wrote short poems about the beauty of nature? a poet named ________________________________ 7. Where was the center of Greek theater? _______________________ What did playwrights in Athens create? a new kind of ____________________________ that had happy _________________________ and still made _______________________ laugh Did they poke fun at political leaders? ____________ Instead, what did the plays tell stories about? _________________ and ________________________________ Who was one of the best known of the new playwrights? ____________________________ Philosophy – Epicurus and Zeno showed the world different ways to look at happiness. 8. Where were the most famous philosophers in the Greek world attracted to? _______________________ Who were two (2) of the most important philosophers? _________________________ and ________________ 9. Who founded a philosophy we now know as Epicureanism? ________________________ What did he teach his students? that _____________________________ was the __________________ of _____________ What did Epicurus believe? that the _______________ to be happy was to seek out _______________________ What does the word epicurean mean today? the love of physical _____________________ such as good _______________ or comfortable _____________________________ What did pleasure mean to Epicurus? spending _________________ with _____________________ and learning not to ___________________ about ______________________ How did Epicureans avoid worrying? by staying out of ___________________________ and public __________________________ 10. Who developed Stoicism? a Phoenician named ___________________ Why did Zeno teach at a building known as the “painted porch” near the city market in Athens? because he could not afford to rent a ___________________ ________________ Where does “Stoicism” come from? __________________, the Greek word for “____________________” 11. For Stoics, where does happiness come from? from following ______________________, not _________________, and doing your __________________ What does stoic used to describe today? someone who is not affected by ______________ or _______________ What did Stoics believe people had a duty to serve? their _________________ Did Epicureans believe that? ________ Greek Science and Math – Hellenistic scientists made major discoveries in math and astronomy. 12. Scientists, especially ________________________________ and _________________________ made major contributions during the __________________________ Era. 13. What do astronomers study? _________________, ______________________, and other heavenly ______________ What did Aristarchus claim? that the ______________ was at the center of the ________________________ and that ___________________ circled the ______________ Did other astronomers accept Aristarchus’s ideas? __________ What did they think was the center of the universe? the ___________________ 14. Who was in charge of the library at Alexandria? an astronomer, _______________________________ What did he conclude? that the ______________________ was round What did he use his knowledge of geometry and astronomy to measure? the Earth’s ______________________, the ____________________________ around the ___________________ 15. Describe how Eratosthenes calculated the curve of the Earth’s surface: _____________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________________ 16. Using his measurements, what was Eratosthenes’s estimated distance around the Earth? _________________ miles How close was his estimate from the actual measurement? ___________ miles What else did he measure? the distance to the ____________ and to the ___________________ 17. Who was the most famous Greek mathematician? _____________________ What does his book, Elements, describe? ___________________ ____________________________ What is plane geometry? _______________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ 18. Who was the most famous scientist of the Hellenistic Era? __________________________ of ___________________ What did he work on? ___________________ ________________________ What is solid geometry? _______________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ He also figured the value of _________ What is this number used to measure? the area of _________________ How is pi usually represented? ____________ 19. Archimedes was also an ________________________ What weapon did Archimedes invent that drove the Romans back from Syracuse when they attacked? __________________________ What are catapults? ___________________________________________________________________________ How long did it take the Romans to capture Syracuse? __________ years Who was killed in the massacre? _____________________________________ Identify Theocritus Aristarchus Eratosthenes Euclid Archimedes