2 - Cloudfront.net
advertisement

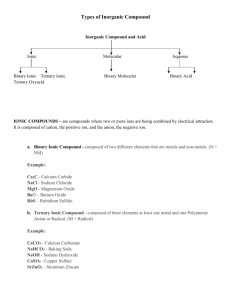
Chemistry: Unit 4 Inorganic Nomenclature Mr. Gower/Blake/Heaton Fig. 2.11 H+ Be2+ I. Background: A. Periodic Table group or _______ 1. Column: _______ family (Similar properties) 2. Row: _______. period Metals Left of staircase (Majority of the elements). 3. _______: Non-metals right of staircase. 4. ___________: Exception: _____(non-metal) H 5. ____________: touching the staircase. Metalloids Exception: ___ Al (metal). Transition Metals Lanthanides Actinides Noble Gases Period Halogens Group Alkali Metals Alkaline Earth Metals H O F Br I N Cl B. Ions (Charged atoms) 1. ________: Cations positively charged (lost e-). 2. ________: negatively charged(gained e-). Anions C. Trends in the periodic table 1. Using the planetary model – (simplified model of 2. Energy levels can contain a maximum of: 2 1st energy level: ____ 8 2nd energy level: ____ 8 (____) 18 3rd energy level: ____ 3. _________ Electrons are the keys to chemical bonds. atom) Ex. Column 1 (____________) Alkali Metals Column 18 (___________) Noble gases H (___ 1 e-) He (___ 2 e-) Li (___e 3 -) Ne (___e 10 -) Na (___e 11 -) Ar (___e 18 -) 1 e- in outer shell Similarities: (________________) ______________ Full outer shell e- to achieve a full outer shell 3. Atoms can gain or lose ___ (more stable). easiest (least energy) i.e. 4. Atoms will do what is _______ gain 2 than to ____ Oxygen has 6 valence e-: easier to _____ lose 6. Group # of valence e- Gain or lose e- Charge x x Lose 1 Lose 2 +1 +2 13 x Lose 3 +3 14 x Lose or gain 4 +/- 4 15 x Gain 3 16 x Gain 2 17 x Gain 1 18 x 1 2 Nonmetals only (above staircase) -3 -2 -1 0 III. Helpful Hints to Memorize Oxyanions See Page 5 A. In learning the formulas and charges of common oxyanions, start with the –ate form. From it follows that: hypo______ite = 2 less oxygens _______ite = 1 less oxygen _______ate per______ate = 1 more oxygen **ALL forms have the SAME charge!** A Guide to Determine Whether the –ate Formula is –XO3 or –XO4: 1 2 13 14 15 16 18 17 1 2 B 3 4 5 6 Transition Metals C N Si P S Cl As Se Br I A Guide to Determine What the Charge of the Oxy-Anion is: 1 2 13 14 15 16 18 17 1 2 3 4 5 6 Transition Metals -3 -2 -1 B C N -4 -3 -2 -1 Si P S Cl -3 -2 -1 As Se Br -1 I B. Examples: BO33Borate = ________ CO32Carbonate = ________ NO3Nitrate = ________ ClO3Chlorate = ________ NO2Nitrite = ________ ClO4Perchlorate = ________ C. “_____” Thio- = Sulfur replacing an oxygen. SO42S2O32Ex. Sulfate = ________ Thiosulfate = ________ OCNSCNEx. Cyanate = ________ Thiocyanate= ________ See Page 2 II. Binary Ionic Compounds A. Background info Non-metal ( _______ 1. Metal / ___________ Metal is always written first). 2. One element ________ ________. loses e- and the other gains e3. ___________ Transfer of e4. Charged ions attract one another (opposites attract). neutral 5. The compound is _________ B. Ex. Sodium & chlorine Na Cl Na+ NaCl (1 Na to every Cl) Cl Ex. Calcium & bromine Br CaBr2 (2 Br for every 1 Calcium) (Metal 1st) Ca2+ Br Ca Ex. (Metal 1st) Br Lithium & oxygen Li2O (2 Li for every 1 Oxygen) Li (Metal 1st) O Li+ O2 Li Ex. Aluminum & sulfur Al S 3+ 2 Al S S Al S Al2S3 (2 Al for every 3 S) C. Shortcut to determining formula (Criss-Cross method): 1. ________ Number from charge becomes the subscript. 2. All ionic compounds are _________ neutral (no + or -). 3. Subscripts are written in ________ lowest possible ratio. 4. The number “1” is never written (It is implied). 5. Examples Ex. Al3+ O2Ex. Li+ O2Al2O3 Li2O (Lithium oxide) Ex. (Aluminum oxide) Ca2+ O2Ca2O2 (Calcium oxide) Ex. CaO Mg2+ N3Mg3N2 (Magnesium nitride) D. 1. 2. 3. Nomenclature of binary ionic compounds (bi = 2). _____ is named first (name of atom). Metal ____________ is named second, ending changed to ____. Non-metal -ide If the metal (cation) can have multiple charges, the charge is written as a roman numeral (IUPAC). (Fe, Cu, Co, Hg, Mn, Sn, Pb) 4. Formula to name: a. Li2O _________________ Lithium oxide b. Al2O3 _________________ Aluminum oxide c. CaO _________________ Calcium oxide d. Mg3N2 _________________ Magnesium nitride Iron (III) ___ oxide Ferric oxide e. Fe2O3 __________________ (___________________) 2(x) + 3(-2) = 0 x = +3 Tin ___ (IV) oxide Stannic oxide f. SnO2 __________________ (___________________) 1(x) + 2(-2) = 0 x = +4 Copper (I) __ chloride (___________________) g. CuCl ___________________ Cuprous chloride 1(x) + 1(-1) = 0 x = +1 ___ (III) nitride (___________________) Manganic nitride h. MnN Manganese ____________________ 1(x) + 1(-3) = 0 x = +3 5. Name to formula: 2+ – a. Beryllium fluoride Be F ____________ BeF2 ___________ b. Potassium bromide K+ Br – ____________ KBr ___________ c. Tin (II) oxide ____________ Sn2+ O2- SnO ___________ d. Cobaltic sulfide Co3+ S2____________ Co2S3 ___________ e. Strontium iodide Sr2+ I – ____________ SrI2 ___________ 6. Polyatomic Ion: A group of atoms with a _______ single charge. Ex. (1) CN- = cyanide (2) NH4+ = ammonium (3) OH- = hydroxide a. Polyatomic ions will _______ always stay together as a group. b. If there is more than one polyatomic ion, it must be placed in ____________. parentheses Examples: Ions Formula Name Fe(OH)2 Iron (II) hydroxide Ferrous hydroxide Ca2+ CN- Ca(CN)2 Calcium cyanide NH4+ O2- (NH4)2O Ammonium oxide Na+ CN- NaCN Sodium cyanide Fe2+ OH- (No Parentheses b/c only 1) Co3+ OH- Co(OH)3 Cobalt (III) hydroxide Cobaltic hydroxide IV. Ternary Compounds: (compounds containing ___ 3 or more elements). 1. Name the _______ cation 2. Find the appropriate name of the _______. anion 3. Formula to name: a. Li2SO4 _______________ Lithium sulfate (III) (_____) b. Fe(NO3)3 _________________________ Iron ___ ferric nitrate 1(x) + 3(-1) = 0 x = +3 c. CdC2O4 Cadmium oxalate __________________ (I) (_______) Copper __ cuprous arsenite d. Cu3AsO3 ___________________________ 3(x) + 1(-3) = 0 x = +1 e. Mn2SiO4 Manganese __ (II) (___________) manganous silicate ________________________________ 2(x) + 1(-4) = 0 x = +2 sulfate f. (NH4)2SO4 Ammonium __________________ 4. Name to formula: a. Potassium thiocyanate: __________ _________ K+ SCNKSCN Al3+ MnO4- _________ Al(MnO4)3 b. Aluminum permanganate: __________ +4 C H O Pb Pb(C2H3O2)4 2 3 2 ___________ c. Plumbic acetate: ____________ Co3+ C2O42- ___________ Co2(C2O4)3 d. Cobalt (III) oxalate: ____________ e. Sodium hypochlorite: __________ Na+ ClO- __________ NaClO V. Nomenclature of Hydrates A. Hydrate: Ionic compound with ______ water molecules stuck in the _______ crystal lattice. The water is included in the ______ name and formula. 1. ZnSO4 7 H20: __________________________ Zinc sulfate heptahydrate 2. CaCO3 3 H2O: __________________________ Calcium carbonate trihydrate 3. Cu2C2O4 2H2O: Copper _________________________________ (I) (cuprous) oxalate dihydrate CaCl2 5H20 4. Calcium chloride pentahydrate: _____________ Cu(C2H3O2)2 H20 5. Cupric acetate monohydrate: _______________________ VI. Binary Molecular Compounds A. Molecular (________) covalent compounds 1. Non-metal to __________. ______of staircase including non-metal Right hydrogen 2. ________ Sharing of electrons. Ex. (Both Cl need “1” electron) Cl Cl 3. Non-metals can often combine in several different ways. Ex. CO CO2 B. Nomenclature of binary molecular compounds: 1. Greek prefixes are used: mono = 1 hexa = 6 di = 2 hepta = 7 tri = 3 octa tetra = 4 nona = 9 penta = 5 = 8 deca = 10 mono is omitted for the 1st element. 2. The prefix “_______” Ex. CO = Carbon monoxide _________________ 3. For oxides the ending “______” o or a is omitted. a. N2O = ____________________ Dinitrogen monoxide b. N2O3 = Dinitrogen trioxide ____________________ c. N2O4 = Dinitrogen tetroxide ____________________ d. NO = ____________________ Nitrogen monoxide e. NO2 = Nitrogen dioxide ____________________ f. NO5 = Nitrogen pentoxide ____________________ Compound Ionic (Charges Cancel Out) Covalent (No Charges) 1. Metal / Non-metal 2. No Prefixes!!! 3. Li20 = Lithium oxide 1. Non-metal only 2. Prefixes 3. I2O4 = Diiodine tetroxide Metal Non-metal Ex. 1. P2O5 _______________________ Diphosphorus pentoxide 2. NCl4 _____________________ Nitrogen tetrachloride VI. Nomenclature (Acids) hydrogen as the positive A. Acids: Compounds that contain __________ ion (H+). H20 (water) & ______ H2O2 (hydrogen peroxide). B. Exceptions: _____ C. Binary Acids: Acids that ___ do ____ not contain oxygen. hydro 1. Use prefix “______” anion 2. Add stem or full name of ______. 3. Add suffix “___”. ic 4. Add the word ______. acid Ex. HBr = _________________________ Hydrobromic Acid Hydrochloric Acid HCl = _________________________ Hydrocyanic Acid HCN = ________________________ D. Ternary Acids: Contain ____ 3 or more elements, __________ including oxygen. 1. Acids formed with anions that contain ______ become -ate -ic acids. ____ HNO3 (NO3- = _______) Nitrate __________ Nitric acid acid HClO4(ClO4- = Perchlorate ___________) Perchloric _____________ H2SO4(SO42- = ________) ___________ Sulfate Sulfuric acid H3PO4(PO43- = ___________) _______________ Phosphate Phosphoric acid 2. Acids formed with anions that contain ____ -ite become ______ -ous acids. HNO2 (NO2- = ________) ____________ Nitrite Nitrous acid Chlorite Chlorous acid HClO2 (ClO2- =_________) _____________ H2SO3 (SO32- =________) ______________ Sulfite Sulfurous acid 3. Name to formula: H+ OCN- (Cyanate) ________ HOCN a. cyanic acid __________________ H2Cr2O7 H+ Cr2O72- (Dichromate) _______ b. dichromic acid ______________________ HClO H+ ClO- (Hypochlorite) _______ c. hypochlorous acid _____________________ H2S H+ S2- (Sulfide) ______ d. hydrosulfuric acid _______________ Compounds Ionic Covalent • Non-metal / Non-metal (Metal / Non-metal) Binary • Uses prefixes, -ide Ternary • 2 elements • 3 or more elements • -ide • Anion is named • Roman numeral • Roman numerals (if needed) (if needed) • ie. Calcium chloride Acids • ie. Calcium carbonate CaCl2 CaCO3 Hydrates • w/ H2O • Uses prefixes • ie. Calcium choride/ Calcium carbonate trihydrate • 3H2O CaCO3 • 3H2O CaCl2 • I2O7 Diiodine heptoxide Starts w/ H+ Binary Ternary • No oxygen • Hydro__ic acid • ie, Hydrochloric acid HCl w/ oxygen • -ate—ic • -ite---ous acid acid • H2CO3 • H2SO3 Carbonic Sulfurous acid acid Carboxylic acids are organic acids characterized by the presence of a carboxyl group, which has the formula -C(=O)OH, usually written -COOH or -CO2H. Carboxylic acids are weak acids that form ions in solution: RCOOH H RCOO COOH carboxyl group Ethanoic acid HC2H3O2 - acetate ion: ethanoate ion 2 C 2H 3O CH 3COO Oxalate ion: COOH carboxyl group HOOC COOH C 2O 2 4 Phthalic acid (IUPAC systematic name : benzene-1,2-dicarboxylic acid) is an aromatic dicarboxylic acid, with formula C6H4(COOH)2. - - C HC HC C C H C C CH Phthalate ion C8H 4O 2 4 Inorganic Nomenclature: Binary Ionic Compounds (p.1) 1. Calcium hydroxide chloride 2. AlCl3 3. Iron (II) / Ferrous iodide 4. Hg2Cl2 5. Sodium hydride 6. MgCl2 7. Zinc bromide 8. MnCl2 9. Ammonium chloride 10. PbS 11. Potassium cyanide 12. MgO 13. Lead (II) / Plumbous 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. Fe(OH)3 Silver oxide HgO Ammonium iodide CuCl Cesium nitride CuS Silver cyanide CdS Zinc sulfide LiBr Inorganic Nomenclature: Ternary Ionic Compounds (p. 2) 1. Sr3(PO3)2 2. Ammonium chromate 3. Co(ClO)2 4. Mercury (II) / Mercuric iodite 5. Ca3(BO3)2 6. Iron (III) / Ferric sulfite 7. Al2(C8H4O4)3 8. Strontium nitrite 9. Cu(C2H3O2)2 10. Beryllium arsenite 11. NaOCN 12. RbIO 13. Mn2(HPO4)3 14. Tin (IV) / Stannic perchlorate 15. Pb(C2O4)2 16. KMnO4 17. (NH4)2Cr2O7 18. Zinc bicarbonate 19. Magnesium thiocyanate 20. Cesium thiosulfate Inorganic Nomenclature: Hydrates (p. 3) 1. CaCl2 · 5H2O 2. Ba(NO3)2 · 3H2O 3. Al2(SO4)3 · 9H2O 4. Zinc sulfate heptahydrate 5. Iron (II) / Ferrous borate tetrahydrate 6. Copper (I) / Cuprous oxalate dihydrate 7. Li2S · H2O 8. Sodium chromate trihydrate 9. Cu(ClO2)2 · 6H2O 10. Barium iodate dihydrate 11. CaBr2 · 10H2O 12. Iron (III) / Ferric thiosulfate pentahydrate 13. Fe(C2H3O2)2 · 7H2O 14. Strontium nitrite tetrahydrate 15. Sn(SO3)2 · 2H2O 16. Potassium thiocyanate octahydrate Inorganic Nomenclature: Binary Covalent Compounds (p. 4) 1. Carbon monoxide 15. dinitrogen tetroxide 2. PBr3 16. PF5 3. Carbon tetrachloride 17. Sulfur dioxide 4. Nitrogen trichloride 18. Dinitrogen trioxide 5. SeO2 19. Hexaboron monosilicide 6. Diphosphorus trioxide 20. Xenon hexafluoride 7. SO3 21. Sulfur dichloride 8. Diphosphorus pentoxide 22. SeF6 9. Carbon dioxide 23. Chlorine dioxide 10. Phosphorus pentaiodide 24. Dinitrogen tetroxide 11. SeO3 25. CS2 12. Sulfur hexafluoride 26. Dichlorine monoxide 13. Dichlorine heptoxide 27. Dihydrogen pentasulfide 14. ClF3 28. CF4 Inorganic Nomenclature: Binary Compounds (p. 5) 1. Diiodine pentoxide 17. XeF4 2. SF6 18. Cl2O7 3. HgBr2 19. CuF2 4. Iron (III) / Ferric chloride 20. Tin (II) / Stannous chloride 5. CoF3 21. CO 6. SO2 22. Ammonium cyanide 7. Boron trifluoride 23. Mn2O3 8. Al(CN)3 24. Strontium cyanide 9. Cadmium sulfide 25. P2O3 10. N2O4 26. Ag3N 11. Cobalt (III) / Cobaltic chloride 27. PbCl4 12. Copper (I) / Cuprous bromide 28. Dihydrogen monoxide 13. Zinc hydroxide 29. Ba(OH)2 14. NH4Cl 30. NO 15. PbS 16. SnF2 Inorganic Nomenclature: Acids (p. 6) 1. Hydrobromic acid 2. Hypochlorous acid 3. Permanganic acid 4. HIO 5. Hydrobromic acid 6. Phosphoric acid 7. Bromic acid 8. Hypobromous acid 9. Nitric acid 10. Perchloric acid 11. Phosphorous acid 12. Iodic acid 13. Chromic acid 14. Arsenic acid 15. Carbonic acid 16. Acetic acid 17. Hydroiodic acid 18. Nitrous acid 19. Dichromic acid 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. 27. 28. 29. 30. 31. 32. 33. 34. 35. 36. 37. 38. Periodic acid Hypobromous acid Hydrochloric acid H2CO3 H2SO3 Arsenous acid Hypoiodous acid H3PO3 HBrO4 HF Sulfuric acid cyanic acid Hydrocyanic acid H3PO4 H2C2O4 H2C8H4O4 H3BO3 Hydrocyanic acid Hydrofluoric acid Inorganic Nomenclature: Problem Set A (p. 7) Part I 1. Calcium hydroxide 18. Tin (IV) / Stannic bromide 2. Silver phosphate dihydrate 19. Tin (II) /Stannous fluoride heptahydrate 3. Silver thiocyanate 20. Lead (II) / Plumbous permanganate 4. Sodium acetate 21. Sodium silicate 5. Ammonium sulfate 22. Dinitrogen pentoxide 6. Zinc sulfide octahydrate 23. Aluminum perchlorate trihydate 7. Cadmium cyanide 24. Mercury (II) / Mercuric acetate 8. Barium iodate 25. Cesium sulfite 9. Copper (II)/Cupric sulfite dihydrate 26. Strontium iodite pentahydrate 10. Copper (I) / cuprous iodide 27. Hydrofluoric acid 11. Iron (III) / Ferric nitrate nonahydrate 28. Beryllium nitride 12. Iron (II) / Ferrous oxalate 29. Calcium bicarbonate/hydrogen carbonate 13. Mercury (I) / Mercurous chloride 30. Manganese (III)/Manganic nitrate tetrahydrate 14. Manganese (II) / Manganous 31. Phosphorus trichloride carbonate 15. Manganese (III) / Manganic hydroxide 32. Iron (III) / Ferric cyanate 16. Barium hypochlorite 33. Aluminum thiosulfate 17. Lead (II) / Plumbous sulfate 34. Hydrobromic acid Inorganic Nomenclature: Problem Set A (p. 7) Part II 35. 36. 37. 38. 39. 40. 41. 42. 43. 44. 45. 46. 47. Al(BrO3)3 · H2O (Hg2)3(PO4)2 Mn2O3 Sr(HCO3)2 · 10H2O FeI2 Fe(IO3)3 · 9H2O Mn(OH)2 Li2C8H4O4 Co2(SO4)3 · 7H2O Co(MnO4)2 CuIO4 Cl2O7 Ag2C2O4 · 2H2O 48. 49. 50. 51. 52. 53. 54. 55. 56. 57. 58. 59. 60. Cu3(BO3)2 SnS Al(C2H3O2)3 CaCrO4 NaClO2 SnCr2O7 Hg(CN)2 (NH4)2SO3 SnCl4 PbCO3 Zn3P2 Cu2SiO4 · 3H2O HNO2 Inorganic Nomenclature: Problem Set B (p. 8) Part I 61. 62. 63. 64. 65. 66. 67. 68. 69. 70. 71. 72. 73. 74. Silver phosphate Cobalt (III)/Cobaltic chloride Beryllium nitrite dihydrate Iron (III) / Ferric permanganate 75. 76. 77. 78. Calcium hydride Dinitrogen pentoxide Iron (III) / Ferric sulfide Magnesium oxalate heptahydrate Ammonium nitrite 79. Nitric acid Aluminum sulfide 80. Rubidium silicate Zinc periodate 81. Sulfur hexafluoride Lead (II) / Plumbous borate 82. Calcium phosphide Sulfurous acid 83. Manganese (IV) oxide Carbonic acid 84. Copper (II) cupric acetate Diiodine heptoxide 85. Mercury (II)/Mercuric bromide dihydrate Barium silicide 86. Barium chromate Potassium bicarbonate/hydrogen carbonate Barium hypobromite pentahydrate 87. Cadmium thiocyanate 88. Calcium monohydrogen phosphate tetrahydrate Inorganic Nomenclature: Problem Set B (p. 8) Part II 89. K2C2O4 · 8H2O 90. CuCl2 · 2H2O 91. Mn2(Cr2O7)3 92. MgHPO4 93. Hg2SO4 · H2O 94. N2I3 95. ClO5 96. AlF3 · 2H2O 97. LiBr 98. H2SO4 99. CaClO3 · H2O 100. Zn(IO)2 101. HI 102. CdO2 103. AgIO 104. SrSO3 · 10H2O 105. 106. 107. 108. 109. 110. 111. 113. 114. 115. 116. 117. 118. 119. 120. Fe(BrO3)3 Pb(ClO4)4 Mn2O3 BF3 Sr2SiO4 H3PO4 HOCN 112. K2O Al2S3 H2CrO4 Be(OH)2 H2C2O4 (NH4)2CrO4 HBrO4 Sn(BrO2)4 LiCl Inorganic Nomenclature: Sample Test #1 (p. 9) Part I 1. 2. 3. 4. Aluminum bromide Hypochlorous acid Phosphorus pentachloride Manganese (II) / Manganous sulfate monohydrate 5. Ammonium iodite 6. Lithium silicate 7. Hydrogen peroxide 8. Sulfur hexafluoride 9. Copper (I) / Cuprous oxalate nonahydrate 10. Boric acid 11. Sodium carbonate trihydrate 12. Silver sulfide 13. Iron (III) / Ferric hydroxide Inorganic Nomenclature: Sample Test #1 (p. 9) Part I 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. dichlorine heptoxide Strontium cyanide hexahydrate Phosphorous acid Mercury (II) / Mercuric oxide Cadmium bromate Rubidium phosphate Zinc phthalate Acetic acid Tin (IV) / Stannic oxide Thiocyanic acid Potassium acetate Cobalt (III) / Cobaltic arsenite Inorganic Nomenclature: Sample Test #1 (p. 10) Part II 26. 27. 28. 29. 30. 31. 32. 33. 34. 35. 36. 37. 38. SnCl2 · 8 H2O AlBO3 Cd2SiO4 N2O5 H2C2O4 (NH4)3PO3 NaH2PO4 HOCN KIO4 Fe(BrO)3 2H2O HF I 2 H9 Hg2(NO2)2 39. 40. 41. 42. 43. 44. 45. 46. 47. 48. 49. 50. Ag3N 3H2O Rb2SO4 H2Cr2O7 PbO2 Zn(MnO4)2 CsOH AlH3 Mn(SCN)3 BeC8H4O4 4H2O Al(IO3)3 HBrO4 Ba(HCO3)2 Inorganic Nomenclature: Sample Test #2 1. Be(CN)2 2. Li3BO3 H2O 3. HSCN 4. H2O 5. ZnC2O4 6. Fe3(PO3)2 7. CaF2 7H2O 8. Al(MnO4)3• 8H2O 9. I7O9 10. HIO 11. Sn(HCO3)2 12. (NH4)2SO3 13. AlN Inorganic Nomenclature: Sample Test #2 (p. 11) Part II 14. HOCN 15. Hg2(ClO3)2 16. BaS2O3 17. SrH2 18. Mn4(SiO4)3 19. HC2H3O2 20. Ca2C 21. CBr4 22. Pb3P4 3H2O 23. CsOH 24. Rb2C8H4O4 25. N2O5 Inorganic Nomenclature: Sample Test #2 (p. 12) Part I 26. 27. 28. 29. 30. 31. 32. 33. 34. 35. 36. 37. 38. Perbromic acid Sodium nitrate tetrahydrate Copper (I) / Cuprous monohydrogen phosphate Mercury (II) / Mercuric silicate Hydrogen peroxide Potassium arsenate nonahydrate Sulfurous acid Tin (IV) / Stannic oxide Silver hydride Sulfur trioxide Lead (IV) / Plumbic phthalate hexahydrate Permanganic acid Cobalt (II) / Cobaltous acetate Inorganic Nomenclature: Sample Test #2 (p. 12) Part II 39. 40. 41. 42. 43. 44. 45. 46. 47. 48. 49. Hydrocyanic acid Dicarbon hexahydride Magnesium oxalate pentahydrate Chlorous acid Rubidium hydroxide Calcium cyanate Cadmium hypobromite Copper (II) / Cupric dichromate Manganese (II) / Manganous sulfide Phosphoric acid Iron (II) / Ferrous hydrogen carbonate / bicarbonate 50. Ammonium arsenite Inorganic Nomenclature: Sample Test #3 1. Fe(SCN)3 · 2H2O 2. LiOH 3. (NH4)2C8H4O4 4. HgC2O4 5. HBrO4 6. Be2C 7. H3AsO4 8. N4O10 9. Na2HPO4 · H2O 10. Hg2(NO2)2 · 8H2O 11. AlN 12. H2S 13. Cd3(PO4)2 Inorganic Nomenclature: Sample Test #3 (p. 13) Part II 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. HClO CsH Mn(HCO3)3 Pb(S2O3)2 P5O8 H3BO3 Sn2SiO4 · 7H2O CuS Ag2SO3 · 3H2O Co2(Cr2O7)3 BrCl6 Zn(CN)2 Inorganic Nomenclature: Sample Test #3 (p. 14) Part II 26. 27. 28. 29. 30. 31. 32. 33. 34. 35. 36. 37. 38. Carbonic acid Sodium thiocyanate heptahydrate Potassium iodite Hydrogen peroxide Sulfurous acid Nitrogen trioxide Manganese (III) / Manganic phosphate pentahydrate Mercury (II) / Mercuric phthalate Ammonium bromate Zinc cyanate Dicarbon hexahydride Hydrocyanic acid copper (I) / Cuprous acetate monohydrate Inorganic Nomenclature: Sample Test #3 (p. 14) Part II 39. 40. 41. 42. Silver hydroxide Potassium dihydrogen phosphate Dibromine heptoxide Iron (II) / Ferrous hydrogen carbonate / bicarbonate 43. Lead (IV) / Plumbic oxide tetrahydrate 44. Phosphorous acid 45. Lithium silicide 46. Manganese (II) Manganous hydride 47. Beryllium monohydrogen phosphate decahydrate 48. Cobalt (III) / Cobaltic arsenate hexahydrate 49. Calcium nitrate 50. Permanganic acid Inorganic Nomenclature: Sample Test #4 Part I 1. Magnesium nitride monohydrate 2. Aluminum nitrate 3. Iron (II) / Ferrous cyanide 4. Mercury (II) / Mercuric silicate 5. Sulfuric acid 6. Ammonium hydroxide 7. Zinc oxalate heptahydrate 8. Potassium permanganate 9. Rubidium cyanate 10. Tin (IV) / Stannic oxide 11. Chlorine tetroxide 12. Lead (II) / Plumbous periodate 13. Silver bicarbonate / hydrogen carbonate trihydrate 14. Cobalt (II) / Cobaltous nitrite 15. Cadmium thiosulfate 16. Hypoiodous acid 17. Lithium dihydrogen phosphate tetrahydrate 18. Calcium acetate 19. Triiodine octoxide 20. Xenon hexafluoride 21. Manganese (III) / Manganic arsenite decahydrate 22. Strontium dichromate 23. Phosphorous acid 24. Cesium borate pentahydrate 25. Manganous / Manganese (II) oxide Inorganic Nomenclature: Sample Test #4 Part I 26. 27. 28. 29. 30. 31. 32. 33. 34. 35. 36. 37. 38. Ca(SCN)2 HIO2 Cd(C2H3O2)2 Al2(Cr2O7)3 Fe4(SiO4)3 Co(CN)2 · H2O ZnF2 · 3 H2O HC2H3O2 Cl2H4 CsClO · 9H2O NH4Cl I3O8 Ba(BrO4)2 39. 40. 41. 42. 43. 44. 45. 46. 47. 48. 49. 50. Hg2F2 HCN Ca2C Ag2C8H4O4 H 2O Pb(NO2)4 Sn(CrO4)2 HF SrS2O3 · 2 H2O HBrO3 Be(SCN)2 Cu(OH)2 Ion Quiz 1 Write the formulas: 1. peroxide 2. bicarbonate 3. dihydrogen phosphate 4. dichromate 5. carbonate 6. phosphate 7. hydroxide 8. arsenate 9. acetate 10. phosphite O22HCO3H2PO4Cr2O72CO32PO43OH AsO43C2H3O2PO33- Ion Quiz 2 1. Cr2O722. OCN3. S2O324. H2PO45. SiO446. Perbromate 7. Hypoiodite 8. Hydroxide 9. Acetate 10. Phthalate 11. Borate Dichromate Cyanate Thiosulfate Dihydrogen phosphate Silicate BrO4IOOHC2H3O2C8H4O42BO33- Ion Quiz 3 1. bicarbonate 2. mercury I & mercury II 3. arsenite 4. phosphate 5. chromate 6. carbide 7. ClO38. NO39. H10. F- HCO3Hg22+ & Hg2+ AsO33PO43CrO42C4chlorate nitrate hydride fluoride Ion Quiz 4 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. Perchlorate Iodite Cyanate Acetate Arsenate PO33S2O32HNO3HPO42- ClO4IO2OCNC2H3O2AsO43Phosphite Thiosulfate Hydride Nitrate Monohydrogen phosphate Ion Quiz 5 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. NO3– C8H4O42– H2PO4– CO32– OCN– Permanganate Acetate Thiocyanate Borate Sulfite Nitrate Phthalate Dihydrogen phosphate Carbonate Cyanate MnO4– C2H3O2– SCN– BO33– SO32– Ion Quiz 6 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. Hydride HC2O42Oxalate CNCyanide SCNThiocyanate Arsenite AsO33O22peroxide Dihydrogen phosphate H2PO4Bicarbonate / Hydrogen carbonate HCO3sulfite SO32BrO- hypobromite Ion Quiz 7 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. Iodate Hydroxide Bicarbonate Oxalate Acetate PO43S2O32Hg22+ NO3H2PO4- lO3OHHCO3C2O42C2H3O2Phosphate Thiosulfate Mercury (I) Nitrate Dihydrogen phosphate Ion Quiz 8 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. Silicate Perbromate Thiocyanate Sulfate Permanganate PO33C8H4O42AsO43NO3Cr2O72- SiO44BrO4SCNSO42MnO4Phosphite Phthalate Arsenate Nitrate Dichromate Ion Quiz (M3) 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. Chromate Chlorate Cyanate Sulfite Dihydrogen phosphate AsO33C8H4O42BO33MnO4HPO42- CrO42ClO3OCNSO32H2PO4Arsenite Phthalate Borate Permanganate Monohydrogen Phosphate Ion Quiz (M4) 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. Oxalate Bromate Cyanide Iodite Hydroxide SO32C2H3O2PO43IO4HCO3- C2O42BrO3CNIO2OHSulfite Acetate Phosphate Periodate Hydrogen carbonate / Bicarbonate Ion Quiz (M5) Write the formulas: 1. peroxide 2. bicarbonate 3. dihydrogen phosphate 4. dichromate 5. carbonate 6. phosphate 7. hydroxide 8. arsenate 9. acetate 10. phosphite O22HCO3H2PO4Cr2O72CO32PO43OH AsO43C2H3O2PO33- EOCP 2.88 Mg2+ HCO3- Sr2+ Cl- Mg(HCO3)2 Strontium chloride Fe(NO2)3 Mn2+ ClO3- Sn4+ Br- Mn(ClO3)2 Tin (IV) (Stannic) bromide Co3(PO4)2 Hg2I2 Cu+ CO32- Li+ N3- Iron (III) (Ferric) nitrite Cobalt (II)(Cobaltous) phosphate Mercury (I)(Mercurous) iodide Copper (I)(Cuprous) carbonate Li3N Al2S3 Aluminum sulfide Name That Ion! H2PO4- Dihydrogen phosphate BO33SCNClO4- Borate Thiocyanate Perchlorate IO2- Iodite CrO4PO43- Chromate Phosphate NO2- Nitrite Name That Ion! BrO3- Bromate C 2H 3O 2OCNMnO4- Acetate Cyanate Permanganate C2O4-2 Oxalate Cr2O72ClO3- Dichromate Chlorate NO3- Nitrate Name That Ion! O22- Peroxide S2O32CO32C8H4O42- Thiosulfate Carbonate Phthalate SiO44- Silicate SO32lO4- Sulfite Periodate AsO33- Arsenite Name That Ion! OH- Hydroxide PO32CO32BrO- Phosphite Carbonate Hypobromite HPO42- SO42ClO- Monohydrogen phosphate Sulfate Hypochlorite AsO43- Arsenate Name That Ion! IO- Hypoiodite BrO4CNBrO2- Perbromate Cyanide Bromite HCO3- IO3ClO2- Hydrogen carbonate / bicarbonate Iodate Chlorite NO3- Nitrate Bingo Game 1 Borate Permanganate Peroxide Silicate Hydroxide Dihydrogen phosphate Thiosulfate Arsenate Phthalate Hydrogen carbonate / bicarbonate Iodate Chlorite Carbonate Oxalate Arsenite Nitrate Bingo Game 1 Cyanide Monohydrogen phosphate Cyanate Dichromate Acetate Bromate Thiocyanate Perchlorate Bromite Iodite Sulfite Periodate Chromate Phosphate Chlorate Nitrite Bingo Game 1 Phosphite Hypochlorite Perbromate Sulfate Hypobromite Hypoiodite Bingo Game 1 Borate Permanganate Peroxide Silicate Hydroxide Dihydrogen phosphate Thiosulfate Arsenate Phthalate Hydrogen carbonate / bicarbonate Iodate Chlorite Carbonate Oxalate Arsenite Nitrate Bingo Game 1 Cyanide Monohydrogen phosphate Cyanate Dichromate Acetate Bromate Thiocyanate Perchlorate Bromite Iodite Sulfite Periodate Chromate Phosphate Chlorate Nitrite Bingo Game 1 Phosphite Hypochlorite Perbromate Sulfate Hypobromite Hypoiodite Bingo Game Hypochlorite Dihydrogen phosphate Arsenate Oxalate Iodate Bingo Game Cyanide Monohydrogen phosphate Acetate Iodite Periodate Chlorate Phosphate Bingo Game 2 Phosphite Permanganate Perbromate Hypoiodite Bromate Thiosulfate Perchlorate Borate Peroxide Silicate Hydroxide Phthalate Hydrogen carbonate / bicarbonate Chromate Dichromate Nitrate Bingo Game 2 Hypobromite Cyanate Thiocyanate Bromite Carbonate Sulfite Arsenite Chlorite Nitrite Ion Quiz 1 Write the formulas: 1. peroxide 2. bicarbonate 3. dihydrogen phosphate 4. dichromate 5. carbonate 6. phosphate 7. hydroxide 8. arsenate 9. acetate 10. phosphite Ion Quiz 2 1. Cr2O722. OCN3. S2O324. H2PO45. SiO446. Perbromate 7. Hypoiodite 8. Hydroxide 9. Acetate 10. Phthalate 11. Borate Ion Quiz 3 1. bicarbonate 2. mercury I & mercury II 3. arsenite 4. phosphate 5. chromate 6. carbide 7. ClO38. NO39. H10. F-