Anatomy 2_3b Brain & Cranial Nerves
advertisement

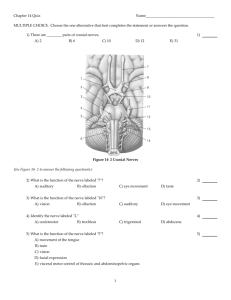
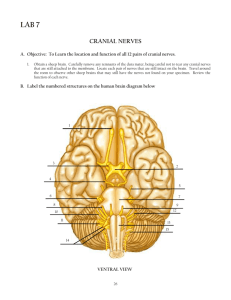
Brain & Cranial Nerves Dr. Michael P. Gillespie Major Parts of the Brain Brain stem – continuous with the spinal cord. Medulla oblongata. Pons. Midbrain. Cerebellum – posterior to the brain stem. Major Parts of the Brain Diencephalon – superior to the brain stem. Thalamus. Hypothalamus. Cerebrum – supported on the diencephalon and brain stem. Largest part of the brain. Brain Blood Supply Arteries Internal carotid arteries Vertebral arteries Veins Internal jugular veins Brain Blood Flow The brain consumes about 20% of the oxygen and glucose used at rest. A brief slowing of blood flow may cause unconsciousness. Brain Blood Flow An interruption of blood flow for 1 to 2 minutes impairs neural function. Total deprivation of oxygen for 4 minutes causes permanent injury. If the blood entering the brain has a low level of glucose, mental confusion, dizziness, convulsions, and loss of consciousness may occur. Blood Brain Barrier The blood-brain barrier (BBB) protects the brain from harmful substances and pathogens. It prevents the passage of many substances from the blood to the brain tissue. Tight junctions seal together endothelial cells of brain capillaries. Astrocytes selectively allow some substances through and not others. Breaching the BBB The BBB prevents the passage of harmful substances into the brain, but it also prevents the passage of useful drugs. Drugs are injected in a concentrated sugar solution to facilitate passage. The high osmotic pressure causes cells lining the barrier to shrink and makes the membrane “leaky”. Protective Coverings Cranial Meninges. Dura mater. Arachnoid mater. Pia mater. Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF) Clear colorless liquid. Protects the brain and spinal cord from chemical and physical injuries. Carries oxygen, glucose, and other needed chemicals from the blood to the neurons and neuroglia. Circulates in the subarachnoid space (between the arachnoid mater and pia mater). Protective Coverings Extensions of the dura mater separate the parts of the brain. Falx cerebri – separates the two hemispheres of the cerebrum. Falx cerebelli – separates the two hemispheres of the cerebellum. Tentorium cerebelli – separates the cerebrum from the cerebellum. Formation of CSF in the Ventricles CSF is formed in the ventricles. Formed by ependymal cells that cover the choroid plexuses of the ventricles. Formation of CSF in the Ventricles There are 4 ventricles. Functions of CSF. Mechanical protection. Shock absorption. Buoys the brain. Chemical protection – optimal chemical environment. Circulation – medium of exchange for wastes and nutrients. Hydrocephalus Abnormalities of the brain can interfere with drainage of CSF from the ventricles and subarachnoid space. CSF pressure increases causing hydrocephalus. In infants this causes the fontanels to budge. Hydrocephalus Tumors, inflammation, developmental malformations can all cause hydrocephalus. Pressure buildup can damage the delicate nervous tissue. A surgeon can implant a drain line called a shunt to divert CSF. In adults, hydrocephalus may occur after head injury, meningitis, or subarachnoid hemorrhage. Brain Stem Between the brain and spinal cord. 3 regions. Medulla oblongata. Pons. Midbrain. Medulla Oblongata A continuation of the spinal cord. Sensory (ascending) tracts and motor (descending) tracts travel through the white matter of the medulla. Many nerves decussate (cross over) in the medulla. Medulla Oblongata Cardiovascular center regulates the heartbeat and the diameter of the blood vessels. Medulla Oblongata The medullary rhythmicity area adjusts the rhythm of the breathing and controls reflexes for vomiting, coughing, and sneezing. Medulla Oblongata The nuclei for the following cranial nerves reside in the medulla: VIII (vestibulocochlear). IX (glossopharyngeal). X (vagus). XI (accessory). XII (hypoglossal). Pons Pneumotaxic area and apneustic area regulate breathing. Nuclei for cranial nerves V (trigeminal), VI (abducens), VII (facial), and VIII (vestibulocochlear). Midbrain The midbrain or mesencephalon contains the superior colliculi (visual actvities) and inferior colliculi (auditory pathways). The midbrain contains the substantia nigra which release dopamine to help control subconscious muscle activities. Loss of these neurons results in Parkinson disease. Cranial nerves III (oculomotor) and IV (trochlear) originate here. Cerebellum The second largest part of the brain. A main function of the cerebellum is to evaluate how well movements are being carried out and correct for discrepancies. This helps to “smooth out” movements. Diencephelon Epithalamus. Contains the pineal gland which secretes melatonin. Thalamus. Relays sensory information to the cortex. Provides crude perception of touch, pressure, pain, and temperature. Diencephelon Subthalamus. Controls body movements. Hypothalamus. Controls and integrates activities of the ANS. Regulates emotional and behavioral patterns. Regulates cicadian rhythms. Regulates eating and drinking behavior. Produces hormones oxytocin and ADH. Cerebrum Sensory areas interpret sensory impulses. Motor areas control muscular movement. Association areas function in emotional and intellectual processes. Basal areas regulate gross muscle movements and regulate muscle tone. Limbic system functions in survival behaviors. Brain Injuries Concussion – an abrupt, temporary loss of consciousness following a blow to the head. Most common brain injury. Signs – headache, drowsiness, lack of concentration, confusion, amnesia. Brain Injuries Contusion – bruising of the brain due to trauma and includes leakage of blood. Signs - immediate loss of consciousness, transient cessation of respiration, decreased blood pressure. Brain Injuries Laceration – tear of the brain usually from a skull fracture or gunshot wound. Rupture of large blood vessels. Consequences – cerebral hematoma (localized pool of blood, usually clotted), edema, and increased intracranial pressure. Cerebral Cortex Areas and Functions Sensory areas – receive and interpret sensory information. Cerebral Cortex Areas and Functions Motor areas – initiate movements. Association areas – deal with integrative functions: Memory. Emotions. Reasoning. Will. Judgement. Personality. Intelligence. Sensory Areas Primary somatosensory area – receives sensations for touch, proprioception, pain, itching, tickle, and thermal sensations. Located in the postcentral gyrus of the parietal lobes. Primary visual area. Primary auditory area. Primary gustatory area – taste. Primary olfactory area. Motor Areas Primary motor area – located in the precentral gyrus of the frontal lobe. Broca’s speech area – coordinates the contractions of speech and breathing muscles. Association Areas Somatosensory association area – integrates and interprets sensations. Visual association area – evaluates what is seen. Auditory association area – evaluates sounds. Association Areas Wernicke’s (posterior language) area – interprets the meaning of speech. Common integrative area. Premotor area – controls learned skilled movements. Frontal eye field area – controls voluntary scanning movements of the eyes. Aphasia An inability to use or comprehend words. Aphasia Damage to Broca’s area results in nonfluent aphasia. Inability to properly articulate to form words. These people know what they wish to say, but cannot speak. Aphasia Damage to the auditory association area results in fluent aphasia. Faulty understanding of spoken words. Word deafness – inability to understand spoken words. Word blindness – inability to understand written words. Cranial Nerve I - Olfactory Type: sensory. Function: smell. Anosmia – loss of sense of smell. Cranial Nerve II – Optic Nerve Type: sensory. Function: vision. Anopia – blindness in one or both eyes. Cranial Nerve III - Oculomotor Type: mixed (mainly motor). Function: movement of the upper eyelid and eyeball. Accomodation of the lens for nearn vision and constriction of the pupil. Strabismus – deviation of the eye in which both eyes don’t focus on the same object. Ptosis – drooping of the upper eyelid. Diploia – double vision. Cranial Nerve IV – Trochlear Nerve Type: mixed (mainly motor). Function: movement of the eyeball. Diplopia and strabismus occur with trochlear nerve damage. Cranial Nerve V – Trigeminal Nerve Type: mixed. Function: conveys impulses for touch, pain, temperature and proprioception. Chewing. Trigeminal neuralgia (tic douloureux) – pain to branches of the trigeminal nerve. Dentists apply anesthetic to branches of this nerve. Cranial Nerve VI - Abducens Type: mixed (mainly motor). Function: movement of the eyeball. With damage to this nerve the eye cannot move laterally beyond the midpoint and usually points medially. Cranial Nerve VII – Facial Nerve Type: mixed. Function: Propriception and taste. Facial expression. Secretion of saliva and tears. Injury produces bell’s palsy (paralysis of facial muscles). Cranial Nerve VIII – Vestibulocochlear Nerve Type: mixed (mainly sensory). Function: conveys impulses for equilibrium and hearing. Injury can cause vertigo, ataxia (muscular incoordination), nystagmus (rapid movement of the eyeball), and tinnitus. Cranial Nerve IX – Glossopharyngeal Nerve Type: mixed. Function: taste and somatic sensations from the posterior 1/3 of the tongue. Elevates the pharynx during swallowing and speech. Stimulates the secretion of saliva. Injury causes decreased salivary secretion, loss of taste, and difficulty swallowing. Cranial Nerve X – Vagus Nerve Type: mixed. Function: taste and somatic sensations. Swallowing, coughing, and voice production. Regulates GI tract and heart rate. Injury interferes with swallowing, paralyzes vocal cords, and causes the heart rate to increase. Cranial Nerve XI – Accessory Nerve Type: mixed (mainly motor). Function: Proprioception. Swallowing, movement of head and shoulders. If the nerves are damaged the SCM and Trapezius become paralyzed. Cranial Nerve XII – Hypoglossal Nerve Type: mixed (mainly motor). Function: Proprioception. Movement of the tongue during speech and swallowing. Injury results in difficulty in chewing, speaking, and swallowing. When protruded, the tongue curls towards the affected side and atrophies on the affected side. Cranial Nerves On Old Olympus’ Towering Tops A Fin And German Viewed Some Hops. This mnemonic device helps you memorize the names of the cranial nerves. The first letter from each word corresponds to the first letter of each cranial nerve.