Lecture 3 Class Activities Membrane Transport Facilitated diffusion
advertisement
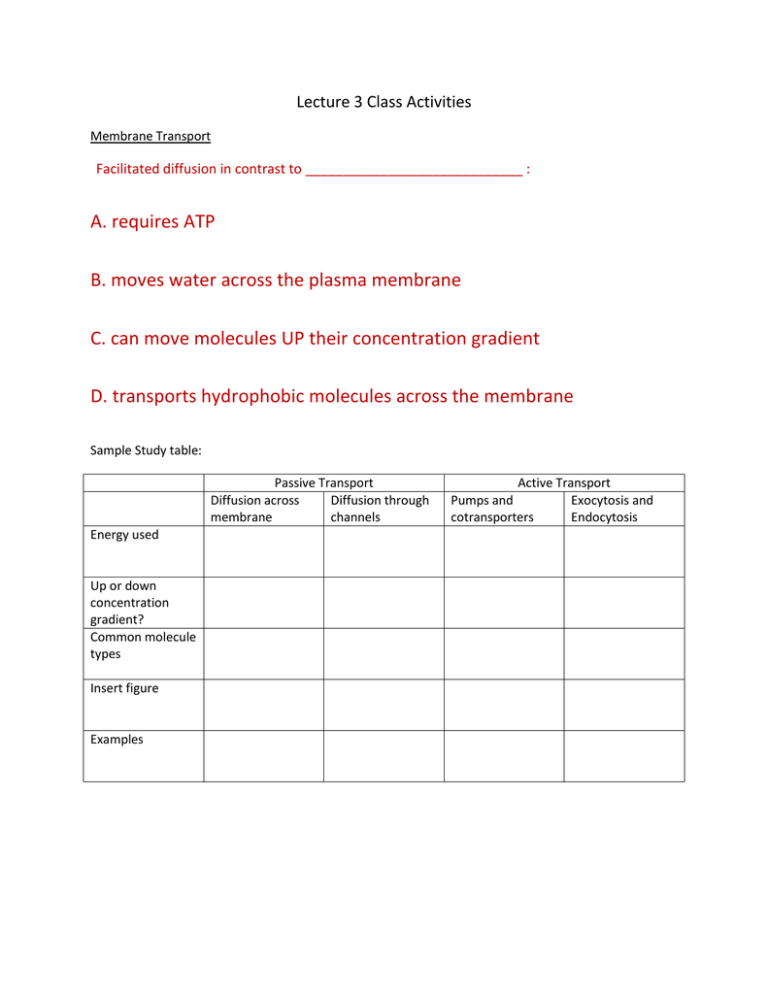
Lecture 3 Class Activities Membrane Transport Facilitated diffusion in contrast to _____________________________ : A. requires ATP B. moves water across the plasma membrane C. can move molecules UP their concentration gradient D. transports hydrophobic molecules across the membrane Sample Study table: Passive Transport Diffusion across Diffusion through membrane channels Energy used Up or down concentration gradient? Common molecule types Insert figure Examples Active Transport Pumps and Exocytosis and cotransporters Endocytosis Water diffuses through aquaporins Application: Salt and water in the gut Cells lining the gut are called enterocytes. (http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0140673668905916) The transport of molecules in the gut Solute transport causes water transport Absorption of cholesterol uses receptor-mediated endocytosis Which is the correct orientation of an endocytosed LDL receptor that is bound to its ligand (represented by the star shape) in the newly formed vesicle shown below? For Online Discussion: Glucose is transported from the gut into epithelial cells using a sodium glucose co-transporters called SGLT1. The sodium gradient used is created by a Na/K pump. A rare disorder called “glucose-galactose malabsorption” is caused by a non-functional SGLT1. This results in water accumulation in the gut and severe diarrhea in newborns because:: A. continued Na/K pumping makes the epithelial cells ______________ to the gut lumen B. high solutes in the gut makes epithelial cells ___________________ to the gut lumen C. water cannot cross a non-functional ________________________ and it remains in the gut.











