blog.Acid and Base
advertisement

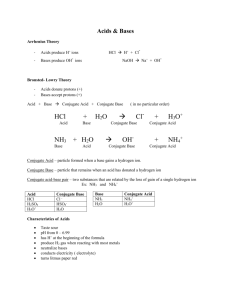
Acid and Base Ch 15 and 16 acids • 1. tastes sour. • 2. conducts an electric current. • 3. Causes certain dyes ( indicators) to change color. • 4. Liberates hydrogen when it reacts with certain metals. • 5. neutralizes basic solutions to form salts. Bases • 1. tastes bitter. • 2. conducts an electric current. • 3. causes certain dyes ( indicators) to change color. • 4. feels slippery. • 5. neutralizes acid solution to form salts. Definition of Acids and Bases • An acid is a source of hydrogen ions (H+) or hydronium ions (H3O+ ) in solution. HCl(aq) + H2O(l) (aq) H3O+ (aq) + Cl- • A base is a source of hydroxide ions (OH-) e.g. NaOH(s) Na+ (aq) + OH- (aq) e.g. NH3 (aq) +H2O(l) NH4+ (aq) + OH-(aq) Naming of acids 1. In a binary acid, the negative anion ends in -ide. The name begins with the prefix hydro- , stem and ends with -ic acid. stem hydro______ ic acid stem hydroflouric acid HF hydrochloric acid HCl HBr Hydrobromic acid 2. In an oxy acid, the negative anion ends in –ate, use the stem and the name ends with -ic acid. ______ ic acid HNO3 H2SO4 H3PO4 CH3COOH nitric acid sulfuric acid phosphoric acid acetic acid 3. In an oxy acid, if the negative anion ends in –ite, use the stem and the name ends with -ous acid. _______ ous acid HNO2 nitrous acid H2SO3 sulfurous acid H3PO3 phosphorous acid Some Common Bases NaOH Sodium hydroxide KOH Potassium hydroxide Ba(OH)2 Barium hydroxide Mg(OH)2 Magnesium hydroxide Al(OH)3 Aluminum hydroxide Learning Check Match the formulas with the names: A. ___ HNO2 1) hydrochloric acid B. ___ Ca(OH)2 2) sulfuric acid C. ___ H2SO4 3) sodium hydroxide D. ___ HCl 4) nitrous acid E. ___ 5) calcium hydroxide NaOH Solution AB4 Match the formulas with the names: A. _4__ HNO2 1) hydrochloric acid B. _5__ Ca(OH)2 2) sulfuric acid C. _2__ H2SO4 3) sodium hydroxide D. _1__ HCl 4) nitrous acid E. _3__ NaOH 5) calcium hydroxide Learning Check Acid, Base or Salt Name CaCl2 ______ _________________ KOH ______ _________________ Ba(OH)2 ______ _________________ HBr ______ _________________ H2SO4 ______ __________________ Solution AB5 Acid, Base or Salt Name CaCl2 salt calcium chloride KOH base potassiuim hydroxide Ba(OH)2 base barium hydroxide HBr acid hydrobromic acid H2SO4 acid sulfuric acid B. Definitions • Arrhenius - In aqueous solution… – Acids form hydronium ions (H3O+) + H3O HCl + H2O H H Cl acid O H H – + O H + Cl H – Cl B. Definitions • Arrhenius - In aqueous solution… – Bases form hydroxide ions (OH-) NH3 + H2O + NH4 H H H N H base O H H – + O N H + OH H H H B. Definitions • Brønsted-Lowry – Acids are proton (H+) donors. – Bases are proton (H+) acceptors. HCl + H2O acid + H3O + Cl base conjugate acid conjugate base Conjugate acid base pairs • conjugate base: the species that remains after an acid has given up a proton • conjugate acid: the species that is formed when a base gains a proton base acid NH3 + H2O + NH4 conjugate acid + OH conjugate base • In the two examples water first acts as a base, then as an acid. • Any species which can both accept and receive protons is called amphiprotic. (also known as amphoteric) • Give the conjugate acid for each of the following: Br – HBr HSO4- H2SO4 CO32- HCO3- • List the conjugate acids for the following Bronsted bases • OH H2O - • CO3 2- HCO3- • NO3- HNO3 • HCO3- HCO3 • CN - HCN • Give the conjugate base for each of the following: HF F- H3PO4 H2PO4- H3O+ H 2O • Polyprotic - an acid with more than one H+ • List the conjugate bases for the following Bronsted acids • H2SO4 HSO4- • HPO42- PO43- • HCO3 - CO32- • H3O+ H2O • H2PO4- HPO42- Review 2: Name the acid, base, conjugate acid and base for each reaction. CH3NH2 + H2O base H3O + HC2H3O2 + H2O acid CH3NH3+ acid base + conjugate base H2PO4 base H2PO4 - + conjugate acid base OH - + conjugate acid acid H3PO4 + H2O acid CH3NH3+ H3O + conjugate base + conjugate acid H3PO4 conjugate acid C2H3O2 conjugate base + CH3NH2 conjugate base Review 2: Name the acid, base, conjugate acid and base for each reaction. H2PO42- + OH- acid base HCN + H2O acid NH3 + base NO3base CNconjugate base H2O NH4 + HCO3 acid + conjugate base base acid + HPO4- conjugate acid H3O + + conjugate acid + conjugate acid CO32conjugate base H2O OH conjugate base + HNO2 conjugate acid