28 - Acids and Bases
advertisement
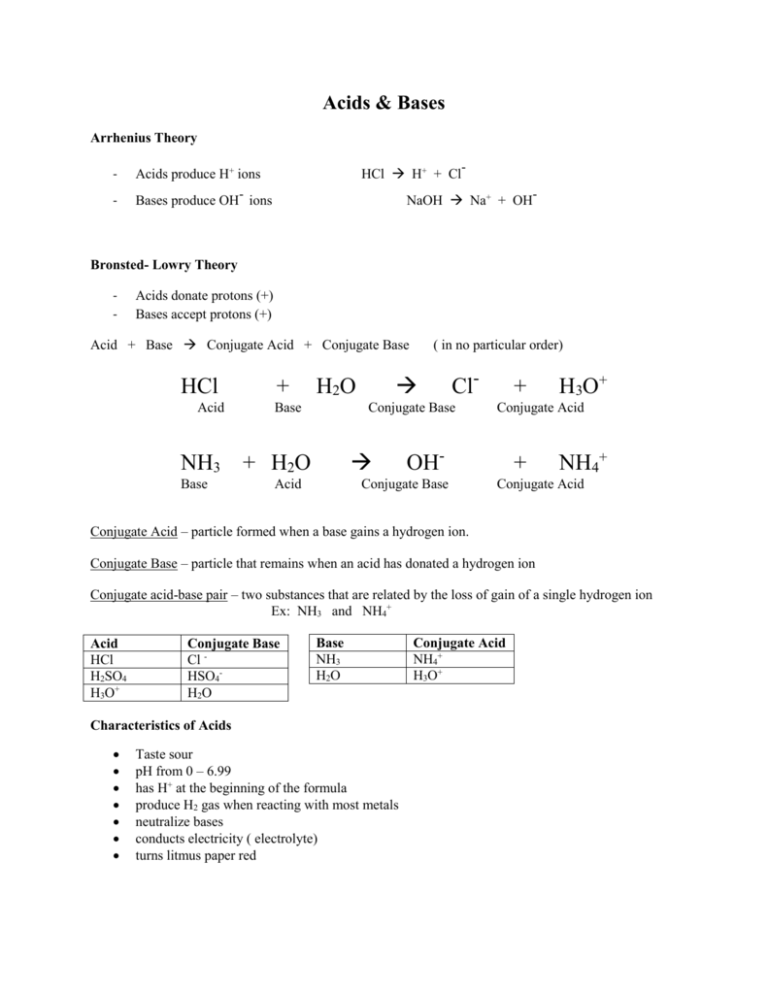
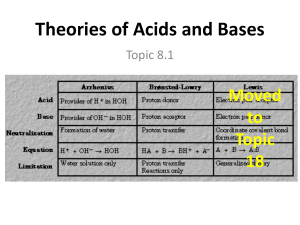
Acids & Bases Arrhenius Theory - HCl H+ + Cl- Acids produce H+ ions Bases produce OH- ions NaOH Na+ + OH- Bronsted- Lowry Theory - Acids donate protons (+) Bases accept protons (+) Acid + Base Conjugate Acid + Conjugate Base HCl Acid NH3 Base + H2O Base ( in no particular order) Cl- Conjugate Base + H2O Acid + Conjugate Acid OH- Conjugate Base H3O+ + NH4+ Conjugate Acid Conjugate Acid – particle formed when a base gains a hydrogen ion. Conjugate Base – particle that remains when an acid has donated a hydrogen ion Conjugate acid-base pair – two substances that are related by the loss of gain of a single hydrogen ion Ex: NH3 and NH4+ Acid HCl H2SO4 H3O+ Conjugate Base Cl HSO4H2O Base NH3 H2O Characteristics of Acids Taste sour pH from 0 – 6.99 has H+ at the beginning of the formula produce H2 gas when reacting with most metals neutralize bases conducts electricity ( electrolyte) turns litmus paper red Conjugate Acid NH4+ H3O+ Examples of Strong Acids HCl HBr HI H2SO4 HNO3 HClO3 HClO4 ** the stronger an acid, the weaker its conjugate base and vice versa** Characteristics of Bases Taste bitter pH between 7.01-14 have OH ions feel slipper ex. Soap neutralize acids turns litmus paper blue Examples of Strong Bases LiOH NaOH KOH RbOH CsOH Mg(OH)2 Ca(OH)2 Sr(OH)2 Ba(OH)2 milk of magnesia Naming Acids Anion (ending) -ide -ite -ate Acid name Hydro - ic -ous -ic Monoprotic – has 1 H HCl Diprotic – has 2 H H2SO4 Triprotic – has 3 H H3PO4 Example HCl hydrochloric acid HNO2 nitrous acid HNO3 nitric acid Anhydrides – acids of bases that have had H2O removed Acidic anhydrides – produce an acid when dissolved in H2O o Acid rain: SO2(g) + H2O(l) H2SO4(aq) Basic anhydrides – produce a base when dissolved in H2O o Na2O(s) + H2O(l) 2 NaOH(aq) Neutralization Reactions - Always form a salt and water Salt – a crystalline compound formed from an acid’s anion and a base’s cation. HCl(aq) + NaOH(aq) NaCl(s) + H2O(l) Acid base Amphoteric – can act as either an acid of a base Ex: H2O (water) salt water