Evolution Slight changes in the inherited characteristic of a species
advertisement

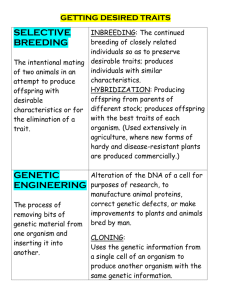
Evolution Slight changes in the inherited characteristic of a species through adaptations over time Charles Darwin Father of Evolution by Natural Selection Natural Selection Selection by the environment of organisms better adapted to survive and reproduce Fitness Physical traits and behaviors that enable organisms to survive and reproduce in their environment Adaptations Inherited changes that allow organisms to be better suited to survive and reproduce in a particular environment Survival of the Fittest The fittest (best adapted) organisms within a particular environment will out-compete those who aren’t as fit Competition (Struggle for Existence) Individuals within a species will struggle to survive and have to compete for limited resources in their environment Over Production of Offpspring More offspring are produced than can survive Differential Survival and Reproduction Organisms with traits favored by the environment will have a higher chance of surviving and reproducing and therefore passing on their traits Genetic Variation Differences in inherited characteristics of species that get passed on to the next generation Things that lead to Genetic Variation Mutations, Sexual Reproduction, and Gene Flow from different populations 4 Processes of Evolution by Natural Selection 1. Competition (Struggle for Existence) 2. Overproduction of offspring 3. Differential Survival and Reproduction 4. Genetic Variation Artificial Selection Process by which humans breed other animals and plants for particular desirable traits. AKA Selective Breeding 5 Evidences of Evolution Fossils 1. Fossils 2. Embryos 3. DNA 4. Anatomy 5. Biogeography Any trace or remains of an organism that has been preserved by natural processes Geographical Distribution The location of a particular organism around the world Embryo Organism in the earliest stages of development Embryological Similarities Comparison of the similarities between the embryological developments of different species Genomics A branch of Biology that sequences and analyzes DNA to determine the function and structure of genomes Genome The complete set of DNA within a single cell of an organism Biochemical Similarities How alike the structure of the DNA and protein molecules are between species Gradualism New species evolving from existing species though changes that add up over long periods of time Cladogram A branching diagram showing evolutionary relationships between species Derived Characteristics A sudden change in the structure or amount of genetic material Structural Similarities Similarities in physical features between species Homologous Structures Similar structurally but each has a different function Analogous Structures Structures with similar functions but have different internal structures Vestigial Structures Remnants of structures that were functional in ancestors but now are reduced in size and serve little to no function Biogeography Equilibrium Species living geographically closer show more similarities, despite differences in environment, than two species living in the same type of environment but geographically far away A state of balance, no change Gene Pool All the different variations of genes in an interbreeding population Genetic Equilibrium A condition where a gene pool is not changing because the evolutionary forces acting on the alleles are equal 5 Conditions for Equilibrium 1. Large breeding population 2. Random Mating 3. No Mutations 4. No Migration 5. No Natural Selection Genetic Drift Chance events that change the genetic composition of a population. Founder Effect The loss of genetic variation when a new colony is formed by a small number of individuals from a larger population Bottleneck Effect Three Types of Selection The dramatic loss of genetic variation due to environmental effects or human activities 1. Stabilizing Selection 2. Directional Selection 3. Disruptive Selection Stabilizing Selection The extreme traits in a population are selected against and the average traits are favored Directional Selection One extreme trait is selected for, resulting in the population shifting towards the other extreme Disruptive Selection The extreme traits are both selected for resulting in a reduction of individuals with the intermediate traits Stabilizing Selection Graph Directional Selection Graph Disruptive Selection Graph