Section One: Activation Energy 1. If you're going hiking this weekend
advertisement
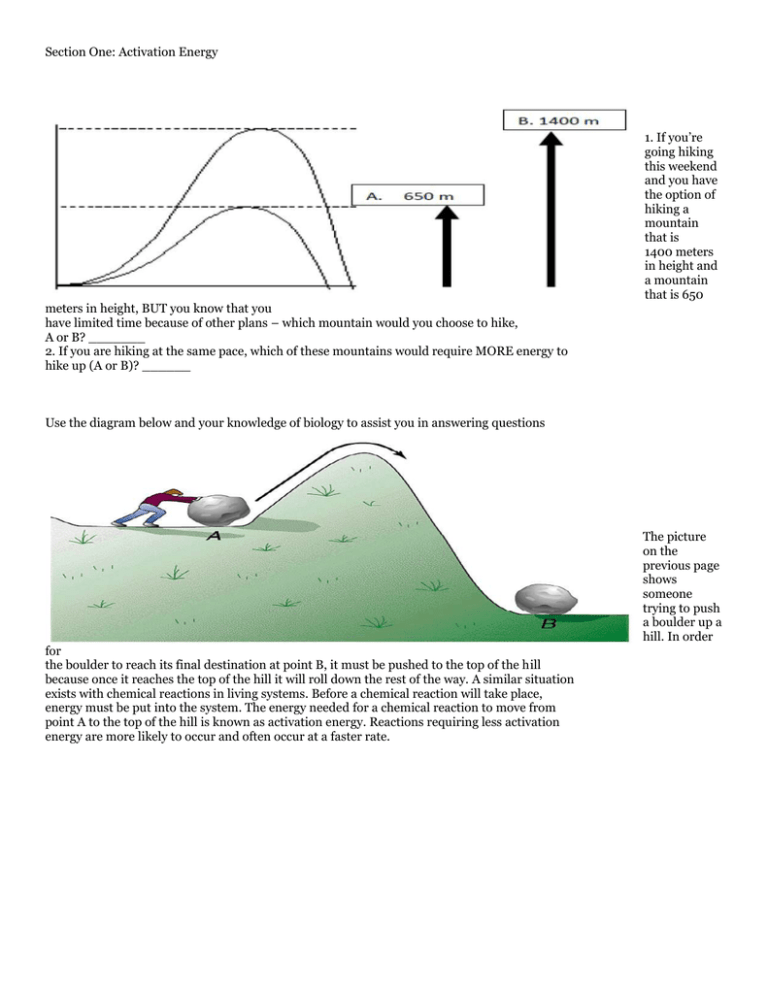
Section One: Activation Energy meters in height, BUT you know that you have limited time because of other plans – which mountain would you choose to hike, A or B? _______ 2. If you are hiking at the same pace, which of these mountains would require MORE energy to hike up (A or B)? ______ 1. If you’re going hiking this weekend and you have the option of hiking a mountain that is 1400 meters in height and a mountain that is 650 Use the diagram below and your knowledge of biology to assist you in answering questions The picture on the previous page shows someone trying to push a boulder up a hill. In order for the boulder to reach its final destination at point B, it must be pushed to the top of the hill because once it reaches the top of the hill it will roll down the rest of the way. A similar situation exists with chemical reactions in living systems. Before a chemical reaction will take place, energy must be put into the system. The energy needed for a chemical reaction to move from point A to the top of the hill is known as activation energy. Reactions requiring less activation energy are more likely to occur and often occur at a faster rate. Page3 3. Define the term activation energy. ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ Comparing the diagram above to the first diagram on page one (the heights of 2 mountains). 4. How does the addition of enzyme change activation energy? ________________________________________________________________ 5. How does the addition of an enzyme change the speed of a reaction? _________________________________________________________________ Page4 Section Two: Lock and Key Concept Use the diagram below and your knowledge of biology to answer the following questions. 6. What are the characteristics that distinguish one key from another? ____________________________________________________________________________ 7. Where are some places that you use keys? ____________________________________________________________________________ 8. Can two different keys pictured above open the same lock? ____________________________________________________________________________ 9. If you had to choose from the word .specific. or .general. to describe a key, which would you choose? ____________________________________________________________________________ Page5 Image modified from http://www.edt-enzymes.com/images/pic_013.gif 10. Looking at the diagram above, how is the enzyme and substrate similar to a lock and a key? ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ 11. Is the chemical reaction in the diagram above a chemical digestion or a synthesis reaction? Use at least one complete sentence to support your answer. ____________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________ 12. The picture above is showing what is known in biochemistry as the .lock and key theory.. Explain why you think this theory is used to describe enzymes. ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ 13. What are some examples from science class or from other areas of your life where the specific shape important for something to work correctly? ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ Page6 Section Three: Factors Influencing Enzyme Activity You can see above what happened to the stack of crayons after they were put through the dryer. Last week, I was really excited about my new crayons, I planned on loaning them to students that forgot to bring a writing tool to class. Unfortunately, I left them in my pocket. 14. How would you describe what happened to my crayons between image A to image B? ______________________________________________________________________________ 15. What caused my crayons to be changed? ______________________________________________________________________________ 16. What are some other things that you have seen .melted. or change shape which impacted their ability to work correctly. Come up with at least 2 other examples. ______________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________ Use the diagram below and your knowledge of biology to assist you in answering questions 17 through 19. Page7 http://regentsprep.org/Regents/biology/units/homeostasis/enzph.gif http://regentsprep.org/Regents/biology/units/homeostasis/enztemp.gif 17. The diagram on the previous page shows what happens to an enzyme when exposed to heat. How is this similar to what happened to my crayons? ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ 18. What term is used to describe when the shape of the enzyme has been altered? ____________________________________________________________________________ 19. Predict how this change in the enzyme's shape will affect the enzyme’s ability to function properly. Use a complete sentence to answer this question. _________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________ Factors Influencing Enzyme Activity pH: the optimum (best) in most living things is close to 7 (neutral). High or low pH levels usually slow enzyme activity Temperature: strongly influences enzyme activity . optimum (best) temperature for maximum enzyme function is usually about 35-40 C. . reactions proceed slowly below optimal temperatures . above 45 C. most enzymes are denatured (change in their shape so the enzyme active site no longer fits with the substrate and the enzyme can't function) Page8 20. Using the information previously provided, identify two conditions that affect enzyme function ______________________________________________________________________________ 21. Provide an explanation for why human enzymes function best at 40 C but enzymes from hot springs bacterium works best at 70 C. ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ 22. What do you think happens to the human enzyme when the temperature increases to 45 C.? ______________________________________________________________________________ 23. Define the term denatured. ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ Page9 Use the graph below and your knowledge of biology to answer questions 24 through 30. 24. At what temperature is the rate of enzyme action highest? ________________ 25. At what temperature(s) is the rate of enzyme action lowest? __________________ 26. Describe the general effect of temperature change on the rate of enzyme action from 0°C to 40°C. _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ 27. What happens to the rate of action for this enzyme above 40°C? ____________________________________________________________________ 28. Predict what would happen to the rate of action of this enzyme if the temperature were increased from 50°C to 60°C. Support your answer. _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ Page10 29. Propose an explanation for the change in rate of enzyme action between 40°C and 45°C. _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ 30. Predict what would happen to our body functions if we were exposed to frigid temperatures (below 0°C) for an extended period of time. Use the graph to support your answer. _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ Use your knowledge of biology and the information in the reading passage below to answer questions 31 to 33. Low grade fevers 38 to 39 C are healthy because they help our body get rid of harmful bacteria/viruses, but when fevers reach of temperature of 105 F / 44 C degrees it is extremely dangerous. If a person runs a fever of 40°C, it may or may not be a good idea to try to lower it by taking medicines such as Tylenol® (acetaminophen) or Motrin® (ibuprofen). 31. How can running a fever of 40°C be helpful to your health? _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ 32. How can running a fever of 40°C be harmful to your health? _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ 33. Instead of using medicines, suggest another method that could be used to lower body temperature. _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________



