09-11 lecture +Q
advertisement

Review
Data: {1, 4, 7, 8, 2, 12, 8}
What is the median?
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
4
5
6
7
8
Review
What scale type is this variable?
Number of lever presses in a 5-min session
A.
B.
C.
D.
Nominal
Ordinal
Interval
Ratio
Review
What scale type is this variable?
Points along Folsom St. between Valmont and Iris
A.
B.
C.
D.
Nominal
Ordinal
Interval
Ratio
Variability
9/11
Variability
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
Central tendency locates middle of distribution
How are scores distributed around that point?
Low variability vs. high variability
Ways to measure variability 10
–
–
–
–
–
3
Range
Interquartile range
Sum of squares
Variance
Standard deviation
4
5
6
7
Maze Attempts
8
9
Frequency (rats)
Frequency (rats)
•
•
•
•
10
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11
Maze Attempts
Why Variability is Important
• Inference
– Reliability of estimators
• For its own sake
31 52 13 43
49 58 100 61
61 97
97 55 31
m = 100
97 106 104
104 106
100105
105 100 108 108 99 97
– Consistency
(manufacturing, sports,
etc.)
105104
104 109 93 97 100 104
104
28
93 108 96 105
M
M
– Diversity (attitudes,
strategies)
87.3
99.1
99 96 105 95 93 92 100 103 103 97
34 175 37 139 106 19 184 88 112 64
178 154 136 103 94
94 181
181 91 109
109 46
46
178
175
76 172 157 22
22 16
16 85
85 142 130
130 151 67
67
121
111.6
100.5
99.5
99
92
103
99 101 106 94
94
102 92 94 96 108
108 98 99
121124160 40 145 127
127 100 82 133 169
169
95 102
95
93 99 101
94 93
101 102 107 92
92 97
166 163 118 148
148 79 25
25 115 73
73 187 70
101 107 92 102
102 103 98
105 95 96
96 107 101
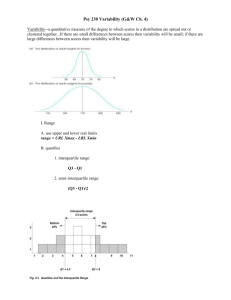
Range
• Distance from minimum to maximum
Measurement unit
or precision
10
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
50
10
45
9
40
8
35
7
30
6
25
5
20
4
–
15
3
10
2
–
5
1
–
0
Frequency (rats)
Frequency (students)
range max( X ) - min( X )
X=
[66.2,depends
78.6, 69.6,on
65.3,
• Sample
range
n 62.7]
• More useful as population parameter
(11Height
– 1) (Inches)
+ 1 = 11
84
82
80
78
76
74
72
70
68
66
64
62
60
58
56
54
52
50
78.6
– 62.7of+ measurement
.1 = 16.0
Theoretical
property
variable
78.65
62.65
= max
16.0 possible
E.g. memory
test:– min
and
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
Rough guidelines, e.g.
height
Maze Attempts
Interquartile range
• Quartiles
–
–
–
–
Values of X based on dividing data into quarters
1st quartile: greater than 1/4 of data
3rd quartile: greater than 3/4 of data
2nd quartile = median
• Interquartile range
– Difference between 1st and 3rd quartiles
– Like range, but for middle half of distribution
– Not sensitive to n more stable
6–3=3
X = [1,1,2,2,2,3,3,4,4,4,4,5,5,5,5,6,6,6,6,6,7,7,7,8]
1st quartile = 3
3rd quartile = 6
Sum of Squares
• Based on deviation of each datum from the mean: (X – m)
• Square each deviation and add them up
SS = å ( X - m)
2
pop
88
94
108
m
115
122
133
145
729 = 272
441 = 212
49 = 72
7 2 = 49
18 2 = 324
30 2 = 900
729 + 441+ 49 + 49 + 324 + 900 = 2492
Variance
• Most sophisticated statistic for variability
• Sum of squares divided by N
– Mean Square: average squared deviation
88
729 = 272
2
441 = 21
49 = 72
94
108
m
115
122
133
s2 =
å ( X - m)
pop
N
145
2
7 = 49
18 2 = 324
30 2 = 900
SS 729 + 441+ 49 + 49 + 324 + 900
s =
=
= 415.3
N
6
2
2
Standard deviation
• Typical difference between X and m
• Again, based on (X – m)2
2
å ( X - m)
2
s =X pop
m
N
N
X = [5, 3, 7, 6, 4, 6, 8, 7, 4, 2, 3, 5]
m=5
• Variance is average squared deviation,
Average
X –so
m =sqrt(variance)
[0, -2, 2, 1, -1, 1,is3,standard
2, -1, -3, -2,
0]
deviation
pop
N
2
= 1.8
Square-root
Square
(X – m)2 = [0, 4, 4, 1, 1, 1, 9, 4, 1, 9, 4, 0]
å ( X - m)
Average
å ( X - m)
pop
N
2
= 3.2
Why squared difference?
• Could use absolute distances, |X - µ|
– Would be more intuitive: average distance from the mean
• Squares have special mathematical properties
– Can be broken into different parts
å X = å ( X - m) + Nm 2
2
2
pop
pop
Sum of Squares:
Differences among scores
Central Tendency:
Common to all scores
Review
Ask people how many hats they own.
Data: {6, 4, 7, 8, 2, 12, 8}
What is the range?
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
2
7
10
11
12
Review
Find the sum of squares of {6, 4, 7, 8, 2, 9}.
Hint: M = 6
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
34
250
12
214
234
Review
A population has a sum of squares of 6400 and a variance
of 16. How big is the population (N)?
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
5
20
400
1600
Not enough information