12-Cranial-Nerves-and-Divisions-of-the-Nervous
advertisement

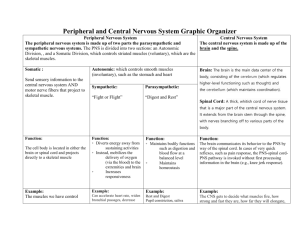
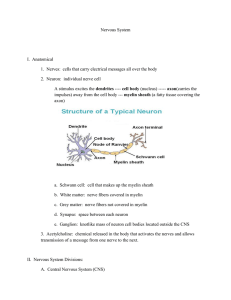
12 Cranial Nerves Olfactory – sense of smell Optic – visual information from the eye to the brain Occulomoter – external eye muscles Trochlear – superior oblique muscles of eye Trigeminal – 3 large branches a. ophthalmic b.maxillary c. mandibular *chewing 6. Abducens – lateral rectus muscles of the eye 7. Facial – taste and facial muscles 8. Vestibulocochlear – a. vestibular b. cochlear * hearing 9. Glossopharyngeal – tongue and throat, corotid sinus which controls blood pressure 10.Vagus – (wonderer) has many widely distributed branches: pharynx, larynx, trachea, heart, lungs, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, and gall bladder. 11.Accessory – “accessory” to the vagus nerve 12. Hypoglossal – “under the tongue” – controls the tongue 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) - brain and spinal cord Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) - Nerves connecting the brain and spinal cord to other parts of the body CNS - structural and functional center of the entire nervous system - consists of the brain and spinal cord - integrates incoming pieces of sensory information, evaluates the information, and initiates an outgoing response PNS - Nerve tissue that lies on the “outer regions” or periphery - Nerves that originate in the brain are called cranial nerves - Nerves that originate in the spinal cord are called spinal nerves Afferent (carry toward) * all incoming sensory pathways Efferent (carry away) *all the outgoing motor pathways Somatic – Carry information to skeletal muscles Autonomic – Carry information to smooth muscle, cardiac muscles, and glands Neuron – excitable cells that conduct the impulses that make possible all nervous system functions * Human brain contains about 100 billion neurons 10% of the nervous system cells Cell body contains nucleus, cytoplasm Axon Dendrite Dendrite “tree” – distal ends are called receptors that receive stimuli that initiate nerve signals - receive signal and conduct electrical signals toward the cell body Axons – conduct impulses away from the cell body * mylenation increases impulse speed