Chapter 2
advertisement
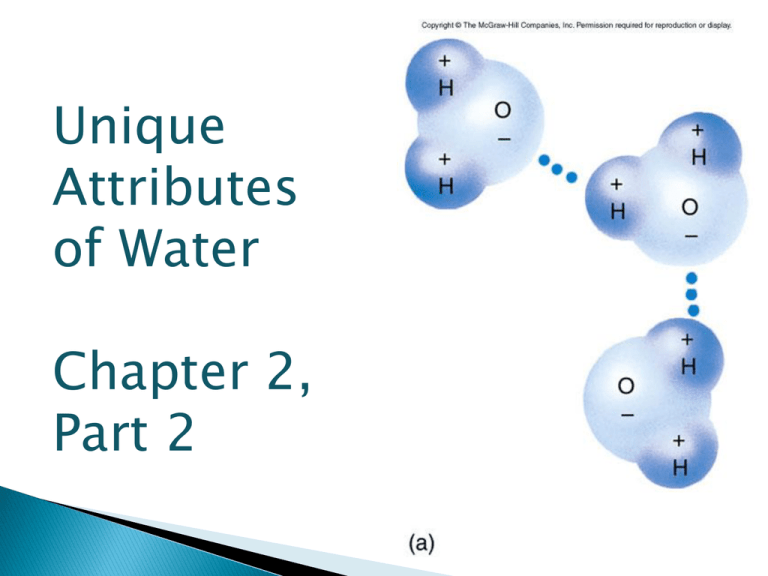
Unique Attributes of Water Chapter 2, Part 2 Water covers 75% of the Earth’s surface. Water is unusual because it is the only compound which exists commonly in all three states of matter. Gas (water vapor) Solid (ice) Liquid (fluid water) Water is a critical component of living systems. Water dominates the intracellular environment. ◦ 75-85% of the cytoplasm of a plant or animal cell is water. ◦ In some organisms, like jellyfish, this value exceeds 95%. In many biological reactions, the H+ OH- of water or are pulled off organic molecules to synthesize water. Individual water molecules are polar molecules because of the electronegativity difference between hydrogen and oxygen. Because of this, water molecules easily form hydrogen bonds with other water molecules or with polar or charged compounds One water molecule can form hydrogen bonds with up to four other water molecules. Water has a number of interesting physical properties because of the importance of hydrogen bonds. Na+-- At any one time any water molecule forms hydrogen bonds with several others, with bonds forming and breaking constantly (in liquid). Cohesion is a measure of the “stickiness” among molecules of the same type. ◦ Water molecules have a high level of cohesion because of these hydrogen bonds that form among molecules. Adhesion is the tendency of one substance to cling to another substance. ◦ Because of hydrogen bonding, water adheres to a wide variety of other substances, such as many biological molecules. ◦ But not at all to others, such as oils. Water has a high specific heat, which means it will absorb a lot of energy before the temperature of the water changes. ◦ It takes energy to break apart the hydrogen bonds The specific heat of water is 4.184 J/g°C, while Tungsten’s specific heat 0.134 J/g°C. Since humans are 60%, we have a high specific heat. This is why our temperature is fairly constant at 98.6°. A mixture is matter that contains two or more substances are not in set proportions A solution is a liquid that contains a homogeneous mix of two or more substances. Matter Pure substances Compounds Mixtures Elements Homogenous Mixtures Heterogeneous Mixture Chicken Noodle Soup Milk O2 Diamond Carbon Dioxide Salt Salt Water Bronze An aqueous solution is a solid, liquid, or gas dissolved in water. The concentration of a solution is the relative amounts of solute and solvent. ◦ ↑ solute in solution, the more concentrated ◦ ↓ solute in solution, the less concentrated Water (H2O) is a good solvent for some substances, but poor for others. Molecules that have regions of polar covalent bond or ionic dissolve well? Or not well? Hydrophilic (water-loving) materials where water molecules surround the materials with hydrogen bonds. When salt (NaCl) is added to water, groups of water molecules form _________ bonds with Na+ and Cl-. These hydrogen bonds between water and ions pull the ions _____________ from the salt. Water’s ability to dissolve hydrophilic compounds is limited. Eventually, there are no more __________ water molecules to form new hydrogen bonds and the solution is saturated. Molecules that are dominated by non-polar covalent bonds do not form hydrogen bonds and do not dissolve in water. Examples of these hydrophobic (water-fearing) compounds are oils and fats. Water molecules will push hydrophobic molecules together to reduce water’s surface area (lowering surface tension). Sprinkle oil droplets on water and eventually they will ______________ into one large drop. Hydrophobic lipids are the major constituent of cell membranes. Among all the molecules in 1 liter of water are a few in which oxygen has stolen the shared electrons completely from one hydrogen atom. H2O⇆ H+ + OH- At any one time, 1 in every 554 million water molecules has dissociated into a hydrogen cation (H+) and a hydroxide anion (OH-). A chemical equation is a way of describing what happens in a chemical reaction. Equation for Photosynthesis Light + 6CO2 + 6H2O Reactants → C6H12O6 + 6O2 Products The arrow indicates the direction the chemical equation is occurring. Most often said as “yields”. Dehydration Synthesis Reaction is a chemical change where water is released and a larger, more complex molecule is made (synthesized). NH2CH2CO-OH + H-NHCH2CO-OH → NH2CH2CO-NHCH2CO-OH +H-OH Hydrolysis Reaction is where water is used to break the reactants into smaller, less complex products ◦ NH2CH2CO-NHCH2CO-OH + H-OH → CH2CH2CO-OH + NHCH2COO-OH An acid is any substance that ________________ the [H+] in a solution. In water, an ionic compound, like HCl, will separate into H+ and Cl- ions, increasing the concentration of H+. Most acids are “proton donors”. A base is any substance that _________ the [H+] in a solution. Some bases remove H + directly: ◦ NH3 + H+ <----> NH4+ These bases are “proton acceptors Others are more indirect: NaOH <---> Na+ + OHOH- + H+ <---> H2O HCl NaOH KOH H2SO4 CH3COOH In biological systems, the hydrogen ion concentration varies over a huge range of values, by 100 million or more. ◦ For example, the concentration of hydrogen ions in the stomach is 1,000,000 times greater than that in the _______ To encompass that range of variation (so many zeroes), the pH scale was developed. pH = -log10 [H+] or [H+] = 10-pH Because the pH values are measured on a log scale a change of pH from 7 to 5 represents a 100x increase in [H+]. ◦ The change is 2 pH units: 102 = 100. A solution with a pH between 0 and 7 is acidic A solution with a pH between 7 and 14 is basic. The intracellular pH is 7.3-7.4 If we add acid to the solution, [H+] will increase (the exponent will be less negative) and pH values will be smaller (moving toward 1). If we add base to a solution, the [H+] will decrease (the exponent will be more negative) and pH values will be larger (moving up to 14). Salts are ionic compounds that do not release either H+ or OH- when dissolved in water. Usually a product (along with water) of a reaction between an acid and a base. In chemistry, a salt is any metal combining with a non-metal. ◦ HCl + NaOH → Na+ + Cl- + H+ + OH- → NaCl + H20 ◦ Examples of Salts: Potassium Chloride (KCl) Calcium Chloride (CaCl2) Copper Sulfate (CuSO4) Many normal cellular processes have the potential to release large quantities of H+ or OH- ions. Buffers are an aqueous solution that contain weak acids or weak bases that tend to maintain constant pH. This is because they can either accept or release hydrogen ions. H2CO3 response to increasing [H+] Carbonic Acid HCO3- + H+ Bicarbonate Ion response to decreasing [H+]









