unit 1.01 study guide
advertisement

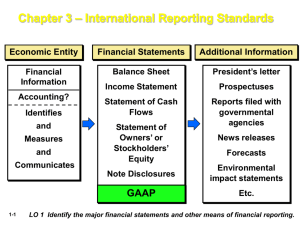
UNIT 1.01 STUDY GUIDE In a routine financial day, accountants are required to make judgments regarding the way to record business financial transactions. The financial goals of the company for which they work often direct their decisions. There is a framework of standard rules known as generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP) to guide their judgments. I. Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP) A. Organizations that develop/format GAAP B. Primary qualities of GAAP C. Secondary qualities of GAAP II. Essential Accounting Constraints, Concepts, Assumptions, and Principles for GAAP (13) A. Constraints 1. Cost effectiveness constraint 2. Materiality constraint 3. Conservatism constraint B. Concepts 1. Recognition concept 2. Measurement concept C. Assumptions 1. Economic entity assumption 2. Going concern assumption 3. Monetary unit assumption 4. Time period assumption D. Principles 1. Cost principle 2. Full disclosure principle 3. Revenue recognition principle 4. Matching principle III. Required Financial Statements for GAAP IV. ISRF and its Effect on GAAP I. Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP) is defined as the set of accepted industry rules, practices, and guidelines for financial accounting. GAAP includes the standards, conventions, and rules accountants follow in recording and summarizing transactions and in the preparation of financial statements. A. Governing organizations behind Generally Accepted Accounting Principles 1. American Institute of Certified Public Accountants (AICPA) 2. The Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB) 3. The Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) a. Two laws, the Securities Act of 1933 and the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, give the SEC authority to establish reporting and disclosure requirements. b. Holds primary responsibility for: (1) Enforcing federal securities laws (2) Regulating the securities industry (3) Regulating the stock market (4) Preventing corporate abuse of investors c. Given enforcement authority by Congress to: (1) Bring civil enforcement actions against individuals and companies who: (a) Commit accounting fraud (b) Provide false information (c) Engage in insider trading (d) Violate securities laws (2) Bring criminal enforcement actions against individuals and companies for criminal offenses. 4. The SEC usually operates in an oversight capacity, allowing the FASB and the Governmental Accounting Standards Board (GASB) to establish these requirements. B. Primary qualities that make accounting information useful for decision making 1. Relevance – The information is capable of making a difference in a decision. Information should have predictive or feedback value, and it must be presented on a timely basis. 2. Reliability - Information must be verifiable, a faithful representation, and reasonably free of error and bias (neutral). C. Secondary qualities that make accounting information useful for decision making 1. Comparability - Information has been measured and reported in a similar manner for different enterprises. 2. Consistency - Information is created and reported using the same accounting treatment to similar events from period to period. II. There are thirteen basic accounting constraints, concepts, assumptions, and principles that GAAP is founded upon. A. Constraints: 1. Cost Effectiveness Constraint: The cost of providing accounting information should not exceed the benefit of the information it is reporting. 2. Materiality Constraint: The requirements of any accounting principle may be ignored when there is no effect on the decisions of users of financial information (immaterial). 3. Conservatism Constraint: Accountants must use their judgment to record transactions that require estimation. This concept helps accountants choose between 2 equally likely alternatives. Therefore, the less optimistic estimate will be chosen when two estimates are judged to be equally likely. B. Concepts: 1. Recognition Concept: An item should be recognized (recorded) in the financial statements when: a. It can be defined by GAAP assumptions and principles. b. It can be measured. c. It is relevant to decision making by users. d. It is reliable. 2. Measurement Concept a. Every transaction is measured by the stated unit of measurement, such as the dollar b. The stated procedure of valuing assets, liabilities, equity, revenue and expenses as defined by GAAP C. Assumptions: 1. Economic Business Entity Assumption: All of the business transactions are separate from the business owner’s personal transactions. 2. Going Concern Assumption: Financial statements are prepared under the assumption that the company will remain in business indefinitely unless there is sufficient evidence otherwise. 3. Monetary Unit Assumption: The accountant assumes a stable currency is going to be the unit of record. The FASB accepts the nominal value of the U.S. dollar unadjusted for inflation as the monetary unit of record. 4. Time Period Assumption: The entity's activities are separated into periods of time, i.e.: months, quarters or years. D. Principles: 1. Cost Principle: Assets are recorded at historical cost, which equals the value exchanged at the time of their acquisition, not at Fair Market Value. 2. Full Disclosure Principle: All information pertaining to the operations and financial position of the entity must be reported within the period of time in question. 3. Revenue Recognition Principle: Revenue is earned and recognized upon product delivery or service completion, without regard to the timing of cash flow. This is also called accrual basis accounting. 4. Matching Principle: The costs of doing business are recorded in the same period as the revenue they help to generate. III. Statements Required by GAAP A. Balance Sheet: shows information about the organization’s resources at one given time. 1. Shows Assets, Liabilities, and Equity 2. Details about cash including cash in the bank, amount owed to creditors, and the value of the company’s assets. B. Income Statement: Shows the flow of revenues over a given period of time, typically a month, quarter, or year. 1. Shows revenue and expenses 2. Shows profit or loss of a company C. Statement of Cash Flow: shows the movement of cash in and out of the business over a specified period. 1. Details cash flows from operating activities, investing activities, and financing activities 2. Shows how changes in the balance sheet and income statement affect cash and cash equivalents D. Statement of Stockholders Equity: shows the changes in the company’s equity throughout the reporting period. 1. Reports profit or loss from the company 2. Reports dividends paid 3. Reports other items that are debited/credited to retained earnings IV. International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) A. Principles-based standards, interpretations, and the framework adopted by the International Accounting Standards Board (IASB) B. Due to numerous companies operating globally, standards that are applicable to all countries need to be developed. C. Framework of IFRS 1. States the basic principles of IFRS 2. Currently being updated and converged with the IASB and FASB 3. The objective is to create a sound foundation for future accounting standards. D. US GAAP becoming IFRS 1. In February 2010, the SEC voted unanimously to publish a statement to reaffirm its longstanding commitment to the goal of a single set of highquality global accounting standards. Additionally, the SEC expressed its continued support for the convergence of US GAAP and IFRS. 2. Beginning in October 2010, the SEC will begin to work on a plan to combine GAAP and IFRS. 3. U.S. companies may move to IFRS in approximately 2015 or 2016 UNIT 1.02 STUDY GUIDE I. The AICPA Code of Professional Conduct A. Principles – provide ideal standards of professional conduct; not enforceable against AICPA members B. Ethical Principles 1. Responsibilities – exercise sensitive and professional moral judgments 2. Public Interest – serve the public interest, honor public trust, and demonstrate commitment to the profession 3. Integrity – perform professional responsibilities with the highest sense of integrity 4. Objectivity and Independence – be independent in fact and appearance in providing auditing or other attestation services 5. Due Care – observe technical and ethical standards, improve competence, and perform to the best of your ability 6. Scope and Nature of Services – follow Code of Professional Conduct in determining scope and nature of services C. Rules – represent minimum standards of ethical conduct; enforceable against AICPA members D. Interpretations of Rules of Conduct 1. Published by AICPA’s Division of Professional Ethics 2. Used when practitioners have frequent questions 3. May be used by a practitioner to justify a departure E. Ethical Rulings 1. Published explanations and answers to questions about rules of conduct 2. Submitted to the AICPA by practitioners and others interested in ethical requirements II. Specific Rules of Conduct A. Independence – a member in public practice shall be independent in the performance of professional services as required by the standards 1. Financial interest in client 2. Immediate family 3. Former practitioners 4. Normal lending procedures 5. Joint relationship with client investor 6. Joint relationship with client investee 7. Director, officer, manager, or employee 8. Litigation between CPA firm and client 9. Bookkeeping services 10. Consulting and other nonaudit services 11. Unpaid fees B. Integrity and Objectivity – member shall be free of conflicts of interest, shall not knowingly misrepresent facts or subordinate his or her judgment to others C. General Standards – member shall comply with the following standards: D. E. F. G. H. 1. Professional competence – undertake only those professional services that can be completed with professional competence 2. Due professional care – exercise due professional care in the performance of professional services 3. Planning and supervision – adequately plan and supervise the performance of professional services 4. Sufficient relevant data – obtain sufficient, relevant data to provide a reasonable basis for conclusions and recommendations Compliance with Standards – must comply with the following standards: 1. Auditing Standards and PCAOB Standards 2. Statements on Accounting and Review Services 3. Statements on Standards for Attestation Engagements 4. Management Consulting Services Standards Accounting Principles 1. GAAP is considered to be any statement proclaimed by an authoritative body designated by the AICPA 2. CPAs must justify any departure from GAAP 3. Departure from GAAP is permitted IF following GAAP would make statements misleading Confidential Client Information – may not disclose any confidential client information without the specific consent of the client. Exceptions are: 1. Subpoenas or summons enforceable by a court order 2. Review of papers related to an ethics division inquiry 3. Review of papers related to a peer review 4. Obligations related to technical standards Contingent Fees 1. Fees to be determined upon a particular result 2. CPAs are forbidden to accept contingent fees for attestation services and tax return preparation Acts Discreditable 1. Retaining client records after they have been requested 2. Discrimination or harassment in employment practices 3. Noncompliance with standards 4. Negligence in the preparation of financial statements or reports 5. Solicitation or disclosure of CPA exam questions and answers 6. Failure to file a tax return or pay tax liability Advertising and other forms of solicitation – false, misleading, or deceptive advertising is prohibited. Examples of unacceptable advertising are: 1. Creates false or unjustified expectation of favorable results 2. Implies the ability to influence any court or similar body or official 3. Client is unaware that there is a likely chance that a stated fee will be substantially increased 4. Other representations that are likely to cause a reasonable person to misunderstand or be deceived. J. Commissions and Referral Fees – compensation paid for recommending a third party’s product or service to a client or recommending a client’s product or service to a third party. Prohibited if the firm also performs: 1. Audit or review of financial statement for the client 2. Compilation of financials in which lack of independence is not disclosed and the financials may be used by a third party 3. Examination of prospective financial information K. Form of Organization and Name 1. Member may practice public accounting only in a form of organization permitted by state law 2. CPA shall not practice public accounting under a firm name that is misleading 3. Ownership of CPA firms by non-CPAs is allowed under certain conditions 4. Firm may not designate itself as a member of the AICPA unless all CPA owners are members of the AICPA I. III. Enforcement of Policies – principally involves the following groups: A. State Boards of Accountancy – can revoke CPA certificate of license to practice B. AICPA Joint Trial Board – can suspend or expel members from the AICPA; less serious and unintentional violations will normally require only corrective and remedial action UNPACKED CONTENT I. Ethical Principles in the AICPA Code of Professional Conduct A. Responsibilities B. Public Interest C. Integrity D. Objectivity and Independence E. Due Care F. Scope and Nature of Services II. Specific Rules of Conduct A. Independence B. Integrity and Objectivity C. General Standards D. E. F. G. H. I. J. K. Compliance with Standards Accounting Principles Confidential Client Information Contingent Fees Acts Discreditable Advertising and Other Forms of Solicitation Commissions and Referral Fees Form of Organization and Name