Key terms 3.1 and Key terms 3.2
advertisement

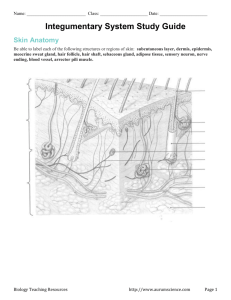
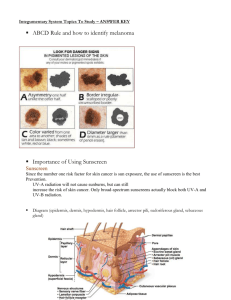
Integument systems ________________________Key Terms 3.1 and 3.2 3.1 Key terms 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. Cutaneous membrane Epithelial membrane Membranes Mucous membranes Pericardium Peritoneum Pleura Serous fluid Serous membrane Synovial fluid Synovial membrane A. The lining of the synovial joint cavity that makes synovial fluid B. Thin sheet or layers of pliable tissue C. The membrane encasing the heart D. The membrane lining the abdominal cavity E. Thin sheets of tissues that line body cavities closed to the outside world F. Thin sheets of tissue that line the body’s internal and external surfaces G. A thin, clear liquid which acts as a lubricant between parietal and visceral membranes H. Another name for skin I. Thin sheets of tissue lining the body cavities open to the outside world J. A clear liquid secreted by synovial membranes that cushions and decreased joint friction. K. Membrane that surrounds the lungs Key Terms 3.2 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. Dermis Epidermal dendritic cells Epidermis Hypodermis Integumentary system Keratin Keratinocytes Melanin Melanocytes Merkel cells Papillary layer Reticular layer Sebaceous glands Sebum Stratum basale Stratum corneum Stratum granulosum Stratum lucidum Stratum spinosum Sudoriferous glands A. Specialized cells that produce melanin B. Clear layer of thick skin found only on the palms of hands, finger, and soles of the feet C. Found between the epidermis and hypodermis; includes nerve endings, glands, and hair follicles D. Located all over the body and produce sebum E. Deepest layer of the epidermis F. Layer of skin located under the dermis and stores fat G. Secretes sweat H. Tough protein found in skin, hair, and nails I. A level of somewhat flattened cells, lies just superficial to the stratum spinosum and inferior to stratum lucidum J. Largest external organ system K. Coat of skin superficial to stratum basale and inferior to stratum granulosum L. An oily substance that keeps hair and skin soft M. Pigment that protects against UV damage N. Initiates an immune response to foreign pathogens O. Outer layer of the epidermis P. Cells that make keratin Q. Outer layer of the dermis R. Skin’s touch receptors S. Outer layer of the skin