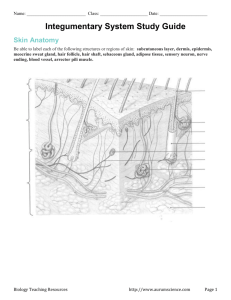
Journal #1: How is the integumentary system (skin) like an onion?
advertisement

Journal #1: How is the integumentary system (skin) like an onion? 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Vocabulary Integument Epidermis Dermis Subcutaneous layer Basal Cells Keratin Carotene Melanin Objective: List the components of the integumentary system and their relationship to each other Specify the functions of the integumentary system Ch.5 Integumentary System Part 1: Layers Pages 153-164 Components of the Integument Cutaneous Membrane Epidermis Dermis Accessory Structures Hair, Nails, & Glands Subcutaneous layer Hypodermis Superficial Fascia/connective tissue Function Protection Excretion Maintenance of Homeostasis Synthesis of Vitamin D Storage of Lipids Detection/ Receptors The Epidermis Stratified Squamous Epithelium No Blood vessels Many Keratinocytes Cells that contain keratin Thin Skin- most surfaces Thick Skin- palms of hands/soles of feet Layers (Strata) of the Epidermis From Deepest to most Superficial Stratum Germinativum Stratum Spinosum Stratum Granulosum Stratum Lucidum Stratum Corneum Stratum Germinativum Hemidesmosomes attach cells to basal lamina Form epidermal ridges and dermal papillae Increase surface area Genetically determined patterns are unique Cells Basal or Germinative Cells (stem cells) Merkel Cells (touch receptors) Melanocytes (skin pigmentation) Stratum spinosum “Spiny Layer” of 8-10 rows of keratinocytes Results from one of the daughter cells from stem cell division being pushed up from the stratum germinativum Langerhans cells Stimulate immune response to microorganisms and cancer Stratum Granulosum “Grainy Layer” of 3-5 layers of keratinocytes Lots of Keratin (tough protein) & Keratohyaline (promotes dehydration) Thin flat cells with decreased permeability Stratum Lucidum In thick skin of palms and soles only Clear layer that covers the stratum granulosum Flat, dense, and filled with keratin Stratum corneum Exposed surface of skin 15-30 layers of keratinized (dead) cells Takes 15-30 days for the cell to move from stratum germinativum to the stratum corneum (2 weeks before it is shed) Water resistant, not waterproof Perspiration Journal #2: Give the layers of the epidermis from the most superficial to the deepest. Vocabulary 9. UV Radiation 10. Cyanosis 11. Vitamin D 12. Epidermal Growth Factor 13. Papillary Layer 14. Reticular Layer 15. Hypodermis Objective: List the components of the integumentary system and their relationship to each other Specify the functions of the integumentary system Skin Color Pigmentation Carotene Orange yellow pigment in epidermal cells Can convert to Vitamin A (needed in the growth of epidermal cells) Melanin Brown, yellow, or black pigment Melanocytes produce it in the stratum germinativum and store in vesicles called melanosomes Dark skinned people have larger melanosomes Synthesis increases with UV exposure Dermal Circulation Red tones produced by hemoglobin Cyanosis- blue tone to skin in RBC’s Other Roles of the Epidermis Steroid Production UV Radiation in epidermal cells in the stratum spinosum and germinativum convert a steroid into cholecalciferol or Vitamin D Helps in bone development and maintenance (Ricketsabnormal bone development due to lack of Vitamin D Epidermal Growth Factor Made by salivary glands and the glands of the duodenum Functions Promotes cell division in stratum germinativum and spinosum Speeds up production of keratin in keratinocytes Stimulates skin repair and development Stimulates activity and secretion in epithelial glands The Dermis Components Papillary Layer Areolar tissue with capillaries, lymph, and sensory neurons Reticular Layer Irregular connective tissue w/collagen fibers extending to subcutaneous layer Blood vessels, lymph, and nerve fibers Characteristics of the Dermis Strength and Elasticity Lines of Cleavage (pattern fibers make) Cut parallel will heal with little scarring Cut at a right angle will have greater scarring Blood Supply Collagen & elastic fibers Water content Arteries to subcutaneous and border reticular layer called cutaneous plexus Innervation Sensory reception Light touch: tactile (Meisners’s) corpuscles Deep pressure & vibration: lamellated (Pacinian) corpuscles Subcutaneous Layer Hypodermis Stabilizes skin in relation to muscles and other organs Areolar and adipose (baby fat) tissue Venous circulation contains a great amount of blood Subcutaneous injection effective