Thermal Physics
advertisement

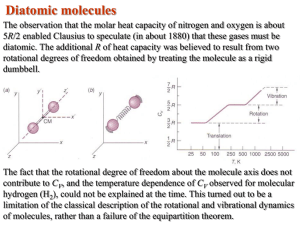
Describe the image ◦ What is it? ◦ What does it measure? ◦ How does it work? What is it? ◦ Scalar ◦ Provides information about how hot or cold something is Measured with a Thermometer ◦ Temperature noted on the thermometer is equal to that of the object when the two are in equilibrium ◦ How do thermometers work? Physical properties of matter can change dependent on temperature Thermometers follow 1 of the principles ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ Thermal Expansion of a liquid Electrical Resistance of a wire Pressure of a gas (in a fixed volume) Linear Expansion of Solids Color of a solid heated to high temperatures How would you make a thermometer? Fahrenheit (1724) ◦ Salt:water:ice mixture and body temperature Celsius (1742) TC = (5/9) (TF - 32) Kelvin (1848) TK = TC + 273.15 ◦ Freezing and boiling point of water ◦ Gas Expansion Coefficient and Celsius ◦ Fundamental unit for temperature ◦ At 0 K, all molecules stop moving (theoretically) Freezes: 32° F = 0° C = 273.15 K Boils: 212° F = 100° C = 373.15 K At standard pressure! 1 atm 760 mm Hg (Torr) 101,325 Pa = 101.325 kPa 1.01325 bar Critical Point – Triple Point – Above this point, the liquid phase and gas phase merge into 1 phase, a supercritical fluid Water, Ice, and Steam exist For Gases: EK = (3/2)k*T ◦ EK Kinetic Energy ◦ T Temperature ◦ k Boltzmann Constant k = 1.38 x 10-23 JK-1 Distribution of KE values Internal E = PE + KE of all particles within the system Potential Energy Kinetic Energy - movement ◦ Bond Energy – energy stored in bonds ◦ Intermolecular forces – attractive energy between particles ◦ Translational - straight line ◦ Rotational – spinning about an axis ◦ Vibrational – back and forth motion centered at a point Solids – mainly vibrational Liquids – mainly vibrational, some rotational, little translational Gases – Mainly translational and rotational Conduction – Physical contact hot cold Convection – movement of fluids cold hot ◦ Particle collisions – no net movement ◦ Gases – slow; Liquids – medium; solids – fast (metals) slow (generally non-metals) ◦ Only fluids ◦ Density differences in fluids Hot – more energy, further apart, lower density Cold – less energy, closer together, higher density Radiation – light is released and absorbed ◦ No matter necessary for transfer ◦ EX: SUN Heat – energy that is transferred due to Temperature – measure of AVG. kinetic Internal Energy – total kinetic energy and temperature differences energy of the molecules in a substance potential energy associated with forces and bonds among the molecules in a substance.