Chapter 10
advertisement

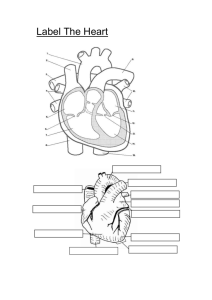
Chapter 10 •Circulation Section 1 •The Body’s Transport System The Cardiovascular System • The cardiovascular system, or circulatory system, consists of the heart, blood vessels, and blood. • The system is carries needed substances to cells and carries waste products from cells. – The cells in blood also helps to fight disease and infecto The Circulatory System • Substances in the body are carried by the blood. – Oxygen from your lungs – Glucose for energy • Waste is also eliminated by cells in the body. – Carbon dioxide from glucose • Certain cells in the blood also fight infection and disease. The Lungs Heart Red is oxygen rich blood Blue is oxygen poor blood The Heart • The heart is a hollow, muscular organ that pumps blood throughout your body – About the size of your fist, located in the center of your chest, right behind your sternum • Each time your heart beats, it pushes blood through the blood vessels of the cardiovascular system – Heart is made out of cardiac muscle The The Heart • The right side of the heart is completely separated form the left side by tissue called the septum. • Each side has 2 compartments, or chambers, an upper and lower chamber. • Each upper chamber is called an atrium – The atrium is the chamber that recieves blood that comes into the heart The Heart • The lower chamber is called a ventricle. – The ventricle pumps blood out of the heart • The atrium and ventricle are separated by valves. – A valve is a flap of tissue that prevents blood from flowing backwards. The Heart • How the heart works – In the first phase the heart relaxes and fills the heart with blood. – In the 2nd phase the heart contracts to pump blood forward. Two Loops • After leaving the heart blood travels in blood vessels through the body. • Arteries are blood vessels that carry blood away from the heart. • Narrow vessels are called capillaries. – In capillaries substances are exchanged between blood and cells. • Veins are what carry blood back to the heart. Two Loops • In the 1st loop blood travels from the heart to the lungs and then back to the heart. • In the 2nd loop blood is pumped from the heart throughout the body and then back to the heart The Heart Two Loops • Blood that flows to the lungs and back, the blood is a dark red, which is oxygen poor. • Blood flows from the right atrium into the right ventricle. • The ventricle pumps the blood to the lungs • The large vessels of blood become thinner, into tiny capillaries • The blood then absorbs oxygen and pumps back to the heart. Two Loops • In the 2nd loop, the left atrium recieves the blood and then moves to the left ventricle. • The blood then moves through the aorta, the largest vein in the body. • The blood then pumps through the veins throughout the body into capillaries and then flows back to the heart to start the cycle again. Section 2 •A Closer Look at Blood Vessels Arteries • If all the veins, arteries and capillaries in your body were connected, they would be 100,000 kilometers long. • When blood leaves the heart, it travels through the arteries. • The first branches of arteries are called coronary arteries. – Other branches carry blood to the brain, intestines and other organs. Arteries • The walls of the arteries are thick. • The walls consist of 3 layers – First layer is epithelial tissue • The smooth surface allows for the blood to flow freely – Second layer is muscle tissue – Outer layer is a flexible connective tissue • This layered effect gives arteries great strength and flexibility Arteries • Your pulse is caused by the alternating expansion and relaxation of the artery wall. • The layer of muscle tissue acts as a control gate of blood flow – So when you eat, your stomach and intestines need more blood – The arteries leading to these organs relax allowing for greater blood flow Capillaries • In the capillaries, materials are exchanged between the blood and the body’s cells. – Materials such as glucose and oxygen pass from the blood to the cells. • Capillary walls are only one cell thick • Diffusion is the process by which molecules move from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration. Veins • After the blood moves through the capillaries it enters large vessels called veins which carry blood back to the heart. • The walls of the veins are like the artery, the have 3 layers, which muscle in the middle Veins Blood Pressure • Blood pressure is like water flowing out of a hose – More water, greater pressure, less water less pressure • Blood exerts a force called blood pressure against the walls of blood vessels • Blood pressure is caused by the force with which the ventricles contract Section 3 •Blood and Lymph Blood • Blood is a complex tissue that has several parts. • Blood is made up of 4 components – Plasma – Red blood cells – White blood cells – Platelets Blood • Most of the materials transported in the blood is plasma • Plasma is the liquid part of the blood – Water makes up 90% of plasma – Other 10% is dissolved materials • Plasma carries glucose, fats, vitamins and minerals • Protein gives plasma its yellow color Blood • Red blood cells take up oxygen in the lungs and deliver it to cells elsewhere in the body • Red blood cells are made mostly of hemoglobin, which is an iron containing protein that binds to oxygen molecules – When combined with oxygen its turns bright red – Carbon dioxide is carried mostly by the plasma • Red blood cells contain no nuclei, and live only 120 days and there are 2 million red blood cell Blood • White blood cells are the body’s disease fighters • These cells either fight disease or tell the brain they need help – Some fight by eating, other fight by releasing chemicals – White blood cells are also larger than red blood cells Blood • Platelets are cell fragments that help to form clots • This series of reactions produce a protein called fibrin • Fibrin weaves a net of fibers across the cut in the skin Blood Blood Types • Sometimes when a person loose a lot of blood, a blood transfusion is necessary. • There are 4 blood types – A, B, AB and O • A means there is an A marker, B means a B marker, AB means there is an A and B marker. O has neither A or B Blood Types • The markers molecules on your red bloods cells determine your blood type and the type of blood you can receive for a transfusion. Blood Types Lymphatic System • The lymphatic system is your body’s drainage system. • The lymphatic system is a network of veinlike vessels that returns the fluid to the bloodstream – It acts like rain gutters carrying excess fluid away • Once the fluid is in the lymphatic system it is called a lymph. – Consists of water and dissolved materials Lymphatic System • As the fluid flows through lymphatic system it passes through knobs called lymph nodes. • Lymph nodes filter lymph, trapping bacteria and other disease causing microorganisms in the fluid. • When the body is fighting disease the nodes become enlarged. – This is called swollen glands. Section 4 • Intergrading Health: Cardiovascular Health Cardiovascular Diseases • Diseases of the cardiovascular system include artherosclerosis and hypertension • Artherosclerosis is a condition in which an artery wall thickens as a result of fatty buildup. – One substance is cholesterol • A heart attack occurs when blood flow to part of the heart is blocked – Cells die during an attack, so there is permanent damage Cardiovascular Disease • Hypertension, or high blood pressure, is the blood pressure is higher than normal. – This makes the heart work harder than it has to • Hypertension and artherosclerosis are closely related diseases. Keeping Healthy • To stay healthy people should: – Exercise and diet – Avoid smoking – Eat a balanced diet low in saturated fats, trans fats, cholesterol, and sodium.