Thoracic Cavity and Respiration
advertisement

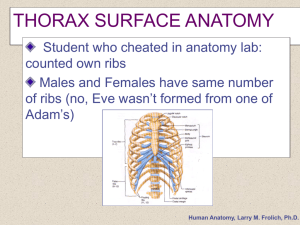
Thoracic Cavity and Respiration • • • • • Alveoli Respiratory Tree Lungs Diaphragm Intercostal Muscles Larry M. Frolich, Human Anatomy, Respiratory Function Alveoli • • • • • Key to lung function Where O2 enters blood, CO2 leaves blood Every alveoli is capillary covered sac Lining of sac is squamous epithelium Also cuboidal epithelial cells that secret surfactant (keeps surfaces from sticking) and cilia (to move mucous and particles up respiratory tree Larry M. Frolich, Human Anatomy, Respiratory Function Respiratory Tree (how does air get to alveoli?) • Branching pattern – – – – – Trachea Primary bronchi (left, right) Secondary bronchi (each lobe) Tertiary bronchi, bronchioles Alveoli • Vessels accompany respiratory tree to alveoli Larry M. Frolich, Human Anatomy, Respiratory Function Larry M. Frolich, Human Anatomy, Respiratory Function LUNGS • Located in Pleural Cavities • Lateral to Mediastinum • Location – Apex posterior to clavicle – Base lays on Diaphragm Pg 618 – Costal Surface = Ant, Lat, Post surfaces contact wall of chest cavity • Root - all vessels, nerves enter each lung – – – – – 2 Pulmonary Veins = carries O2 blood from each lung to heart 1 Pulmonary Artery = carries De-O2 blood to each lung Primary Bronchi Nerves –Lymph Vessels Larry M. Frolich, Human Anatomy, Respiratory Function LOBES OF LUNGS • Left Lung = 2 lobes – – – – Upper Lower Oblique Fissure Cardiac Notch • Right Lung = 3 lobes Pg 622 – – – – – Upper Middle Lower Oblique fissure Horizontal fissure Larry M. Frolich, Human Anatomy, Respiratory Function Specific Location of Lungs • Right Lung – – – – – – 1” above Rib 1 Crosses Costal Cartilage 6 Midclavicular at Rib 6 Midaxillary at Rib 8 Vertebral Border at Rib 10 Inferior border 2 rib widths above diaphragm • Left Lung – 1” above Rib 1 – Deep to Manubroclavicular joint – Midsternally to Rib 4 – Jogs to left, continues to Rib 6 – Midaxillary Rib 8 – Vertebral Border at Rib 10 Larry M. Frolich, Human Anatomy, Respiratory Function Action of the Diaphragm • Primary muscle of respiration (involuntary) – Contraction during inspiration • Increases volume of thoracic cavity • Decreases pressure of thoracic cavity • Air moves into lungs (highlow pressure) • Forced contraction (voluntary) – Used for defecation, urination, labor • Increases pressure in abdominal cavity • Pushes on abdominal organs to move contents out Larry M. Frolich, Human Anatomy, Respiratory Function Anatomy of the Diaphragm • Skeletal Muscle • Dome-shaped (relaxed) • Divides thoracic & abdominal cavities • Attachments – Origin: Inferior Internal rib cage – Insertion: Central tendon Superior View • Innervated by right + left PHRENIC Nerves Pg 288 Larry M. Frolich, Human Anatomy, Respiratory Function INTERCOSTAL MUSCLES • Lift ribs to expand chest cavity for inspiration • Three layers Larry M. Frolich, Human Anatomy, Respiratory Function