Electron Configuration
advertisement

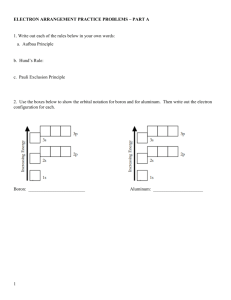
Electron Configuration • Objective – Today I will be able to: • Calculate the electron configuration for elements on the periodic table • Evaluation/ Assessment – Informal assessment – student responses when reviewing electron configuration problems. Listening to group interactions on practice sheets – Formal Assessment – collecting and analyzing responses to electron configuration worksheet 2 Lesson Sequence • Warm – Up • Explain: How to write electron configurations • Elaborate: write electron configurations with a partner for questions 1-18 • Evaluate: review the questions as a class (informal assessment) • Explain: electron configurations in 3d orbitals and Aufbau diagrams • Elaborate: Students will complete 19-36 on electron configuration WS with a partner • Evaluate: review the questions as a class (informal assessment) • Explain: abbreviated electron configurations • Elaborate: Students will add a column to the WS and repeat write the abbreviated configuration • Evaluate: Abbreviated configurations will be reviewed as a class (informal assessment) • Exit Ticket Warm - Up • According to the modern atomic theory (Schrodinger’s model) where are the electrons located? • According to the Bohr model, where are the electrons located? Objective • Today I will be able to: – Calculate the electron configuration for elements on the periodic table Homework • Have a great afternoon! Agenda • • • • Warm – Up Electron Configuration Notes Electron Configuration Practice Exit Ticket Electron Configuration Label and color your periodic table to match the periodic table on the next slide… Electron Configuration n 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 p-block s-block d-block n-1 f-block n-2 Electron Configuration • “address” of where each individual electron is located in an atom 2 1s Number of electrons in the orbital Energy Level (n) Orbital (Principal) Energy Level • Symbol = n • As atoms get bigger, there are more electrons, therefore more energy levels • Fill the lowest energy levels first (ground state) • Within each energy level, we have one or more sublevels • These sublevels are called orbitals Orbitals • Based on modern model of atom • 3-D region around the nucleus indicating the probable location of the electron • 4 types of orbital (low high energy) – s –p –d –f Orbital Shapes Orbitals cont. • Each sublevel can hold a specific amount of electrons – S=2 – P=6 – D=10 – F=14 Now we can put these ideas together and write an electron configuration for an atom… Examples • Sodium (Na) – Has 11 electrons (when neutral) – Electron Configuration: • 1s22s22p63s1 • Cobalt (Co) – Has 27 electrons (when neutral) – Electron Configuration • 1s22s22p63s23p64s23d7 Warm-Up • Complete the electron configuration worksheet you received yesterday • Don’t forget to use your periodic table! Objective • Today I will be able to: – Calculate the electron configuration for elements on the periodic table Homework • Complete the Electron Configuration Practice Worksheet Agenda • • • • • Warm-Up Group Practice: Using the Aufbau Diagram Practice 4-5 Abbreviated Electron Configurations Exit Ticket Group Practice • Lets try Hydrogen through Neon • DO NOT WRITE ANY OF THIS DOWN • Just follow along and participate as I show you how to use the orbital diagram and how to write electron configurations Aufbau Diagram • Instead of using the periodic table as a road map, you can use the aufbau diagram to determine the order that the electrons occupy the different energy levels • Electrons fill the lowest energy orbitals first Aufbau Diagram Why does 4s come before 3d? • 3d is of slightly higher energy than 4s, but 4s is further from the nucleus • It takes less energy for a 3d electron to form pairs then a 4s electron Complete Electron Configuration Practice Worksheet 4-5 Just do the evens! Abbreviated Electron Configuration • Scientists are lazy • We need a shorthand way to represent electron configuration • How do we do this? – Noble Gas Configuration Noble Gas Configuration • The last column on the periodic table is referred to as the noble gases • To write in abbreviated configuration: – Find the last noble gas within the configuration – Write the symbol – Write the remaining configuration • Example – Ca - 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 • Noble Gas Configuration = [Ar] 4s2 Noble Gas Configuration • Writing Noble Gas Configurations for ions is a little bit different • Must account for an electron being gained or lost – Chlorine Ion = Cl-1 • [Ne] 3s2 3p6 – Sodium Ion = Na+1 • [He] 2s2 2p6 Electron Configuration Practice Worksheet Complete the worksheet for homework! Exit Ticket • Write the electron configuration for sulfur