Dermal Layers - Cloudfront.net
advertisement

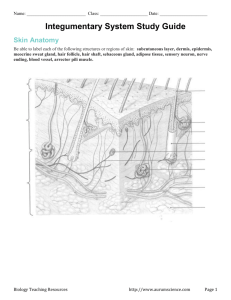
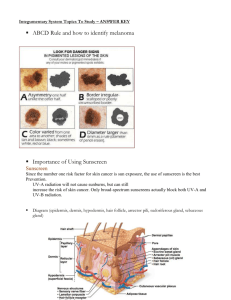
Dermal Layers Chapter 6 Dermal Layers Skin is a m________ membrane and is made of epithelial tissue and c_________ e__________ connective tissue. epithelial The e______ layer is called the e__________. epidermis The c_________ connective tissue layer is called the d________. dermis Below these two layers is another layer which is not part of the skin, but is still vital to the skin’s function. This layer is called the subcutaneous s_______ ____ layer, or the h___________. hypodermis This layer consists of adipose tissue. Epidermis • Outermost layer of the skin • 4 or 5 layers – Stratum corneum – (Stratum lucidum) – Stratum granulosum – Stratum spinosum – Stratum basale • Stratified squamous epithelial tissue – Avascular Epidermis Epidermis • Functions – Prevents water loss (keratinized cells of stratum corneum) – Keeps out disease-causing microorganisms Stratum Basale • • • • Deepest epidermal layer Closest to dermis 1-cell thick Cell division – Pushes older cells toward surface of the skin • Basement membrane is deep to stratum basale Stratum Spinosum • • • • • Superficial to stratum basale Several cells thick Less cell divison Flattened/irregular cells Spinelike projections from cells Stratum Germinativum • Stratum basale + Stratum spinosum = Stratum germinativum • Growing layers – Where cell division occurs Stratum Granulosum • Superficial to stratum spinosum • Very thin, 2-3 cells thick • As cells move up from the stratum basale, they die and become flatter • Keratinization – Older cells harden – Keratin protein Stratum Lucidum • Bonus layer • Thickened skin of palms and soles Stratum Corneum • Most superficial layer of epidermis • Many layers of tough, tightly packed dead epidermal cells – Thickest layer of the epidermis (20-30 cells thick) • Dead cells completely filled with keratin – Water resistant • 30-40 days from creation in stratum basale until flake off at stratum corneum Epidermis Cells of the Epidermis • Stem cells – undifferentiated cells found only in stratum basale • Keratinocytes – cells that make keratin (most cells in epidermis) • Melanocytes – make melanin, found only in stratum basale • Merkel cells – touch receptors, attached to nerve cells • Dentritic cells (Langerhans cells) – macrophages that guard against foreign microbes/pathogens, alert immune system Dermis • Deep to epidermis • Binds epidermis to underlying tissues • Blood vessels in the dermis supply nutrients to all layers of the skin • Dense connective tissue • 2 layers – Papillary layer – Reticular layer Papillary Layer • Areolar connective tissue • Lots of blood vessels • Dermal papillae – Capillary loops – Sensory cells – Fingerprints Reticular Layer • Dense connective tissue • Stretch marks – Dermal tearing Hypodermis • Subcutaneous layer – Sub- = below – Cut- = skin • Deep to the dermis • Adipose, loose connective tissues – Insulation – Major blood vessels • Infants/elderly have less, more sensitive to cold HOMEWORK • pg. 116 #1-2 • pg. 117 #1-3 • Daily Quiz #12 tomorrow!