Writing the Constitution - Constitutional Convention 55
advertisement

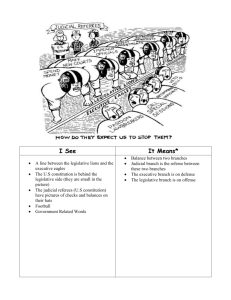
Writing the Constitution Constitutional Convention 55 delegates who created Articles of Confederation meet in Philadelphia in May 1787 to discuss how they could change or improve Articles of Confederation Delegates from every state except Rhode Island were present; they were worried that any changes would leave them with less power George Washington - most respected – elected President of Convention Ben Franklin oldest delegate there (81) James Madison , 36, has been doing a lot of research on history, politics and commerce. Is most prepared delegate. JAMES MADISON Madison recorded proceedings of convention to share with future Americans. Refused to publish when he was alive; was published 4 years after his death in 1840 . MADISON FAMILY CEMETARY Alexander Hamilton, NY, favored strong, central government Talks were kept secret (even though hot, windows closed) so delegates could explore every issue without pressure from public Delegates are hopelessly divided . They cannot agree on how to fix Articles, so they decide to abandon the Articles and write a new constitution Virginia makes a proposal known as the Virginia Plan . Drafted by Edmund Randolph and James Madison which consisted of: Edmund Randolph James Madison Three braches of government: the legislative, executive and judicial branches 1. Legislative Branch would be responsible for writing and passing laws a. Legislative Branch would have two houses b. The number of seats/members each state would have in Congress would depend on that state’s population (small states disliked this) 2. Executive Branch - enforce /carry out laws passed by Congress • President: Leader of the country and Commander in Chief of the military. • Vice President: President of the Senate and becomes President if the President is unable to serve. • Departments: Department heads advise the President on policy issues and help execute those policies. • Executive Agencies: Makes regulations to help implement laws. • Independent Agencies: Help carry out policy or provide special services 3. of Judicial courts carried out Branch - system to decide if laws are fairly U.S. Supreme Court - 2013 Small states object Virginia Plan to Small states feared large states could easily outvote them with more members in the houses. William Patterson of New Jersey presents small states’ New Jersey Plan which consists of: William Patterson Three braches of government just like the Virginia Plan : the legislative, executive and judicial branches Difference: legislature to have only one house with each state having one representative in legislature. Similarity: Both plans have presented three branches of gov’t.