Chapter 16 Section 4
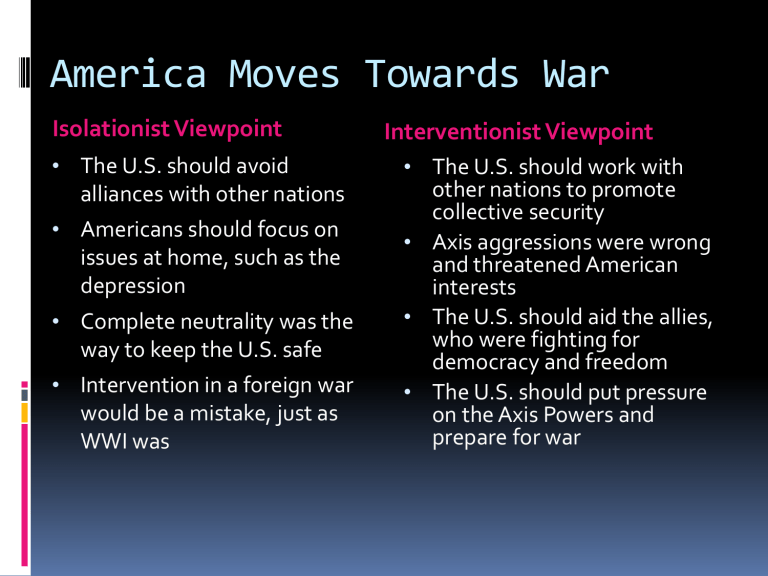
America Moves Towards War
•
•
•
•
Isolationist Viewpoint
The U.S. should avoid alliances with other nations
Americans should focus on issues at home, such as the depression
Complete neutrality was the way to keep the U.S. safe
Intervention in a foreign war would be a mistake, just as
WWI was
Interventionist Viewpoint
•
•
•
• The U.S. should work with other nations to promote collective security
Axis aggressions were wrong and threatened American interests
The U.S. should aid the allies, who were fighting for democracy and freedom
The U.S. should put pressure on the Axis Powers and prepare for war
Moving Cautiously Away from Neutrality
FDR issued an official proclamation of neutrality
On Sept. 8, after 6 weeks of debates, FDR persuades Congress to pass “cash-and-carry”
FDR argues we must help France & Britain to defeat Hitler to keep us out of the war
1940, FDR tries to provide Britain “all aid short of war”
The Lend-Lease Plan
•
•
•
•
This was a economic declaration of war against
Germany & the Axis
FDR tells nation if Britain fall, Axis powers are free to conquer the world
– U.S. must become the “arsenal of democracy”
By late 1940, Britain has no more cash to buy
U.S. arms
1941 Lend-Lease Act – U.S. to lend or lease supplies for defense
– lend weapons & other supplies to any country whose defense was vital to the U.S.
Lend Lease Aid Given by the
United States
Year
1941 (March –
December)
1942
1943
1944
1945 (January –
August)
Total
British
$1.1 billion
$4.8 billion
$9.0 billion
$10.8 billion
$4.4 billion
Soviet Union
$20.0 million
$1.4 billion
$2.4 billion
$4.1 billion
$2.8 billion
$30.1 billion $10.7 billion
The Atlantic Charter
August, FDR & Churchill meet and issues the
Atlantic Charter – A joint declaration of war aims
Fight Europe first then Pacific
Charter is basis of “A Declaration of the
United Nations” or Allies
Allies – nations that fight the Axis powers; 26 nations sign the Declaration
Shoot on Sight
•
•
•
•
German U-boats fire on U.S. ships
Fall of 1941, USS Reuben
James is sunk killing more than 100 sailors
FDR orders the navy to shoot
U-boats on sight
U-boat attacks lead Senate to repeal ban on arming merchant ships
Japan’s Ambitions in the Pacific
•
•
•
• Japan had dreams of creating a vast colonial empire
July, 1941, Japan seizes
French bases in
Indochina
– U.S. cut off steel & oil to
Japan
Japan needs oil from U.S. or must take Dutch East
Indies oil fields
Japan started peace talks
Peace Talks are Questioned
1941, U.S. breaks Japanese codes; learns
Japan planning to attack the U.S.
Peace talks with Japan last about 1 month
November 5, Tojo starts to plan for the attack on Pearl Harbor
December 6, Japanese envoy instructed to reject all U.S. proposals
The Attack on Pearl Harbor
December 7, 1941, the
Japanese attacks Pearl
Harbor
2,403 Americans killed;
1,178 wounded
Over 300 aircraft, 21 ships destroyed or damaged
Attack on Pearl Harbor
Reaction to Pearl Harbor
December 8, Congress approves FDR’s request for declaration of war against Japan
December 11, Germany & Italy declared war on the U.S.
The U.S. was unprepared to fight in both the
Atlantic & Pacific Oceans
Chapter 16 Section 4 Quiz
•
1.)What act allowed the U.S. to sell weapons to nations at war as long as they paid cash?
• a.) Selective Services Act
• b.) Kellogg-Briand Act
• c.) Neutrality Act
•
6.) What form of media was used by Pres.
Roosevelt to reveal America was at war?
• a.) Television
• b.) Magazine
• c.) Radio
• 2.) Why did the Americans start selling weapons to nations at war?
• a.) Pres. Roosevelt thought it would help France and Great Britain
• b.) Pres. Roosevelt thought it would bring
America out of a depression
• c.) Pres. Roosevelt wanted America to get involved in the war
• 3.) What countries formed the Axis power?
• a.) Germany, Italy and Japan
• b.) Germany, France and Italy
• c.) U.S., France and Great Britain
• 4.) What was the name of the act that created the draft?
• a.) Selective Services Act
• b.) Neutrality Act
• c.) War Draft Act
• 5.) What president had three terms?
• a.) Pres. Hoover
• b.) Pres. Franklin Roosevelt
• c.) Pres. Theodore Roosevelt
• 7.) What act was passed that allowed America to lend money and weapons to Great Britain?
• a.) Neutrality Act
• b.) Lend-Lease Act
• c.) Weapons Act of 1914
• 8.) Which country broke their pledge and attacked when they promised they wouldn’t?
• a.) Germany attacked the Soviet Union
• b.) The Soviet Union attacked Germany
• c.) They both attacked each other
•
9.) What future enemy did America send lendlease weapons to in WWII?
• a.) Germany
• b.) Italy
• c.) Russia
• 10.) What was the name of German submarines that attacked at night?
• a.) Wolf Packs
• b.) Pack attackers
• c.) Stealth Bombers
Chapter 16 Section 4 Quiz
Con’t.
•
16.) What base did the Japanese attack?
•
11.) What new technology helped Americans track down German submarines?
• a.) Pearl Harbor
• a.) Radar and Sonar • b.) Nuremburg
• b.) Television • c.) Guantanamo Bay
• c.) Telescope
• 12.) What was the name of the agreement between 26 nations where the nations agreed to military cooperation?
• a.) United Nations
• b.) United Arab Emirates
• c.) Allied Nations
•
17.) How many Americans died during the attack of Pearl Harbor?
• a.) 2403
• b.) 24, 030
• c.) 243
•
13.) When Japan attacked East Asia, who was the only nation that could stop them?
• a.) Great Britain
• b.) France
• c.) United States
•
14.) What did the U.S. do to Japan first?
• a.) Cut off trade
• b.) Invaded their nation
• c.) Bombed them
• 18.) How many ships were sunk during the attack of Pearl Harbor?
• a.) 21 ships
• b.) 12 ships
• c.) 112 ships
•
19.) How many ai
• rcraft were destroyed during the attack of Pearl
Harbor?
• a.) over 300
• b.) over 3000
• c.) Under 100
• 15.) What year did the Japanese attack
Americans?
• a.) 1941
• b.) 1914
• c.) 1951
•
20.) Give the name of the speech by Pres.
Roosevelt in response to Pearl Harbor?
• a.) I Have a Dream
• b.) The Fourteen Points bulletin
• c.) Today is a Day That Will Live in Infamy







