February 23, 2009
Objective: Discuss the effects of
nondisjunction
Drill:
What is crossing over? What phase of
meiosis does it occur?
Nondisjunction
Review: What is a mutation?
Mutation: A change in the nucleotide
sequence of DNA
– A single nucleotide change can have
serious effects
Chromosomal mutation
A chromosomal mutation involves a change
in the structure or number of chromosomes
4 types of chromosomal mutations:
– Deletion: loss of all or part of a
chromosome
– Duplication: extra copy of all or part of a
chromosome
– Inversion: reverses the direction of parts
of a chromosome
– Translocation: part of one chromosome
breaks off and attaches to another
chromosome
Nondisjunction
Other types of chromosomal
mutations alter the number of
chromosomes found in the cell.
Nondisjunction: The failure of
homologous chromosomes or
sister chromatids to separate
during meiosis.
– Produces gametes that
have too many or too few
chromosomes
Normal meiosis
Nondisjunction
Disorders due to Nondisjunction
In humans, a zygote with
45 chromosomes has only
one copy of a particular
chromosome
monosomy
In humans, a zygote with
47 chromosomes has three
copies of a particular
chromosome
trisomy
– Example Down syndrome
(trisomy 21)
Nondisjunction in the Sex
Chromosomes
Nondisjunction can also affect the sex chromosomes,
where there can be too many or too few X or Y
chromosomes (XX- normal female, XY-normal male)
Examples of disorders:
– XXY (Klinefelter’s syndrome)
– XO (Turner’s syndrome)
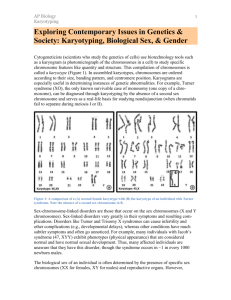
Karyotype
Karyotype: a picture of chromosomes in a dividing cell that
are arranged in pairs by size.
– First 22 pairs are autosomes
– Last pair are the sex chromosomes
Karyotype A
* Normal male
Karyotype B
* Turner’s syndrome
* Only 1 sex chromosome (X)XO
* Webbed neck, short
stature, and infertility
* Female
Karyotype C
* Cri du chat syndrome
* Deletion of short arm
of chromosome 5
* Distinctive cry, low
birth weight, respiratory
problems, may have a
shortened lifespan
X
Y
* Female
Karyotype D
* Klinefelter’s
syndrome
* 2 X chromosomes
and 1 Y (XXY)
* Tall, sterile, feminine
characteristics, sometimes
mentally retarded
* Male
Karyotype E
* Normal female
Karyotype F
* Down syndrome
* 3 copies of
chromosome 21 (Trisomy
21)
* Mental retardation,
characteristic facial
features, short stature,
and heart defects
* Male