Earth*s Environmental Systems
advertisement

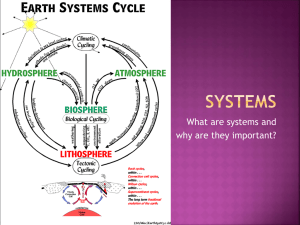
Earth’s Environmental Systems Chapter 3 – Environmental Science Central Case After reading the Central Case, who do you think is responsible for the Gulf of Mexico’s dead zone? What do you think is the best way to go about solving the problem? Section 1 – What properties of matter are most important to environmental systems? Chemistry is CENTRAL in understanding what environmental problems are occurring and in how to correct them. We begin this chapter with an introduction to basic chemistry…. Section 1 – What properties of matter are most important to environmental systems? Matter – Mass – Volume - Atoms – Element - Section 1 – What properties of matter are most important to environmental systems? Parts of the atom Nucleus – Protons – Atomic Number – Neutrons – Electron Cloud Electrons Section 1 – What properties of matter are most important to environmental systems? Bonding Covalent bonds – Ionic bonds Section 1 – What properties of matter are most important to environmental systems? Molecules and Compounds Molecules Compounds – Organic molecules – Inorganic molecules – Hydrocarbons – Section 1 – What properties of matter are most important to environmental systems? Solutions Section 1 – What properties of matter are most important to environmental systems? Macromolecules Proteins Hormones Enzymes Nucleic Acids Carbohydrates Lipids Section 1 – What properties of matter are most important to environmental systems? Water Properties of water Cohesion Adhesion Resistance to temperature change Ice density Universal solvent Section 1 – What properties of matter are most important to environmental systems? Acids, bases, and pH Acid Base pH Section 2- What types of systems play roles in environmental science? System Inputs Outputs Earth’s systems Inputs Outputs Section 2- What types of systems play roles in environmental science? Feedback loops Negative feedback loops Positive feedback loops Section 2- What types of systems play roles in environmental science? Earth’s “spheres” Geosphere Lithosphere Biosphere Atmosphere Hydrosphere Section 3 – What are the characteristics of the Earth’s spheres? The Geosphere 3 parts Crust Mantle Core Plate tectonics Section 3 – What are the characteristics of the Earth’s spheres? Plate Boundaries Divergent plate boundaries Transform plate boundaries Convergent plate boundaries Section 3 – What are the characteristics of the Earth’s spheres? Biosphere Atmosphere Layers Troposphere Stratosphere Mesosphere Thermosphere Section 3 – What are the characteristics of the Earth’s spheres? Hydrosphere Earth’s water The water cycle Evaporation Transpiration Precipitation Condensation Section 3 – What are the characteristics of the Earth’s spheres? Hydrosphere Groundwater Aquifers Section 3 – What are the characteristics of the Earth’s spheres? Nutrient cycling Law of Conservation of Matter Nutrients Biogeochemical cycles Section 3 – What are the characteristics of the Earth’s spheres? The Carbon Cycle Section 3 – What are the characteristics of the Earth’s spheres? The Phosphorus Cycle Section 3 – What are the characteristics of the Earth’s spheres? The Nitrogen Cycle