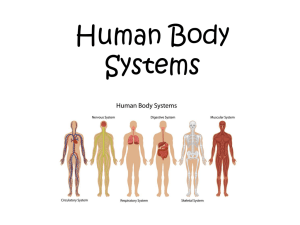
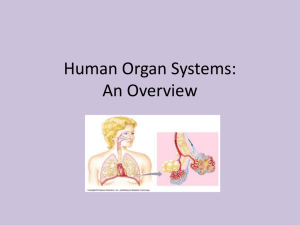
Organs Of The Bodies
advertisement

A system of organs and tissues, including the heart, blood, blood vessels, lymph, lymphatic vessels, and lymph glands, involved in circulating blood and lymph through the body. fist-sized, muscular organ that pumps blood through the body It is a smooth straight muscle. The Pulmonary! It’s responsible for pumping the blood to every cell in the body. It is also responsible for pumping blood to the lungs, where the blood gives up carbon dioxide and takes on oxygen. The Systemic! The blood leaves the heart through the aorta, goes to all the organs of the body through the systemic arteries. Then returns to the heart through the systemic veins. There are three types of vessels arteries, veins, and capillaries. Arteries-a blood vessel that conveys blood from the heart to any part of the body. veins-tubes conveying blood from various parts of the body to the heart. Capillaries-smallest of blood vessels. They serve to distribute oxygenated blood from arteries to the tissues of the body. Also to feed deoxygenated blood from the tissues back into the veins. Valvular stenosis is the result of diseases such as rheumatic fever, that causes the opening through the valve to become so narrow that blood can flow through difficulty. Atherosclerosis is a degenerative disease that results in narrowing of the coronary arteries. This is caused by fatty deposits, most notably cholesterol, on the interior walls of the coronary arteries. Valvular stenosis is the result of diseases such as rheumatic fever, that causes the opening through the valve to become so narrow that blood can flow through difficulty. Atherosclerosis is a degenerative disease that results in narrowing of the coronary arteries. This is caused by fatty deposits, most notably cholesterol, on the interior walls of the coronary arteries. Stained Cross sections through coronary artery (left) and a coronary artery with lipid deposits in its walls (right). Heart transplants started to take place in1967 Also started using Cyclosporine known as a drug to help fight rejections in 1982. Coronary artery disease that is a condition and especially one caused by atherosclerosis that reduces the blood flow through the coronary arteries to the heart muscle and typically results in chest pain or heart damage “Father of Cardiovascular Medicine” receiving his doctorate for studding medicine in 1602. Studied the mechanics of blood flow in the human body. The group of organs that break down food and absorb the nutrients used by the body for fuel. The organs in the digestive system, in the order in which food travels through them, are: Pregastric Digestion Mouth Esophagus Stomach Small Intestine Large Intestine Rectum Anus first portion of the alimentary canal that receives food and saliva. The lovely Mouth It is the muscular passage connecting the mouth or pharynx with the stomach It’s an expanded section of the digestive tube between the esophagus and small intestine. It’s longest section of the digestive tube and consists of three segments forming a passage from the pylorus to the large intestine such as Duodenum, Jejunum, Ileum. The average length of an average humans small intestines are up to 6-7 meters. the lower part of the alimentary canal, extending from the pylorus to the anus. Within the large intestine, three major segments are recognized such for the cecum, colon, and the rectum. stores solid waste until it leaves the body through the anus. The liver serves wide variety It’s the alargest glandofinbody the functions, including detoxifying body and performs an astonishingly large number of tasks that impact all body systems. Small lobe of liver- Metabolize and store carbohydrates, which are used as the source for the sugar (glucose) in blood that red blood cells and the brain use. Large lobe of liverManufacture (synthesize) proteins, including albumin (to help maintain the volume of blood) and blood clotting factors. elongated organ, light tan or pinkish in color, that lies in close proximity to the duodenum. Endocrine System! The system of glands that produce endocrine secretions that help to control bodily metabolic activity. Functions of the system! Endocrine system is a collection of 'glands' that produce hormones. These hormones are very important for regulating metabolism process, growth of the body and sexual development. The glands release the hormones into the blood stream and are transported to the various cells and body parts. When the hormones reach the target site, they bind to the receptor cells with a lock and key mechanism. Problems that may occur! Diabetes, Growth Disorders, Osteoporosis, Polycystic Ovary Syndrome, and also Thyroid Disorders. Facts! consists of a collection of small glands that regulates a number of vital functions of our body. There are six major glands that form the endocrine system in the human body. They are the hypothalamus, pituitary, adrenal, thyroid, pineal and reproductive glands or gonads It’s integral part of the substance of the brain. A small cone-shaped structure, it projects downward, ending in the pituitary (infundibular) stalk, a tubular connection to the pituitary gland. The main endocrine gland. It is a small structure in the head and is called the master gland because it produces hormones that control other glands and many body functions including growth. The pituitary consists of the anterior and posterior pituitary. One of a pair of small glands, each of which sits on top of one of the kidneys. The adrenal is made up of an outer wall (the cortex) and an inner portion (the medulla). The designating or of a large ductless gland lying in front and on either side of the trachea and secreting the hormone thyroxin, which regulates body growth and metabolism: the malfunctioning or congenital absence of this gland can cause goiter, cretinism. A reproductive gland (ovary or testis) that produces germ cells (gametes). Facts! As the body's chemical messengers, hormones transfer information and instructions from one set of cells to another. The Hormone levels can be influenced by factors such as stress, infection, and changes in the balance of fluid and minerals in blood. skin and the related structures that cover and protect the body. The human integumentary system is composed of the skin, and includes glands, hair, and nails. regulates its temperature, and receives sensory information from the environment. Largest organ in the body. It is 15% of the body weight. contained in the outer epidermis layer, and the dermis contains the nerve endings, blood vessels, and elastic fibers. It controls temperature and water balance. The sweat evaporates, cooling the body. Skin glands produce sweat to cool the body when it's too hot. Alopecia Areata, Psoriasis, Warts, Dermatitis, Athletes Foot. You can also have skin rashes. All these can form any where on your body. Hair follicles are lined with cells that synthesize the proteins that form hair. A sebaceous gland that secretes the oily coating of the hair shaft, capillary bed, nerve ending and small muscle are associated with each hair follicle. Hair, scales, feathers, claws, horns, and nails are animal structures derived from skin. The hair shaft extends above the skin surface, the hair root extends from the surface to the base or hair bulb. include protection, regulation of body temperature, sensory reception, water balance, synthesis of vitamins and hormones, and absorption of materials. An Acidic secretions from skin glands also retard the growth of fungi. Sensory receptors in the skin include those for pain, pressure (touch), and temperature. Skin cells synthesize melanin and carotenes, which give the skin its color. The skin also assists in the synthesis of vitamin D. Children lacking sufficient vitamin D develop bone abnormalities known as rickets. The skin is selectively soluble to fatsoluble substances such as vitamins A, D,E,AND K, as well as steroid hormones such as estrogen. Substances like this enter the bloodstream through the capillary networks in the skin. Muscles! A tissue composed of fibers capable of contracting to effect bodily movement. Cardiac Muscle Skeletal Muscle and visceral Muscle! These are the three very important muscles of the bodies. pump the blood to the different parts of the body. made up of cardiac tissue and its job is to pump the blood. Skeletal Muscle! Skeletal Muscle Skeletal muscle, which is attached to bones by tendons, is associated with the body's voluntary movements. Skeletal muscle is striated muscle. Unlike cardiac muscle, the cells are not branched. Visceral Muscle! Visceral muscle, is found in various parts of the body such as the arteries, the bladder, the digestive tract, as well as in many other organs. very specialized tissue that has both the ability to contract and the ability to conduct electrical impulses. Smooth Involuntary (Smooth) Muscle Tissue Muscle diseases! Myopathy, Chronic fatigue syndrome, Fibromyalgia, Muscular dysophy, Dermatomyositis, Polymyositis, Rhabdomyolysis, and Compartment syndrome Excretory System! The main organ of the urinary system is the kidney. The kidney performs dual tasks of filtering out wastes and purifying blood, The main function of the kidneys is to filter out wastes. Other organs in the urinary system include; the urinary bladder, the ureters, and the urethra. Immune System! The body’s main defense against all foreign substances. Without the immune system, the human body would die immediately from all the bacteria, which is the skin and more. Integumentary System! It’s mainly skin. Also offers protection to the underlying layers from the sun. serves in body temperature regulation. Nerve System! This masters the controlling and communicating system of the body. Every thought, action, and emotion reflects is the action of this system. Communicating of electrical signals, that are rapid, specific, and usually cause almost immediate responses. Reproductive System! male’s reproductive system is to manufacture sperm and deliver them to the female’s reproductive tract where fertilization may occur. female’s reproductive system involved in producing eggs in conceiving by carrying babies when the sperm of the male has been transferred over. Resperatory System! supplies the body with oxygen, and the air is inhaled through the nose or mouth. travels into the pharynx, passes through the larynx, and down the trachea then trachea branch and air reaches the lungs where it will diffuse into the blood via the alveoli. Skeletal System! system that supports us and gives us our shape. Cartilage is largely composed of water and contains no nerves or blood vessels. Bone provide other important functions for us other than giving shape to the body. THE END!!! I have learned so much within each system. All of them I know a lot more info. on them. That was my power point for all the 10 Systems in the body!