Natural Selection
advertisement

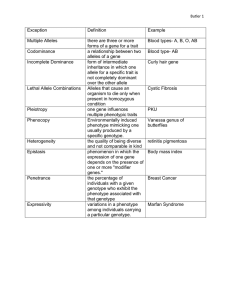
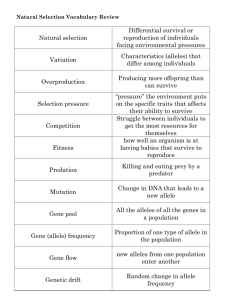
More Natural Selection Info • Describe Natural Selection including the 3 things needed for it to occur • Define adaptation • List and describe five examples of natural and artificial selection Natural Selection • 1. There is competition for limited resources • 2. There is natural variation (behavior, traits) • 3. The variation is inherited • The outcome of variation in heritable traits that affect survival and reproduction Adaptation • The consequence of natural selection is adaptation • Adaptation: some heritable aspect of form, function, behavior or development that improves the odds for surviving or reproducing in a given environment. Artificial Selection http://www.gly.uga.edu/railsback/1122/1122Dogs.jpeg Artificial Selection http://www.bio.miami.edu/dana/160/artificialselection.jpg Natural Selection http://www.museums.org.za/bio/insects/cockroaches/ http://home-supplies.best-emporium.com/cat-125/Cleaning-Sanitation/Cleaning-Chemicals/Rodenticide-Insecticides Natural Selection Staphylococcus aureus: antibiotic resistance Population Information • Define population • Describe the basis and source of heritable variation within a population • If there are heritable variations within a population, when does evolution not occur? How would you define POPULATION? • all organisms that constitute a specific group (species) in a specific habitat/environment Review of Genetics • • • • • • Cells are the basic unit of life Cells have DNA DNA contains genes Genes code for proteins, usually enzymes Genes that differ slightly are called alleles Different alleles make different forms of the same enzyme • These enzymes determine an organisms phenotype • Alleles can be inherited Population Genetics • Gene pool: all the alleles of all the genes in all the individuals in a population • Each organism will have a unique combination of alleles and, therefore, a unique phenotype • Unique combination of alleles – – – – – Mutation Crossing-over Independent assortment Fertilization Change in chromosome number or structure Population Genetics • Allele frequency: relative proportion of one allele for one gene • Evolution: change in the allele frequency within a population How does Evolution Occur? • Describe how evolution can occur – – – – – Mutation No gene flow Small population size Non-random mating Natural selection • Disruptive • Directional • Stabilizing Violation of equilibrium: mutation • Mutations are rare (1/100,000 gametes) • Mutations can be: – Helpful • Depends on environment – Neutral – Harmful • Lethal mutation Gene Flow • Individuals, and their alleles, move into and out of populations • The physical flow counters the effects of: – mutation – natural selection – genetic drift Small Population Size • Hypothesis: how often will you get tails? • Flip a coin ten times: – # heads – # tails • Everyone flip a coin ten times: – # heads – # tails • Discuss the difference between 10 and 200 events: sampling error Small Population • Random events can have drastic effects on the allele frequencies in a small population: Genetic Drift • Two examples: – Founder effect – Bottleneck phenotypes of original population Founder Effect A seabird carries a few seeds, stuck to its feathers, from the mainland to a remote oceanic island. phenotype of island population Bottleneck Effect: Elephant seal Reduction of a population’s gene pool produced when a few members survive the widespread elimination of a species. Año Nuevo State Park http://www.aad.gov.au/default.asp?casid=1239 Non-random mating • Do humans mate randomly? • How do people pick a mate? Non-random mating: 3 types • Assortive – shifts genotype frequency – Organisms choose a mate with the same genotype as themselves. – Organisms choose a mate with a different genotype from themselves. • Self-fertilization – shifts genotype frequency – Organism mates with itself • Sexual selection –shifts allele frequency – Some genotypes mate more successfully than others Assortive Mating Self-fertilization Sexual selection http://subjunctive.net/photoblog/2003/peacock-wooing-peahen.jpg Natural Selection • Evolution due to natural selection results from unequal reproduction of various alleles • Natural selection acts on phenotypes but affects genotypes • Adaptations help an individual survive and reproduce Agents of Natural Selection • Abiotic factors – Climate – Geology – Other non-living factors • Biotic factors – Competition • Food, Shelter, Mating – Interspecies Interactions • Predation – Sexual Selection Number of individuals Number of individuals Directional Selection Range of values at time 1 Range of values at time 2 Number of individuals 3 Modes of Natural Selection: Range of values at time 3 Number of individuals Number of individuals Stabilizing Selection Range of values at time 1 Range of values at time 2 Number of individuals 3 Modes of Natural Selection: Range of values at time 3 Number of individuals Number of individuals Disruptive Selection Range of values at time 1 Range of values at time 2 Number of individuals 3 Modes of Natural Selection: Range of values at time 3