Cells - Images
advertisement

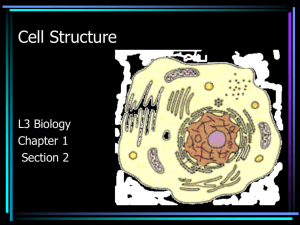
Cells What is a cell? • Structural and functional unit of all organisms. • Some can work independently (on their own) to carry out all of life’s processes. • Some cells have organelles, some don’t. Organelles are small, specialized cellular subunits separated from the rest of the cell by membranes. • Organelles help a cell to move molecules, create and store energy, and store information. Important People and Cells • Robert Hooke (1665) – coined the word “cell” to describe what he saw when looking at slices of cork under a microscope. • Antony Van Leeuwenhoek (1600s) – invented the microscope. • Schwann (animal cells), Schleiden (plant cells), and Virchow – Between the 3 of them they came up with the Cell Theory. The Cell Theory • All living things are made of cells. • Cells are the basic unit of all living things. • All cells come from other living cells of the same kind. Basic Cell Structure (Three Basic Parts) • Cell Membrane. A thin, flexible boundary surrounding the cell. • Cytoplasm. The watery, jelly-like part of the cell that contains salts, minerals, and the cell organelles. • Genetic Material. The area of the cell where the DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) is stored. It regulates all cell activities. Diagram of a typical animal (eukaryotic) cell, showing subcellular components. Organelles: (2) nucleus (11) cytoplasm Microscopes Compound Light Microscope Scanning Electron Microscope • Invented in the 1590s. • Allows limited view of a cell. • Invented in 1920s. • Allows us to see individual organelles. • Transmission electron microscope allows scientists to see cells in greater detail; it uses a beam of electrons to take 3-D pictures of cells. Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic Cells Prokaryotic • Does not have a true nucleus. • Genetic material is not enclosed in a membrane. • They have no membranebound organelles. • Bacteria are prokaryotic cells. Eukaryotic • Has nucleus surrounded by membrane. • DNA is located in nucleus. • Has several membranebound organelles. • Tend to be larger than prokaryotes. • Plants and animal cells are both eukaryotic. Parts of a Eukaryotic Cell • Plastid – structures used in photosynthesis and product storage. Only in plants. • Cell Wall – Rigid membrane around plant cell; provides shape and support. In plants only. • Vacuoles – spherical storage sac for food and water; larger in plants. • Golgi Apparatus – flattened membrane sacs for synthesis, packaging, and distribution. Parts of Eukaryotic Cells (cont’d) • Mitochondria – Rod-shaped double membranous structures where cellular respiration (energy release) takes place. • Endoplasmic Reticulum – Folded membranes having areas with and without ribosomes used for transport of RNA and proteins. • Nucleus – control center of the cell; location of hereditary material (DNA); surrounded by nuclear envelope/membrane. Parts of Eukaryotic Cells (cont’d) • Ribosomes – structures that manufacture proteins; found on endoplasmic reticulum and floating in cytoplasm. • Lysosomes – sperical sac containing enzymes for digestive functions; recycling center of cell. • Cell membrane – Membrane surrounding the cell that allows some molecules to pass through; also called bilipid layer. Parts of Eukaryotic Cells (cont’d) • Cytoplasm – Jelly-like substance in the cell around the nucleus and organelles; site of many metabolic cycles and protein synthesis. • Microfilaments/Microtubules – fibers and tubes of protein that move internal cell parts. • Nucleolus – inside nucleus; site of ribosome production. • Nuclear envelope/membrane – double membrane that surrounds nucleus. Parts of Eukaryotic Cells (cont’d) • Centrioles – short tubes necessary for cell reproduction in some cells. In animal cells only. • Cilia – Short, hair-like extensions on the surface of some cells; used for movement and food gathering. Animal cells only. • Flagella – Long, whip-like extension on the surface of some cells; used for movement. Animal cells only.