Slide 1 - Department of Management Studies
advertisement

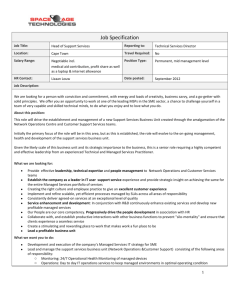
Presentation on “Incentives and facilities for small and medium enterprises (SME) provided by our government.” Prepared by “Brainstorming Group” Overview SMEs have assumed special significance for poverty reduction programs and potential contribution to the overall industrial and economic growth in Bangladesh. This report focuses on incentives and facilities for SME provided by our Government. We have tried our best to give an overview on SME sector in Bangladesh Government Organizations’ activities for SME development Bangladesh Small and Cottage Industries Corporation (BSCIC). SME Foundation BASIC Bank Bangladesh Bank Bangladesh Krishi Bank These play important roles for implementing Government policies by adopting strategies and programs efficiently for SME development. So we have made a study on these organizations to identify the activities and programs for SME development. Definations of SMEs According to “Industrial Policy 2010” of Bangladesh the definations of SME: Manufacturing enterprise: Small enterprise: An enterprise would be treated as small with capitalized costs excluding land and building, is between BDT 50 lacs to BDT 10 crores.The number of workers is between 25 and 99. Medium enterprise: An enterprise would be treated as medium with capitalized costs excluding land and building, is between BDT 10 crores and BDT 30 crores.The number of workers is between 100 and 250. Definations of SMEs Non-manufacturing activities: (such as trading or other services) Small enterprise: An enterprise would be treated as small with capitalized costs excluding land and building, is between BDT 5 lacs and BDT 1 crore and it has less than 25 employees. Medium enterprise: An enterprise would be treated as medium with capitalized costs excluding land and building, is between BDT 1 crore and BDT 15 crore and it has maximum 100 employees. Govt. policy under “Industrial Policy 2010” for SME Government will encourage SME entrepreneurs through providing adequate loan and training programs to create strong position of SME. SME will be re-financed continuously by BB through three re-financing funds. Women entreprenuers will get priority for SME loan . 15% of total loan will be for them and the interest rate will be 10%. ICT Industries will get priority for govt. assistance. Institutional Arrangements for SME development BSCIC has been the key public sector agency responsible for supporting SME promotion for a long time. Bangladesh Bank,BASIC Bank,SME Foundation, Bangladesh Krishi Bank, Janata Bank etc. The private sector efforts through participation of MIDAS and selected NGOs (especially GB, BRAC and Proshika) have been worked especially in SME promotion. Government Organizations for SME development Bangladesh Small and Cottage Industries Corporation (BSCIC) SME Foundation Bangladesh Bank BASIC Bank Bangladesh Krishi Bank Others (Janata Bank, Agrani Bank, Rupali Bank) Bangladesh Small and Cottage Industries Corporation( BSCIC) BSCIC provides assistance in all other matters relating to development and expansion of small and cottage industries (SCI). Its major functions are as follows : Promotion and registration of small and cottage industries Conducting advisory and industrial promotion services including training of entrepreneurs, skill development of artisans and craftsmen, creation of jobs for SCIs etc. Construction. and development of industrial estates with necessary infrastructural facilities for SCIs. Development of linkages between SCIs and large and medium sized industries. Goals of BSCIC which are focusing on SME development A. To assist private entrepreneurs for establishing new Small, Medium & Cottage Industries (SMCIs) unit upto 2015. i) Total : 0.409 million unit ii) Small Industry : 0.086 million unit iii) Medium : 0.008 million unit iv) Cottage Industry : 0.315 million unit Goals of BSCIC which are focusing on SME development B. To create labour force employment facilities through new Small, Medium & Cottage Industries (SMCIs). i) Total : 3.06 million ii) Small Industry Sector : 1.54 million iii) Medium : 0.52 million iv) Cottage Industry Sector : 1 million v) Percentage of new labour force employment (Total L/F 2005-2025: 3.80%) vi)Percentage of total labour force employment: 8.28% Goals of BSCIC which are focusing on SME development C. Contribution to GDP : 30% (Tk.1050 billion ) (To raise GDP in Small, Medium & Cottage Industries sector from 5% to 30%) D. To raise daily income of employed poor labour force people in SMCIs sector from 1 US$ to 3 US$ through poverty alleviation programs/projects undertaken by BSCIC and through private sector investment. Cumulative Small, Medium & Cottage Industry unit and employment will reach by 2025 (figure in million). Category of Industry Unit Employment Small 0.171 2.915 Medium 0.013 0.863 Cottage 0.904 2.852 Total 1.088 6.630 The stretegy of BSCIC for implementing proper incentives and facilities for deveopment of SME Strategy 1: Upgrade technological and management capabilities of SMEs. Strategy 2: Develop SME’s entrepreneurs and human resources Strategy 3: Enhance SMCI’s access to markets Strategy 4: Strengthen financial support system for SMCI’s Strategy 5: Foster an environment conducive for business development Strategy 6: Develop micro-enterprises and community enterprises Strategy 7: Develop networking among SMCI’s and clusters The BSCIC provides services to the private sector entrepreneurs Pre investment counseling Industrial information dissemination Scouting for entrepreneurs Extension services Entrepreneurship development Project appraisal (technical, financial, economic and management) Feasibility study Credit arrangement Sanction of enterprises Supervision of project implementation Infrastructure development Management and skill development The BSCIC provides services to the private sector entrepreneurs Product development Design and prototype development and distribution Raw material arrangement Diagnostic studies Sub-contracting arrangement Innovative production process and technology Quality control Market survey of products Marketing (including export) arrangement Literature on products and process from home and abroad Research and development Inter-organization co-ordination. SME FOUNDATION Non-Trading organization To develop SME for employment creation and national economic growth To implement govt. SME policy Policy advocacy and research Credit wholesalling program (9% interest rate) Capacity building and skilled development Technology development and uses Access to information Women entrepreneur development Business support services Product quality development and quality certification assistance BASIC Bank limited and SME State owned and specialized bank 50% fund for SMEs financing Maximum loan for Small Enterprises 50 lac Prefer 25 SME sectors BASIC KALYANI for women entrepreneur Collateral free maximum loan 5 lac @ 10% interest rate Maximum loan payment period 3 to 5 years Bangladesh Krishi Bank and SME Providing loan for SME to reduce proverty to implement vision 2021. Loan for women enterpreneur with simple conditions. Two types of loan (Project loan and Current capital or Cash Credit) Small Enterprise Loan limit Service and trading 50 thousands to 50 lac Manufacturing 50 thousands to 1 crore Medium enterprise Loan limit Service and trading 50 lac to 10 crore Manufacturing 1 crore to 15 crore Project loan interest rate 12% and payment period = grace period + 5 years. Current capital / Cash credit interest rate 12.5% and payment period 1 year. Bangladesh Bank and SME development Separate SME and special programs department Annual SME loan target for banks Priority for small and women entreprenuer Region and sector based financing Training Three layer monitoring system Available information for SME loan and promotion Outsourcing for SME loan program Bangladesh Bank and SME development Motivation for SME loan providing Specific funds for women entrepreneur Help desk for women entrepreneur Low interest rate for women entrepreneur(Bank rate+5%) Collateral free loan upto 25 lacs for women entrepreneur SME loan for ICT sector Help for increasing grace period Key Issues and challenges faced by SMEs. Liberalization and Global competition New Emerging Technologies. Skill Development. Finance. Information. Recommendations Indigenous R&D capabilities should be developed quickly. Most manufacturing processes are today electronically controlled. Hence, adequate skill has to be developed for using and maintaining electronic components and control devices. Designated financial institutions should not only be encouraged but also be helped to develop expertise in industrial financing, technology assessment and acquisition of relevant sectoral knowledge. Free information assistance will have to be provided to potential investors in the SME sector for developing project proposals. Recommendations Bangladeshi workmen are unable to produce goods from the standard specifications. This deficiency has to be removed quickly by establishing appropriate training and skill development facilities. Selection, acquisition and application of the appropriate technology for production. Compliance with Quality Assurance and environmental friendliness standards, through adoption of TQM, ISO 9000, ISO 14000, etc., and necessary training for practicing these. Institutional facilities are needed for entrepreneurship development, including particularly capturing the high entrepreneurial ability of the women of Bangladesh. Conclusion Success of SMEs development in Bangladesh depend on following aspects: Tecnological development Skill development Up to date information Close co-ordination between entrepreneurs and government institutions.