Human Body notes
advertisement

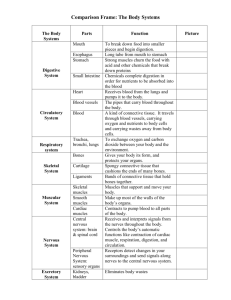
Human Body Systems Endocrine System Controls body functions by using chemicals that are made by the endocrine glands. Gland- a group of cells that make special chemicals for your body. Hormone- a chemical messenger made in one cell or tissue that causes a change in another cell or tissue in another part of the body - Flow through bloodstream Organs and/or Glands Pituitary Gland- “master gland” – this gland has many functions like helping the thyroid function properly, skeletal growth, and regulating the amount of water in the blood Adrenal Glands- release the hormone called epinephrine(adrenaline) to help the body respond to danger Pancreas- regulates blood glucose levels in the blood Thyroid gland- increases the rate at which you use energy (metabolism) Organs and/or Glands cont. Parathyroid-regulates calcium levels in the blood Thymus gland- regulates the immune system, which helps your body fight disease. Ovaries- in females, produce hormones needed for reproduction Testes- in males, produce hormones needed for reproduction. Parts of the Integumentary System 1. 2. 3. Skin Hair Nails ** Largest organ system on the body. Function of Integumentary System Covers your body and helps maintain homeostasis. Homeostasis- maintaining a constant internal state in a changing environment Layers of Skin Epidermis- outermost layer of skin ( about 2 sheets of paper thick) Dermis-The thicker layer of skin that lies beneath the epidermis Skeletal System Functions 1. 2. 3. 4. Ribs protect heart and lungs. Vertebrae protects your spinal cord. Skull protects the brain. Bones store minerals. Skeletal muscles pull on bones to produce movement. Some bones are filled with marrow that makes blood cells. Organs of Skeletal System Bones Cartilage Connective Tissue Muscular System Made up of muscles that let you move. Smooth muscles- found in digestive tract and walls of blood vessels Cardiac muscle- found only in the heart Skeletal muscles- attach to your bones for movement Voluntary – muscle action under your control Involuntary – muscle action not under your control Urinary System Function The organs that remove waste products from the blood. Part of the Excretory system-releases waste from body: Urinary System- through urine Integumentary System- through sweat Respiratory System- releases carbon dioxide Parts of the Urinary System Kidneys- pair of organs that constantly clean the blood. Nephrons- filters in the kidneys that remove waste from the blood where urine is formed, water and nutrients are moved back into the blood vessels to recirculate in the body. Ureter- tube that carries urine to bladder. Bladder- stores urine until it can be released from the body. Urethra- tube that expels urine out of body. Nervous System Function Gathers and interprets information, then it responds to that information as needed. Central Nervous System(CNS)- brain and spinal cord Peripheral Nervous System(PNS)- all parts of nervous system except for brain and spinal cord, it consists of the nerves. The Central Nervous System CNS Cerebrum- the largest part of the brain, and controls voluntary movements and allows you to sense touch, light, sound, odors, taste, pain, heat, and cold. Cerebellum- 2nd largest part of brain and processes sensory information from your body, such as skeletal muscles and joints. EX. Your body’s balance. Medulla-part of brain that connects to spinal cord and controls involuntary processes, such as blood pressure, body temperature, heart rate, and involuntary breathing. Spinal Cord-about as big around as your thumb, the nerves in the spinal cord allow the brain to communicate with the peripheral nervous system or nerves. The Lymphatic System Function A group of organs and tissues the collect excess fluid from the blood and return it to your blood. This system helps fight pathogens (a microorganism that causes disease or a virus). Parts of this system Lymph- the fluid and particles that are absorbed into lymph capillaries. Lymph node-small bean shaped masses of tissue that remove pathogens and dead cells from the lymph. Thymus-produces T cells that are ready to fight infection. Spleen- largest organ in this system, stores and produces lymphocytes(attack or mark pathogens in the blood) Tonsils-lymphatic tissue located in the nasal cavity and at the back of the mouth on either side of the tongue. Lymphocytes in the tonsils trap pathogens that enter the throat. The Cardiovascular System (Circulatory System) Maintains homeostasis (stable internal environment) in the body. Carries nutrients and Oxygen to cells and removes waste such as excess water and carbon dioxide from the cells. Also, helps regulate chemical signals by carrying hormones throughout the body. Parts of this System Heart- made of cardiac muscle, and has 4 chambers(right atrium and right ventricle, left atrium and left ventricle) The right atrium and right ventricle receive oxygen-poor blood through veins from the body and pump it to the lungs to release carbon dioxide and pick up oxygen The left atrium and left ventricle receive oxygen rich blood from the lungs and pump it out to the body through arteries Blood Vessels Arteries- have thicker vessel walls and carry blood away from the heart to the body Capillaries- tiny blood vessels(only one cell thick) that allow the exchange of nutrients, oxygen, and other substances between the bodies cells and the blood Veins- after leaving capillaries blood enters the veins which carry blood back to the heart Types of Circulation Pulmonary Circulation- circulation of blood between heart and lungs Systemic Circulation- the circulation of blood between the heart and the rest of the body. Blood Connective tissue made up of plasma, red blood cells, platelets, and white blood cells. Plasma- fluid part of blood contains water, minerals, nutrients, sugars, proteins, other substances, red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. Red Blood Cells(RBC’s)- each rbc has hemoglobin which is an oxygen – carrying protein. RBC’s transport oxygen around the body. White Blood Cells(WBC’s)- attack pathogens(bacteria, viruses, other microscopic particles that make you sick) and help clean wounds. Platelets-pieces of larger cells found in bone marrow, fragments pinch off into bloodstream, when you get a cut or scrape platelets clump together to plug the area and reduce blood loss. The Respiratory System Function A group of organs that take in oxygen(O2) and get rid of carbon dioxide (CO2 ). Respiraton- the process by which the body takes in oxygen and gets rid of carbon dioxide. VS. Cellular Respiration- at the individual cell level glucose + oxygen taken into the mitochondria of each cell and converted to make energy. Organs in Respiratory System Pharynx- or throat, air passes from nose through throat the pharynx branches into two tubes the esophagus(leads to stomach) and the larynx(contains vocal cords) that leads to lungs. Trachea- or windpipe carries air passing from the larynx to the lungs Bronchi- trachea splits into two branches called bronchi, one connects to each lung and each bronchus inside the lung branches into smaller tubes called bronchioles. Alveoli- each bronchiole branches to form tiny sacs called alveoli(this is where oxygen and carbon dioxide exchange)