The Circulatory System
advertisement

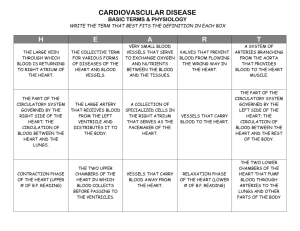
UNIT 3 – PART 1 CIRCULATORY & EXCRETORY SYSTEMS 1 THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM 2 FUNCTIONS • To transport O2 to the cells of the body so that cells may do cellular respiration • To Transport nutrients to the cells of the body • To transport CO2 and cellular wastes away from the cells 3 PARTS • Heart • Blood Vessels • Blood 4 COMPONENTS OF BLOOD • Red blood cells • White blood cells • Platelets • Plasma 5 WHAT ARE RED BLOOD CELLS? • Also called erythrocytes • Transport oxygen • Shaped like disks • Produced in the red bone marrow • Contain Hemoglobin • An iron containing protein that binds to oxygen • Gives blood a red color 6 WHAT ARE WHITE BLOOD CELLS? • Also called leukocytes • Produced in the red bone marrow • Can live for days, months or even years • Guard against infection, fight parasites, and attack bacteria • Can leave the circulatory system and go into the immune system fighting infection 7 WHAT ARE TWO KINDS OF WHITE BLOOD CELLS? • Phagocytes (eating cells) • Engulf and digest disease causing bacteria • Lymphocytes • Produce antibodies that are proteins to help destroy pathogens 8 WHAT ARE PLATELETS? • Cell fragments needed for clotting • Made in bone marrow • Clotting process • Platelet comes in contact with edges of broken blood vessel and becomes sticky • A cluster of platelets gathers around the wound forming a clot (scab) 9 WHAT IS PLASMA? • Fluid part of blood (mostly made of water) • Straw colored • Transport fatty acids, hormones and vitamins • Regulate osmotic pressure and blood volume • Fight viral and bacterial infections • Aid in blood clotting 10 TYPES OF BLOOD VESSELS • Arteries • Large and thick-walled • Carry blood from the heart to the rest of the body 11 TYPES OF BLOOD VESSELS • Veins • Smaller than arteries and not as thickwalled • Carry blood from the rest of the body back to the heart 12 TYPES OF BLOOD VESSELS • Capillaries • Tiny blood vessels with walls that are only one cell thick • Oxygen and nutrient absorption take place in the capillaries • Also move CO2 and waste products into the blood from cells 13 THE HEART 14 BLOOD FLOW THROUGH THE HEART • Oxygen poor1.) Superior and inferior vena cava 2.) Right Atrium • Oxygen rich5.) Left Atrium 6.) Left Ventricle 3.) Right Ventricle 7.) Aorta 4.) Lungs 8.) Body 15 BLOOD FLOW THROUGH THE BODY • Pulmonary circulation • Right side of the heart pumps blood from the heart to the lungs • Systemic circulation • Left side of the heart receives blood from the lungs and pumps it to the rest of the body 16 CLOSED VS. OPEN CIRCULATION • Closed circulation – blood is contained in a system of vessels and forced through them by a heart or heart-like organ • Open circulation – blood is partially contained in a system of vessels; a heart or heart-like pump pushes the blood though spongy tissues 17 18 THE EXCRETORY SYSTEM FUNCTION OF THE EXCRETORY SYSTEM • Maintains homeostasis in the body by removing waste products from the cells and expelling them from the body • Single-celled organisms can use active transport or diffusion • Multicellular organisms must have a complete system PARTS OF THE EXCRETORY SYSTEM • Kidneys : 1. remove waste products from the blood 2. maintain blood pH 3. regulates total blood volume by controlling water content in blood • Ureters • Urinary Bladder • Urethra • Skin – releases excess salts and water through pores • Lungs – remove excess carbon dioxide from the blood PARTS OF THE EXCRETORY SYSTEM KIDNEY STRUCTURE • 2 regions of kidney • Renal cortex-outer region • Renal medulla-inner region • Nephrons • Functional units • (~1 million each kidney) STEP 1: FILTRATION Materials filtered from the blood by the nephron are called filtrate 1. Water 2. Salts 3. Glucose 4. Amino acids 5. Urea (the waste product of amino acid breakdown) STEP 2: RE-ABSORPTION • Amino acids, fat, glucose and most water - returned to the blood. • Urine - urea, excess salts and water; stays in the nephron STEP 3: EXCRETION Flow of Urine: Nephron Ureters Urinary bladder • Average bladder capacity is 500 ml (16 oz) • ~48 gallons of filtrate are processed each day; 1% is excreted as urine (~ .5 gallon) Urethra 26 HOMEOSTASIS BY MACHINE • Dialysis - blood is passed through a filtration system other than the kidneys and returned to the body Hemodialysis - machine Peritoneal dialysis