identical daughter cells
advertisement
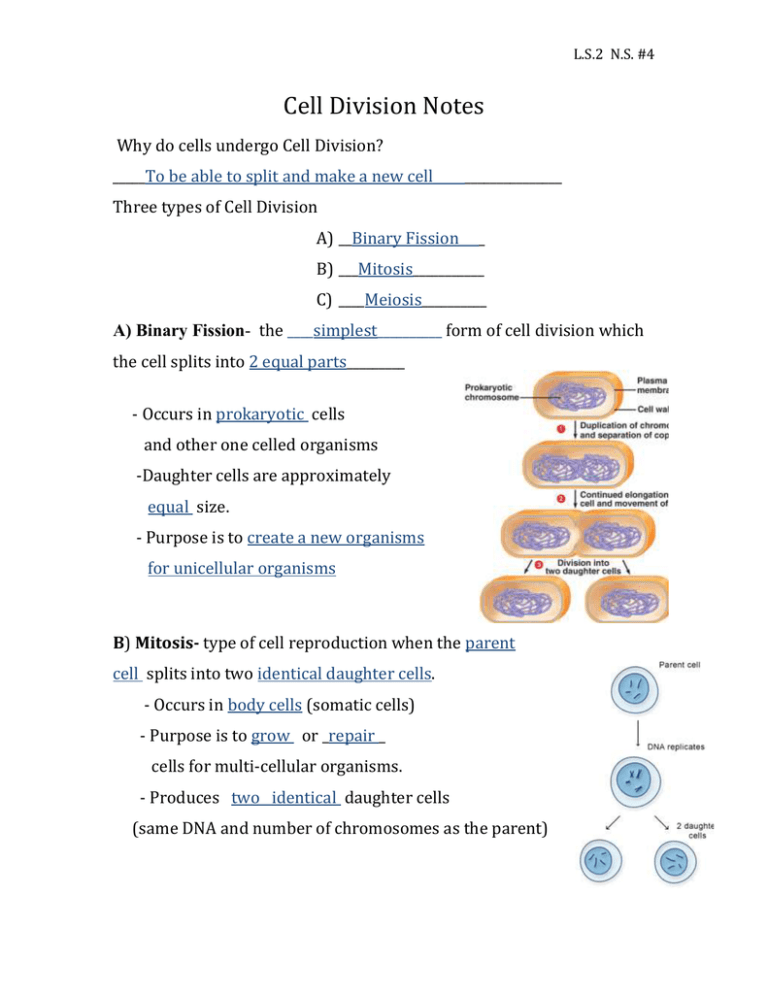
L.S.2 N.S. #4 Cell Division Notes Why do cells undergo Cell Division? _____To be able to split and make a new cell _______________ Three types of Cell Division A) __Binary Fission _ B) ___Mitosis___________ C) ____Meiosis__________ A) Binary Fission- the ____simplest__________ form of cell division which the cell splits into 2 equal parts_________ - Occurs in prokaryotic cells and other one celled organisms -Daughter cells are approximately equal size. - Purpose is to create a new organisms for unicellular organisms B) Mitosis- type of cell reproduction when the parent cell splits into two identical daughter cells. - Occurs in body cells (somatic cells) - Purpose is to grow or _repair _ cells for multi-cellular organisms. - Produces two identical daughter cells (same DNA and number of chromosomes as the parent) L.S.2 N.S. #4 C) Meiosis- type of cell reproduction which produces cells that have ___half___ the amount of _____DNA_____ as the parent. -Occurs only in ___sex ___ _____cells________ (gametes) - Purpose is to ____half___ the amount of chromosomes to create ____4____ daughter cells - Each daughter cell has half the amount of ___chromosomes____ as the parent, which later can be united for an organism to undergo ___sexual __ ______reproduction____ Cell Cycle: Three phases for the cell cycle _____Interphase______ Stage 1 ____M-Phase_____ Stage 2 ____Cytokinesis_______ Stage 3 Stage 1: ____Interphase__________- first stage of the cell cycle which _____chromosomes_____ and other cell materials are ____copied___. -Cell is doing all the “____prep____” work to divide. -DNA ___replicates___ (makes a copy) - ____Nucleus is visible__________ -_____Centrioles pair______________ L.S.2 N.S. #4 Stage 2: ____M-Phase____________ the cell is going through the actual “phases” of mitosis or meiosis The 4 phases of mitosis Phase 1: ______Prophase_______ Phase 2: _______Metaphase______ Phase 3: _______Anaphase_______ Phase 4: _______Telophase________ Phase 1: ______Prophase________ - ___Nuclear__ ____Membrane__ starts to disappear - Chromosomes become _____visible____ - __Centrioles___ begin to separate and ____spindle__ ____fibers___ begin to form L.S.2 N.S. #4 Phase 2: ______Metaphase___________ - “Meta” think ____middle_______ - Chromosomes line up in the ____middle_______ of the cell - ___Centrioles_____ move to opposite poles of the cell -___Spindle fibers form_________ Phase 3: ____Anaphase_______________ - “Ana” think _____away_________ - Chromosomes start to ___pull___ ___away____ toward opposite poles of the cell. - Each side of the cell has the __original___ number of chromosomes. Phase 4: ______Telophase_______ -__Nuclear___ ____Membrane___ begins to form around new set of chromosomes. - Spindle fibers disappear - Cell membrane “__pinches____ __in___” beginning to form ___2___ daughter cells L.S.2 N.S. #4 Stage 3: _____Cytokinesis______- last stage of the cell cycle - ____Cytokinesis__ - division of the cytoplasm. - Forms __2__ ______daughter____ _____cells____ L.S.2 N.S. #4 Meiosis has __2__ rounds of cell division Mitosis Meiosis - Produces __2__ daughter cells - Produces _____4_____ daughter that are ___identical__ to the that have __half____ the DNA of parent parent - __1 round of cell division - ____2____ rounds of cell division - Used for __growth__ and - Used to make ___gametes _ for ___repair____ sexual reproduction





