business ownership
advertisement

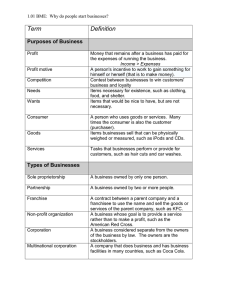
BUSINESS OWNERSHIP Concept: Introduce students to the major forms of business ownership and the advantages and disadvantages of each. Objectives Understand what a Proprietorship is. Understand what a Partnership is. Understand what a Corporation is. BUSINESS OWNERSHIP 1. Discuss a Proprietorship: How is it formed? What are the advantages and disadvantages? o Have students suggest which businesses, or types of businesses, are likely to be Proprietorships. Examples, small shops, butchers, home businesses, independent outlets…. 2. Discuss Partnerships. How are they formed? What are the advantages and disadvantages? o Talk about the fact that partnerships are common in professions lawyers, accountants, architects, surveyors, estate agents, vets, etc. o What are the implications of not having a Partnership agreement? o Use a scenario to illustrate personal liability: Suppose you form a partnership with two other people. What if one of your partners fires an employee who then sues the partnership for wrongful discharge? And what if the jury returns a verdict for $100,000 for the employee? You and your two partners will each be personally responsible for paying the full $100,000. To satisfy the six-figure verdict, the fired employee can go after your personal assets as well as partnership assets. Your home, your personal bank accounts and your car are all at risk. 3. Discuss Corporations: How are they formed? What are the advantages and disadvantages? Solidify the concept that a corporation is a separate entity Talk about shareholders and the buying of stock Talk about the Board of Directors and the relationship to company management Using examples from the Yellow Pages, ask students to think about how these businesses are owned, how they are run and how financing was raised (this can be done in the groups or as a class). Discuss responses to ensure students understand the rational for each choice. Name__________________________ Class: _________________________ Date_________________ Business Ownership There are three distinct ways to form a business and each method has particular variations, advantages, and disadvantages depending on the circumstances of the business and the industry. The following is a summary of each of three main categories of ownership. PROPRIETORSHIP (often called Sole Proprietorship) This is the form a business takes when no other form is pursued: It is the default format. In a proprietorship, even though the business records must be kept separate from the owner’s personal financial information, the business is part of the owner: • If the business is sued, the owner is sued • If the owner dies, the business ceases to exist and the assets become part of the owner’s estate • If the business makes money, the owner reports it as “income from business” on his or her personal tax return. A proprietorship is simple; it requires nothing more than the filing of the requisite civic, state, or federal business licenses. The cost of this simplicity though, is the legal liability placed on the owner for the operations of the business. The lack of hassle and high degree of autonomy in a proprietorship are usually enough to convince the first-time business owner to start a proprietorship. PARTNERSHIP This is a proprietorship that is owned by more than one person. Partnerships are often formed as a way to access the capital and expertise of more than one person. There is no requirement for additional paperwork and the partnership arrangement can be created in a variety of ways: • When more than one person contributes assets • When more than one person performs work of the business (controlling, directing, etc…) • When more than one person withdraws profits from the business. Because there is no official paperwork required, a partnership can come about http://www.moneyinstructor.com/inadvertently (by the actions just mentioned) and without anything to the contrary, the ownership is assumed to be equal. This means that any partner can commit the business to obligations or be sued for debts of the business. To avoid these obvious pitfalls, a Partnership Agreement is often drawn up specifying the proportion of ownership, duration of the agreement, conditions for withdrawal, division of responsibilities, and disposition of the business in the event of a partners’ death. Copyright 2007 Money Instructor Name__________________________ Date_________________ A Limited Partnership is a variation where the liability of the business is limited to one or some of the partners. In this situation, there must still be a general partner who has no liability limit. The tax implications of a partnership are the same as a proprietorship whereby each partner reports drawings on his or her personal income tax report. A Joint Venture is a general partnership, which is created with a specific project in mind. It generally dissolves once the project has been completed. Members of the joint venture are exposed to full legal liability. CORPORATION This the most formal path of business ownership and it requires paying a fee to set up a business entity that is separate from the owners. The law recognizes a corporation as an entity that is separate from its owners. Features of the Corporation include: • The owners of a corporation are called shareholders • Shareholders buy stock in the Corporation • The shareholders elect a Board of Directors to oversee the major policies and decisions • The corporation has a life of its own and does not dissolve when ownership changes • Shareholders are not personally liable for the debts of the business (owners may be required to waive this protection when securing debt or equity financing) • A corporation is a separate legal entity that files its own income taxes Characteristics of Business Organizations: Sole Proprietorship Partnership Owner(s) Only one owner Limited by owner’s life or choice Yes Two or more partners Many shareholders Business Life Owner Personally Liable for Business debts Business records separate from owner(s) Advantages Corporation Limited by owner’s life or choice Unlimited life Yes No Yes Yes Yes • Easy to organize • Owner has total control • Owner receives all income • Easy to organize • Partners receive all income • More than one person contributes funds to the • Shareholders have limited liability • Funds can be raised through the sale of stock Copyright 2007 Money Instructor Name__________________________ Date_________________ Continuity of business despite ownership changes business • Additional expertise Disadvantages • Owner is responsible for business liability • Owners often have difficulty raising funds • Life of business limited to owner • Partners all have liability • Partners will disagree on some business decisions • Must share profits with others • The act of incorporation takes time and money • Many regulations that must be followed Copyright 2007 Money Instructor Name__________________________ Date_________________ Student Worksheet – Business Ownership 1. What are the three main types of business ownership? 2. Of the three types of business ownership, which one is the most difficult to set up? 3. The owners of a Corporation are called ___________ ________. 4. Which of the following is a characteristic of a Joint Venture? a. There is no personal liability b. The partnership is formed for a specific project c. The partnership lasts indefinitely d. All of the above 5. List three ways a partnership can be formed without a Partnership Agreement. 6. Give two reasons why you would consider forming a Corporation versus a Partnership or Proprietorship. 7. In a Corporation, who controls and directs the business? a. Managers b. Employees c. Stockholders d. Board of Directors 8. In a Proprietorship, the ____ ______ controls and directs the business. 9. In a Corporation, the ____ ____ __ elect the Board the Directors. Copyright 2007 Money Instructor Name__________________________ Date_________________ Worksheet ANSWERS – Business Ownership 1. What are the three main types of business ownership? Proprietorship Partnership Corporation 2. Of the three types of business ownership, which one is the most difficult to set up? Corporation 3. The owners of a Corporation are called ___________shareholders________. 4. Which of the following is a characteristic of a Joint Venture? e. There is no personal liability f. The partnership is formed for a specific project g. The partnership lasts indefinitely h. All of the above 5. List three ways a partnership can be formed without a Partnership Agreement. When more than one person contributes assets When more than one person controls or directs the business When more than one person withdraws profits from the business 6. Give two reasons why you would consider forming a Corporation versus a Partnership or Proprietorship. 7. In a Corporation, who controls and directs the business? a. Managers b. Employees c. Stockholders d. Board of Directors 8. In a Proprietorship, the ____owner______ controls and directs the business. 9. In a Corporation, the ____shareholders____ __ elect the Board the Directors.