Chapt15 Lecture 13ed Pt 3
advertisement

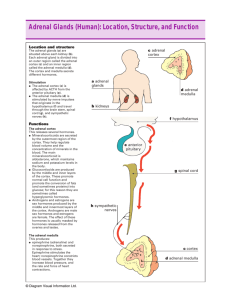
Human Biology Sylvia S. Mader Michael Windelspecht Chapter 15 Endocrine System Lecture Outline Part 3 Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. 1 15.4 Adrenal Glands 6. Adrenal glands • Glands that sit on top of the ________ • 2 parts of each gland – Adrenal medulla: controlled by the nervous system – Adrenal cortex: portions are controlled by ACTH from the anterior pituitary 2 15.4 Adrenal Glands The adrenal glands Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. adrenal gland kidney adrenal cortex connective tissue capsule zona glomerulosa adrenal medulla adrenal cortex (a) zona fasciculata zona reticularis adrenal medulla (b) Figure 15.12 The adrenal glands. 3 15.4 Adrenal Glands Adrenal medulla • Inner portion of the adrenal glands • Hypothalamus initiates stimulation of hormone secretion in the adrenal medulla • Produces hormones that allow a short-term response to stress (“fight or flight” response) – Epinephrine (adrenaline) – Norepinephrine 4 15.4 Adrenal Glands Adrenal cortex • Outer portion of the adrenal glands • Produces hormones that provide a long-term response to ______ 5 15.4 Adrenal Glands Adrenal cortex • 2 major types of hormones – Glucocorticoids • regulate carbohydrate, protein, and fat metabolism. • suppress the body’s inflammatory response. • e.g., cortisol and cortisone 6 15.4 Adrenal Glands Adrenal cortex – Mineralocorticoids • regulate salt and water balance. • e.g., aldosterone (targets the kidney) 7 15.4 Adrenal Glands Summary of the adrenal glands Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. stress hypothalamus Neurosecretory cells produce hypothalamicreleasing hormone. path of nerve impulses Stress Response: Long Term Glucocorticoids Protein and fat metabolism instead of glucose breakdown. neuron cell body Anterior pituitary secretes ACTH. sympathetic fibers spinal cord (cross section) ACTH epinephrine Reduction of inflammation; immune cells are suppressed. Mineralocorticoids Sodium ions and water are reabsorbed by kidney. norepinephrine Blood volume and pressure increase. Stress Response: Short Term Heartbeat and blood pressure increase. Blood glucose level rises. glucocorticoids Muscles become energized. adrenal medulla adrenal cortex Figure 15.13 Response of the adrenal medulla and the adrenal cortex to stress. mineralocorticoids 8 15.4 Adrenal Glands Adrenal glands can malfunction • _______________ – hyposecretion of glucocorticoids by the adrenal cortex, characterized by bronzing of the skin Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. a. Figure 15.15 Addison disease. b. a: © Custom Medical Stock Photo; b: © NMSB/Custom Medical Stock Photo 9 15.4 Adrenal Glands Adrenal glands can malfunction • ________________ – hypersecretion of glucocorticoids by the adrenal cortex, characterized by weight gain in the trunk of the body but not the arms and legs Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. (both): Courtesy Shannon Halverson Figure 15.16 Cushing syndrome. 10 15.5 Pancreas 7. Pancreas • Fish-shaped organ behind the stomach • Composed of 2 tissues – ______________: produces and secretes digestive juices 11 15.5 Pancreas 7. Pancreas – ____________ (islets of Langerhans): produces and secretes hormones 1. Insulin – secreted when blood glucose is high; stimulates the uptake of glucose by cells (muscle and liver) 2. Glucagon – secreted when blood glucose is low; stimulates the breakdown of glycogen in the liver 12 15.5 Pancreas Regulation of blood glucose Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. inslin Liver stores glucose from blood as glycogen. 80x B cells in pancreatic islet Muscle cells store glycogen and build protein. After eating, pancreas secretes insulin into blood. Adipose tissue uses glucose from blood to form fat. Glucose level drops. Homeostasis (normal blood glucose) Glucose level rises. Between eating, pancreas secretes glucagon into blood. Liver breaks down glycogen to glucose. Glucose enters blood. A cells in 80x Pancreatic islet Figure 15.18 Blood glucose homeostasis. Adipose tissue breaks down fat. glucagon (both): © Victor P. Eroschenko 13